
Draw a neat labeled diagram of the urinary system and explain the formation of urine.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Excretory system is a biological system which eliminates unwanted or excess materials from our body. Also, it helps to maintain the chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to our body. Kidney filters unwanted substances from blood and produces urine to excrete them. There are three main steps involved in the formation of urine.
Complete answer:
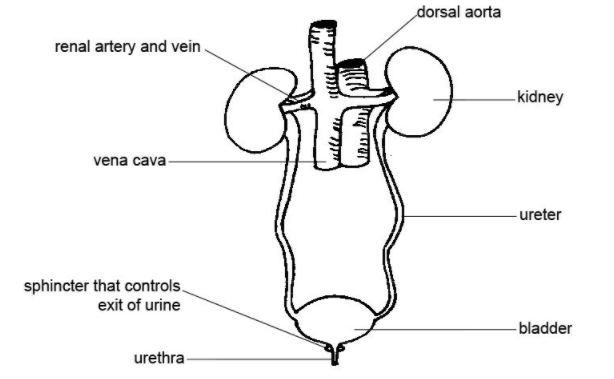
The urinary system or the renal system consists of the ureters, bladder, kidneys and urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to control levels of metabolites and electrolytes, regulate blood pressure and blood volume, eliminate waste from the body, and regulate blood pH.
There are three main steps of the urine formation: glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and then secretion. These processes ensure that only excess water and waste are removed from the body.
-Glomerular filtration
Each kidney has over 1 million tiny structures known as nephrons. Each nephron contains a glomerulus, which is the site of blood filtration. The glomerulus is a network of capillaries and it is surrounded by a cuplike structure called the glomerular capsule or the Bowman’s capsule. As blood flows through glomerulus, blood pressure pushes solutes and water from the capillaries through the filtration membrane, into the capsule. This filtration process begins the urine formation process.
-The Filtration Membrane Keeps Large Proteins and Blood Cells in the Bloodstream.
Through a specialized layer of cells inside the glomerulus, blood pressure pushes fluid from capillaries into the glomerular capsule. This layer allows small solutes and water to pass but blocks large proteins and blood cells. These components remain in the bloodstream. The filtrate flows from the glomerular capsule into the nephron.
-Moving the nutrients and water Back into the Bloodstream
The glomerulus filters small solutes and water out of the bloodstream. The resulting filtrate contains waste and some other substances that the body needs: glucose, amino acids, smaller proteins and essential ions. When these filtrates exit the glomerulus, it flows into a duct in the nephron known as the renal tubule. As it moves, some water and the needed substances are reabsorbed through the tube wall into the adjacent capillaries.
-Hydrogen Ions and Waste Ions Secreted from the Blood Complete the Formation of Urine.
The filtrate absorbed in glomerulus flows through the renal tubule, where water and nutrients are reabsorbed into capillaries. At the same time, hydrogen ions and waste ions pass from capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is secretion. The secreted ions then combine with remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into the collecting duct. It passes out of kidneys into the ureter through the renal pelvis, and down to the bladder.
Note: The main excretory system is the urinary system. But it is not the only excretory system in our body. Respiratory system eliminates waste products in the form of gas. Similarly, some waste products are eliminated from our body through skin, biliary system and gastrointestinal tract.
Complete answer:

The urinary system or the renal system consists of the ureters, bladder, kidneys and urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to control levels of metabolites and electrolytes, regulate blood pressure and blood volume, eliminate waste from the body, and regulate blood pH.
There are three main steps of the urine formation: glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and then secretion. These processes ensure that only excess water and waste are removed from the body.
-Glomerular filtration
Each kidney has over 1 million tiny structures known as nephrons. Each nephron contains a glomerulus, which is the site of blood filtration. The glomerulus is a network of capillaries and it is surrounded by a cuplike structure called the glomerular capsule or the Bowman’s capsule. As blood flows through glomerulus, blood pressure pushes solutes and water from the capillaries through the filtration membrane, into the capsule. This filtration process begins the urine formation process.
-The Filtration Membrane Keeps Large Proteins and Blood Cells in the Bloodstream.
Through a specialized layer of cells inside the glomerulus, blood pressure pushes fluid from capillaries into the glomerular capsule. This layer allows small solutes and water to pass but blocks large proteins and blood cells. These components remain in the bloodstream. The filtrate flows from the glomerular capsule into the nephron.
-Moving the nutrients and water Back into the Bloodstream
The glomerulus filters small solutes and water out of the bloodstream. The resulting filtrate contains waste and some other substances that the body needs: glucose, amino acids, smaller proteins and essential ions. When these filtrates exit the glomerulus, it flows into a duct in the nephron known as the renal tubule. As it moves, some water and the needed substances are reabsorbed through the tube wall into the adjacent capillaries.
-Hydrogen Ions and Waste Ions Secreted from the Blood Complete the Formation of Urine.
The filtrate absorbed in glomerulus flows through the renal tubule, where water and nutrients are reabsorbed into capillaries. At the same time, hydrogen ions and waste ions pass from capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is secretion. The secreted ions then combine with remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into the collecting duct. It passes out of kidneys into the ureter through the renal pelvis, and down to the bladder.
Note: The main excretory system is the urinary system. But it is not the only excretory system in our body. Respiratory system eliminates waste products in the form of gas. Similarly, some waste products are eliminated from our body through skin, biliary system and gastrointestinal tract.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




