
Draw labelled block diagram of radio transmission system.
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: The basic process of a communication system is to transfer/exchange a particular information conveniently and without loss of information to the user. For the process to occur, there must be a source of information, this information is supposed to be transferred in suitable form without any loss of information, then the information must be received by then receiver in its original form. Think what necessary steps and devices can be used to achieve this process with high accuracy. After this, draw a labelled block diagram to represent the process.
Complete step by step answer:
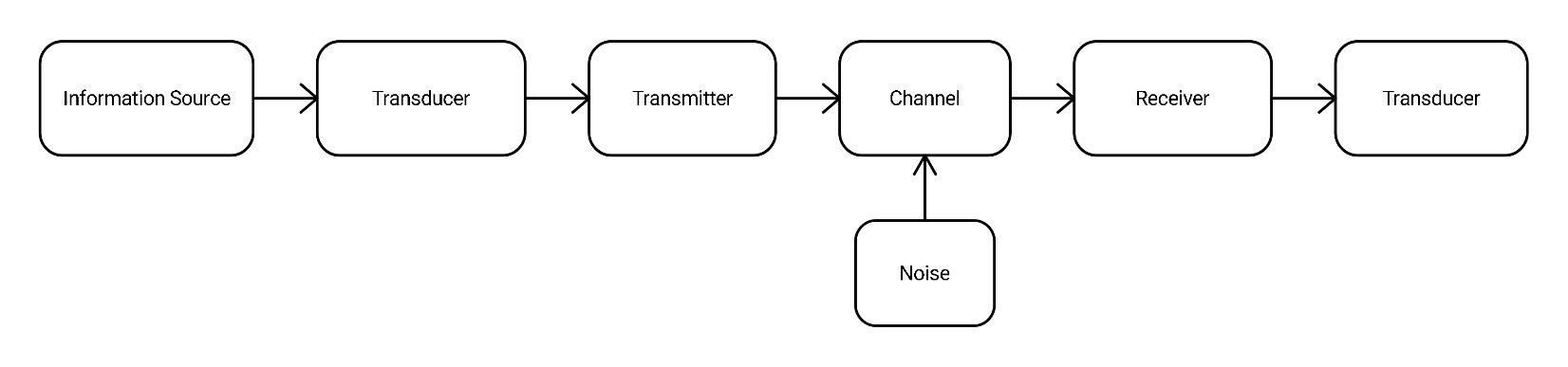
Information Source: The main purpose of the communication system is to exchange information. The system gets the information from the Information Source. This information consists of various types of information such as messages, words, audio, video, etc. The desired information is fetched from the source.
Transducer: Precisely input transducer. A transducer converts one form of energy to another form of energy. In a communication system, the transducer converts the information into electrical signals. The information which was of some type is now transferred as an electrical signal.
Transmitter: The transmitter processes the electrical signal in different aspects. Or you can say it modulates the properties required to be changed to transfer the signal. For e.g. amplification and frequency modulation.
Channel: To transfer any information, medium is a must requirement. In the communication system, the channel is the medium. The channel can be point-to-point or broadcast channel. Example of point-to-point is transfer of electromagnetic waves for telephone transmission. In the broadcast channel, the information is received by various stations through a single transmitter. While the signal passes through the channel, noise is added. Noise is an unwanted signal which interferes with the main information signal.
Receiver: The receiver receives the electrical signal. Demodulation of the electrical signal is done because the received signal was previously modulated. Hence, demodulation is a must.
Transducer: Precisely output transducer. The electrical signal is now converted to the desired form or the original form.
Now, if you collect all the data discussed above, the block diagram can be given as shown
Note:
The noise interferes with our signal and causes error in the communication system. The noises can be of internal as well as external type. Natural and man-made noises are the cause of external noise. The internal noise is generated by the equipment in the system itself. To overcome this, various techniques are used, such as making a signal which differs by noise in large aspects, allotting the desired signal a range of frequency so that noise does not interfere with it.
Complete step by step answer:
Information Source: The main purpose of the communication system is to exchange information. The system gets the information from the Information Source. This information consists of various types of information such as messages, words, audio, video, etc. The desired information is fetched from the source.
Transducer: Precisely input transducer. A transducer converts one form of energy to another form of energy. In a communication system, the transducer converts the information into electrical signals. The information which was of some type is now transferred as an electrical signal.
Transmitter: The transmitter processes the electrical signal in different aspects. Or you can say it modulates the properties required to be changed to transfer the signal. For e.g. amplification and frequency modulation.
Channel: To transfer any information, medium is a must requirement. In the communication system, the channel is the medium. The channel can be point-to-point or broadcast channel. Example of point-to-point is transfer of electromagnetic waves for telephone transmission. In the broadcast channel, the information is received by various stations through a single transmitter. While the signal passes through the channel, noise is added. Noise is an unwanted signal which interferes with the main information signal.
Receiver: The receiver receives the electrical signal. Demodulation of the electrical signal is done because the received signal was previously modulated. Hence, demodulation is a must.
Transducer: Precisely output transducer. The electrical signal is now converted to the desired form or the original form.
Now, if you collect all the data discussed above, the block diagram can be given as shown

Note:
The noise interferes with our signal and causes error in the communication system. The noises can be of internal as well as external type. Natural and man-made noises are the cause of external noise. The internal noise is generated by the equipment in the system itself. To overcome this, various techniques are used, such as making a signal which differs by noise in large aspects, allotting the desired signal a range of frequency so that noise does not interfere with it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




