
Draw a block diagram of a simple radio receiver.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint - Start the solution by describing the general concept behind a radio. Then draw a well-labelled block diagram of the radio receiver. It is also a good idea to explain each unit of the block diagram individually.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Radio - It is a signaling and communication technology. Radio uses waves in the electromagnetic spectrum between frequency ranges of $30Hz$ and $300GHz$.These waves are generated by an electronic device known as a transmitter. The waves emitted by the transmitter are picked up by antenna, an electronic device installed on the radio.
The block diagram of a simple radio receiver
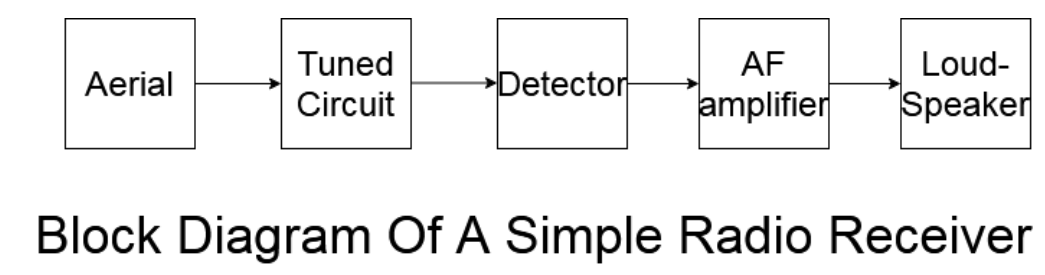
The components of this system are as follows –
Aerial - Aerial, is more commonly known as antenna. This is the component of the radio that makes it a wireless device. Antenna receives electromagnetic waves emitted from transmitter stations. An antenna is usually in the form a metal rod or a metal dish ( like the one you use for services like Tata sky, Dish-TV)
Tuned Circuit – They consist of an inductor coil and a capacitor, and are used to tune and select the radio stations, present on a particular frequency and reject the rest.
Detector – It is a device or circuit, used in a radio to extract desired signal from the carrier wave, a process called demodulation.
AF amplifier- It is a component of radio that amplifies the low power electronic audio signals, so that it becomes strong enough to drive loudspeakers and headphones.
Loudspeaker – A loudspeaker is essentially a speaker that receives audio signal and converts it into physical sound waves.
Note - A block diagram is essentially a diagram that shows a simple schematic form based on the general arrangement of components in a complex system. Block diagrams like other visual aids, make the process of understanding and explaining complex systems easy and more efficient.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Radio - It is a signaling and communication technology. Radio uses waves in the electromagnetic spectrum between frequency ranges of $30Hz$ and $300GHz$.These waves are generated by an electronic device known as a transmitter. The waves emitted by the transmitter are picked up by antenna, an electronic device installed on the radio.
The block diagram of a simple radio receiver

The components of this system are as follows –
Aerial - Aerial, is more commonly known as antenna. This is the component of the radio that makes it a wireless device. Antenna receives electromagnetic waves emitted from transmitter stations. An antenna is usually in the form a metal rod or a metal dish ( like the one you use for services like Tata sky, Dish-TV)
Tuned Circuit – They consist of an inductor coil and a capacitor, and are used to tune and select the radio stations, present on a particular frequency and reject the rest.
Detector – It is a device or circuit, used in a radio to extract desired signal from the carrier wave, a process called demodulation.
AF amplifier- It is a component of radio that amplifies the low power electronic audio signals, so that it becomes strong enough to drive loudspeakers and headphones.
Loudspeaker – A loudspeaker is essentially a speaker that receives audio signal and converts it into physical sound waves.
Note - A block diagram is essentially a diagram that shows a simple schematic form based on the general arrangement of components in a complex system. Block diagrams like other visual aids, make the process of understanding and explaining complex systems easy and more efficient.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




