
How can I draw axial and equatorial bonds in glucose?
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: Glucose is a carbohydrate which is named so because of the presence of the carbon hydrogen and oxygen in its structure.
The structure of the glucose has six of these carbon atoms and an aldehyde group along with the alcoholic groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:There are a number of steps, following which we will be able to draw the axial and equatorial bonds in a glucose molecule. But first we need to know what are axial and equatorial bonds.
The substituents which are present in the ring but are not part of the ring, can show these axial and equatorial bonds. The bonds which are connecting the non-ring substituent or atoms and the ring, which are present at about $90{}^\circ $ to the plane of the ring, are termed as axial bonds.
Whereas, the bonds which are present at only small angles with the plane of the ring, are termed as the equatorial bonds.
Now at first we will draw the Fischer projection of the glucose, which is,
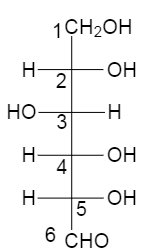
Next we will draw this same glucose molecule in the form of a cyclohexane chair.
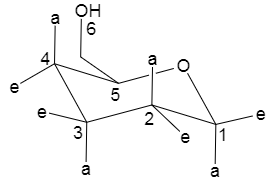
Now we will replace the signs ‘a’ and ‘e’ with the actual substituents which are hydroxide and hydrogen moieties. Now, we will look at the Fischer projection and put the substituents accordingly.
The final structure of the glucose, having axial and equatorial bonds, would look like,
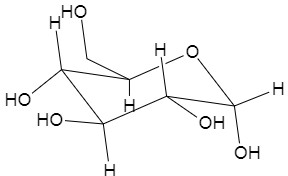
Note: The axial bonds of the glucose are the bonds which are present in the $90{}^\circ $ angle with the place of the ring. Whereas, equatorial bonds are those which are present in smaller angles with the plane of the ring.
The structure of the glucose has six of these carbon atoms and an aldehyde group along with the alcoholic groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:There are a number of steps, following which we will be able to draw the axial and equatorial bonds in a glucose molecule. But first we need to know what are axial and equatorial bonds.
The substituents which are present in the ring but are not part of the ring, can show these axial and equatorial bonds. The bonds which are connecting the non-ring substituent or atoms and the ring, which are present at about $90{}^\circ $ to the plane of the ring, are termed as axial bonds.
Whereas, the bonds which are present at only small angles with the plane of the ring, are termed as the equatorial bonds.
Now at first we will draw the Fischer projection of the glucose, which is,

Next we will draw this same glucose molecule in the form of a cyclohexane chair.

Now we will replace the signs ‘a’ and ‘e’ with the actual substituents which are hydroxide and hydrogen moieties. Now, we will look at the Fischer projection and put the substituents accordingly.
The final structure of the glucose, having axial and equatorial bonds, would look like,

Note: The axial bonds of the glucose are the bonds which are present in the $90{}^\circ $ angle with the place of the ring. Whereas, equatorial bonds are those which are present in smaller angles with the plane of the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




