
How to draw a BN molecular orbital diagram?
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: An orbital diagram explains how the orbitals of the atoms in the molecule are going to split when they are involved in bonding to form a molecule. Molecular orbitals are different from the atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is given to draw the molecular orbital diagram for BN molecules.
-We should know the atomic number of the atoms involved in the bonding to draw the orbital diagram.
- The atomic number of Boron is 5 means the number of electrons in boron are 5.
- Out of those 5 electrons, three electrons are valence electrons.
- Coming to nitrogen, the atomic number of nitrogen is 7, which means nitrogen contains 7 electrons.
- Out of seven electrons, five electrons are valence electrons in nitrogen.
- Therefore the total number of valence electrons in boron and nitrogen are 8 valence electrons.
- We have to fill the electrons from the lowest energy level from $\sigma 2s$ .
- We know that $\sigma 2s$ orbital can accommodate 2 electrons.
- The next two electrons are going to enter into ${{\sigma }^{*}}2s$ .
- There are two more electrons and they are going to enter into $\sigma 2p$ .
- At last the two electrons from eight valence electrons are going to enter into ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$ orbitals one in each orbital due to the same energy level of ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$.
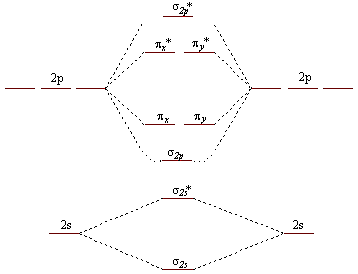
- The BN molecule is paramagnetic in nature due to the presence of unpaired electrons in ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$ orbitals.
Note:
To draw the energy level diagram of any molecule we should know the number of electrons present in the given molecule and we have to know how many valence electrons are present in the molecule.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is given to draw the molecular orbital diagram for BN molecules.
-We should know the atomic number of the atoms involved in the bonding to draw the orbital diagram.
- The atomic number of Boron is 5 means the number of electrons in boron are 5.
- Out of those 5 electrons, three electrons are valence electrons.
- Coming to nitrogen, the atomic number of nitrogen is 7, which means nitrogen contains 7 electrons.
- Out of seven electrons, five electrons are valence electrons in nitrogen.
- Therefore the total number of valence electrons in boron and nitrogen are 8 valence electrons.
- We have to fill the electrons from the lowest energy level from $\sigma 2s$ .
- We know that $\sigma 2s$ orbital can accommodate 2 electrons.
- The next two electrons are going to enter into ${{\sigma }^{*}}2s$ .
- There are two more electrons and they are going to enter into $\sigma 2p$ .
- At last the two electrons from eight valence electrons are going to enter into ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$ orbitals one in each orbital due to the same energy level of ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$.

- The BN molecule is paramagnetic in nature due to the presence of unpaired electrons in ${{\pi }_{x}}$ and ${{\pi }_{y}}$ orbitals.
Note:
To draw the energy level diagram of any molecule we should know the number of electrons present in the given molecule and we have to know how many valence electrons are present in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




