
Draw a diagram showing the expansion stroke of a steam engine.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: According to thermodynamics, there are two types of cycles, namely the two-stroke cycle and the four-stroke cycle. The four-stroke cycle engine contains four phases, namely, induction/intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion/power/ expansion stroke and the exhaust stroke.
Complete answer:
A steam engine is a heat engine which converts steam energy to mechanical energy, which it turns does work. The pressure produced by the steam is used to move the piston in the cylinder. It follows the principle of external combustion.
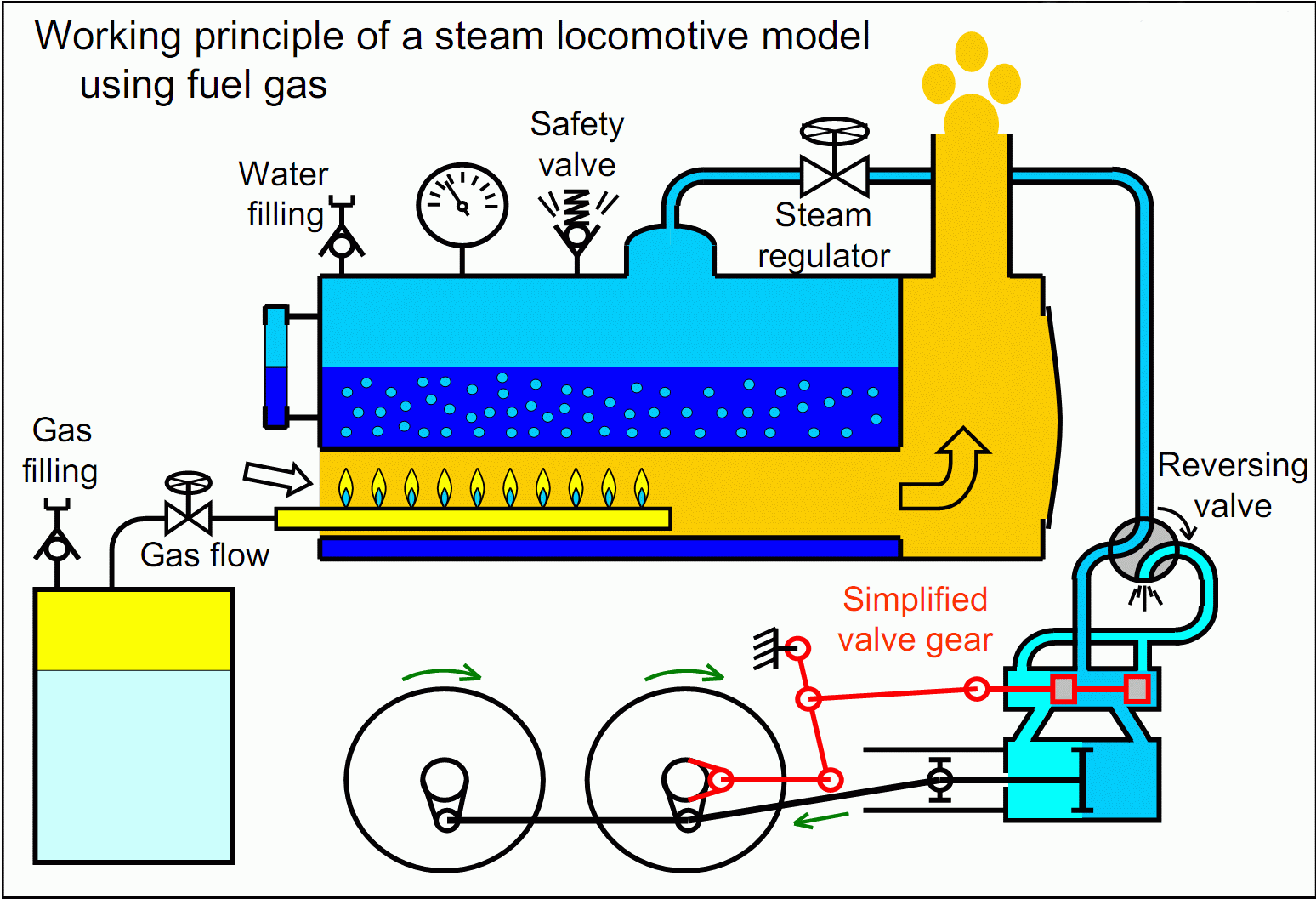
The thermodynamic cycles are described based on the number of strokes to complete a cycle.
Generally the stroke of an engine contains four phases, namely, induction/intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion/power/ expansion stroke and the exhaust stroke.
The induction/intake stroke:
Here the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws the fuel into the combustion chamber.
The compression stroke:
Here the fuel is compressed by a piston. This results in reducing the volume of the fuel. Followed by the ignition of the fuel.
The combustion/power/expansion stroke:
Here the ignited fuel expands, and pushes the piston outward. This creates the necessary force to start the engine power.
The Exhaust stroke:
Here the piston moves inwards, pressing the gas. This pressure makes the gas exist the cylinder through the exhaust valve. When the process ends, the exhaust valve closes, while the intake valve opens, to take in fresh fuel.
Note:
According to thermodynamics, there are two types of cycles, namely the two-stroke cycle and the four-stroke cycle. There are two more cycles, namely the five-stroke and six-stroke cycle, which are less common. Also another important term used in steam engines, is the stroke length, which describes how far the piston travels in the cylinder.
Complete answer:
A steam engine is a heat engine which converts steam energy to mechanical energy, which it turns does work. The pressure produced by the steam is used to move the piston in the cylinder. It follows the principle of external combustion.

The thermodynamic cycles are described based on the number of strokes to complete a cycle.
Generally the stroke of an engine contains four phases, namely, induction/intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion/power/ expansion stroke and the exhaust stroke.
The induction/intake stroke:
Here the piston moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws the fuel into the combustion chamber.
The compression stroke:
Here the fuel is compressed by a piston. This results in reducing the volume of the fuel. Followed by the ignition of the fuel.
The combustion/power/expansion stroke:
Here the ignited fuel expands, and pushes the piston outward. This creates the necessary force to start the engine power.
The Exhaust stroke:
Here the piston moves inwards, pressing the gas. This pressure makes the gas exist the cylinder through the exhaust valve. When the process ends, the exhaust valve closes, while the intake valve opens, to take in fresh fuel.
Note:
According to thermodynamics, there are two types of cycles, namely the two-stroke cycle and the four-stroke cycle. There are two more cycles, namely the five-stroke and six-stroke cycle, which are less common. Also another important term used in steam engines, is the stroke length, which describes how far the piston travels in the cylinder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




