
Draw a labelled diagram of non-striated muscles.
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint:It is under voluntary or involuntary regulation, and morphologically, striated or non-striated, muscle tissue may be functionally divided.
Three muscle types can be defined by implementing these classifications: skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Voluntary and striated skeletal muscle, involuntary and stressed cardiac muscle, and involuntary and non-striated smooth muscle.
Complete answer:
The smooth muscle is a non-striated muscle that is involuntary. It is divided into two subgroups; smooth muscle of a single unit (unitary) and multiunit. The entire package or sheet contracts as a syncytium within single-unit cells.
In the walls of hollow organs, including the liver, intestines, urinary bladder and uterus, and in the walls of passages, such as the circulatory system arteries and veins, and the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive system tracts, smooth muscle cells are found
The ciliary muscle, a kind of smooth muscle in the pupils, dilates and contracts the iris and changes the shape of the lens. In the skin, in reaction to cold weather or anxiety, smooth muscle cells cause hair to stand erect. A large portion of the volume of the cytoplasm of the smooth muscle cells is consumed by the molecules myosin and actin, which together have the capacity to contract and, through a chain of tensile structures, make the entire smooth muscle tissue contract with them. The smooth muscle does not contain the protein troponin; instead, calmodulin (which plays a regulatory role in the smooth muscle) the significant proteins expressed within smooth muscles are caldesmon and calponin.
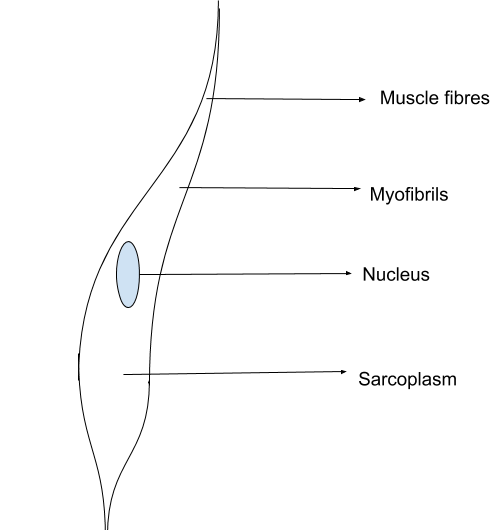
Note:The actin and myosin filaments are very thin and loosely arranged, so there are no striations. The cells are spindle-shaped and have a single nucleus.
Three muscle types can be defined by implementing these classifications: skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Voluntary and striated skeletal muscle, involuntary and stressed cardiac muscle, and involuntary and non-striated smooth muscle.
Complete answer:
The smooth muscle is a non-striated muscle that is involuntary. It is divided into two subgroups; smooth muscle of a single unit (unitary) and multiunit. The entire package or sheet contracts as a syncytium within single-unit cells.
In the walls of hollow organs, including the liver, intestines, urinary bladder and uterus, and in the walls of passages, such as the circulatory system arteries and veins, and the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive system tracts, smooth muscle cells are found
The ciliary muscle, a kind of smooth muscle in the pupils, dilates and contracts the iris and changes the shape of the lens. In the skin, in reaction to cold weather or anxiety, smooth muscle cells cause hair to stand erect. A large portion of the volume of the cytoplasm of the smooth muscle cells is consumed by the molecules myosin and actin, which together have the capacity to contract and, through a chain of tensile structures, make the entire smooth muscle tissue contract with them. The smooth muscle does not contain the protein troponin; instead, calmodulin (which plays a regulatory role in the smooth muscle) the significant proteins expressed within smooth muscles are caldesmon and calponin.

Note:The actin and myosin filaments are very thin and loosely arranged, so there are no striations. The cells are spindle-shaped and have a single nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




