
Draw canonical structures of the following:
a. Anisole
b. Benzaldehyde
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: In chemistry, canonical structures of a chemical compound is a method of representing the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions like sulphate, phosphate ions, where the bonding cannot be completely explained in terms of a single Lewis structure.
Complete answer:
Some basic guidelines to draw resonance or canonical structures are as follows:
1. All canonical structures must be valid Lewis structures i.e., the canonical structures formed must strictly obey rules for drawing Lewis structures.
2. All structures must have the same atom connectivity and differ only in arrangement if electrons, i.e., in the different structures atoms never move but only electrons move.
3. Formal charge on the individual atom may be different but the net charge i.e., the sum of all charges for all the canonical structures must be the same.
4. Three electron transformations can take place while forming canonical structures i.e., $\pi $ bond forms another $\pi $ bond, $\pi $ bond forms the lone pair of electrons and lone pair of electrons form a $\pi $ bond.
5. Curved arrow notation is used to indicate the electron movement in each canonical structure.
Now, the canonical structures for each given compound are as follows:
a. Anisole:
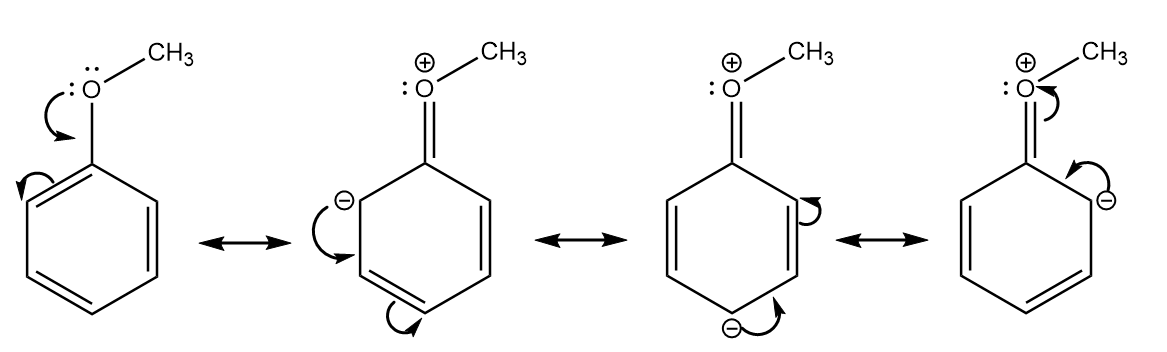
b. Benzaldehyde:
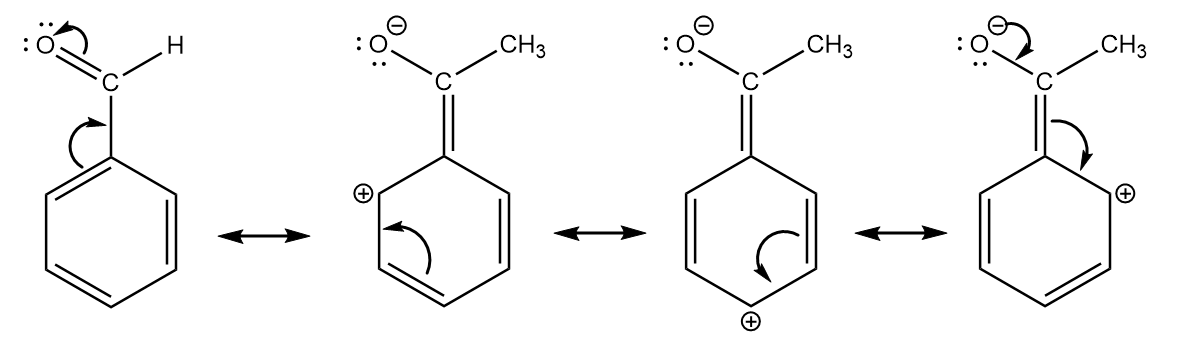
Note:
It is important to note that while drawing canonical or resonance structures, sigma bonds never move and only $\pi $ electrons and lone pairs of electrons can be moved from a higher electron density area to a lower electron density area. Also, remember that greater the number of resonance or canonical structures, greater is the stability of the species.
Complete answer:
Some basic guidelines to draw resonance or canonical structures are as follows:
1. All canonical structures must be valid Lewis structures i.e., the canonical structures formed must strictly obey rules for drawing Lewis structures.
2. All structures must have the same atom connectivity and differ only in arrangement if electrons, i.e., in the different structures atoms never move but only electrons move.
3. Formal charge on the individual atom may be different but the net charge i.e., the sum of all charges for all the canonical structures must be the same.
4. Three electron transformations can take place while forming canonical structures i.e., $\pi $ bond forms another $\pi $ bond, $\pi $ bond forms the lone pair of electrons and lone pair of electrons form a $\pi $ bond.
5. Curved arrow notation is used to indicate the electron movement in each canonical structure.
Now, the canonical structures for each given compound are as follows:
a. Anisole:

b. Benzaldehyde:

Note:
It is important to note that while drawing canonical or resonance structures, sigma bonds never move and only $\pi $ electrons and lone pairs of electrons can be moved from a higher electron density area to a lower electron density area. Also, remember that greater the number of resonance or canonical structures, greater is the stability of the species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




