
Draw the circuit diagram of a full-wave rectifier by the use of two p-n junction diodes and describe its working. Represent the input and output waveforms.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Full-wave rectification is a rectifier, which rectifies the negative component of the input voltage into a positive voltage, then converts it into pulse current which is a direct current using a diode bridge configuration. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step-by-step solution
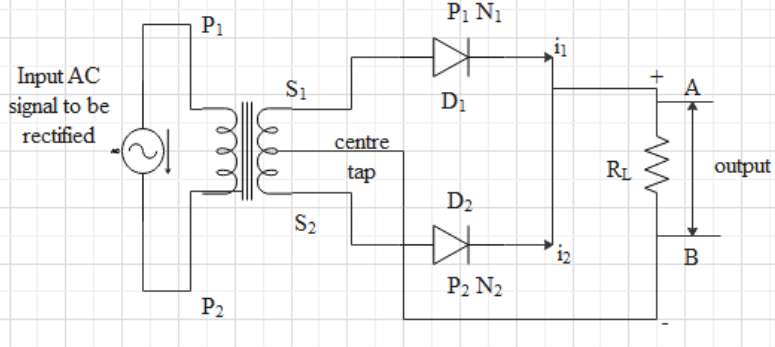
First of all, let us draw the circuit diagram and also let us explain the working. The AC input voltage across the secondary ${{S}_{1}}$ and ${{S}_{2}}$varies the polarity after each half cycle. Let us assume during the first half cycle of the input AC signal, the terminal ${{S}_{1}}$ be the positive relative to center tap O and ${{S}_{2}}$ be the negative relative to O. Then diode ${{D}_{1}}$ will be in forwarding bias and diode ${{D}_{2}}$ will be in reverse biased. Hence the diode ${{D}_{1}}$ conduct while diode ${{D}_{2}}$ will not conduct.
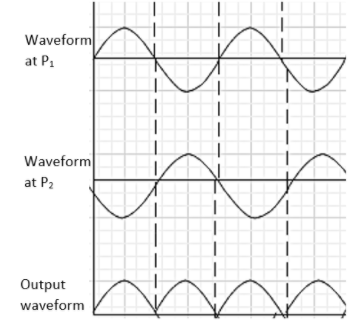
In the next half-cycle, the terminal ${{S}_{1}}$ will be negative with respect to center tap O and ${{S}_{2}}$ is positive relative to O. then diode ${{D}_{2}}$ is forward bias and diode ${{D}_{1}}$ is reverse biased. Therefore diode ${{D}_{2}}$ conduct while diode ${{D}_{1}}$ does not. The direction of current in the load resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ will be the same from A to B for both the half cycles. Hence for the input AC signal, the output current will be a continuous series of unidirectional pulses.
Note: The Bridge Rectifier circuits are commonly useful in power supply for different appliances because they are capable of converting the High AC voltage into Low DC voltage. By the way, the half-wave rectification avoids just the negative voltage component with the use of a single diode before changing to DC.
Complete step-by-step solution
First of all, let us draw the circuit diagram and also let us explain the working. The AC input voltage across the secondary ${{S}_{1}}$ and ${{S}_{2}}$varies the polarity after each half cycle. Let us assume during the first half cycle of the input AC signal, the terminal ${{S}_{1}}$ be the positive relative to center tap O and ${{S}_{2}}$ be the negative relative to O. Then diode ${{D}_{1}}$ will be in forwarding bias and diode ${{D}_{2}}$ will be in reverse biased. Hence the diode ${{D}_{1}}$ conduct while diode ${{D}_{2}}$ will not conduct.
In the next half-cycle, the terminal ${{S}_{1}}$ will be negative with respect to center tap O and ${{S}_{2}}$ is positive relative to O. then diode ${{D}_{2}}$ is forward bias and diode ${{D}_{1}}$ is reverse biased. Therefore diode ${{D}_{2}}$ conduct while diode ${{D}_{1}}$ does not. The direction of current in the load resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ will be the same from A to B for both the half cycles. Hence for the input AC signal, the output current will be a continuous series of unidirectional pulses.


Note: The Bridge Rectifier circuits are commonly useful in power supply for different appliances because they are capable of converting the High AC voltage into Low DC voltage. By the way, the half-wave rectification avoids just the negative voltage component with the use of a single diode before changing to DC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




