
How do you draw the condensed structural formulas of four structural isomers of the carboxylic acid that have the molecular formula $ {C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2} $ ?
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :The carboxylic acid is considered as the organic compound which tends to contain a functional group known as the carboxylic group in the compound. In the process of deprotonation the carboxylic acid tends to yield the carboxylate anion which helps in the formation of soaps. The general formula of the carboxylic acid is $ R - COOH $ , here the $ COOH $ is the carboxylic group and $ R $ is a rest molecule which is attached to the carboxylic group.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structural isomers are known as constitutional isomers. The functional groups and the atoms present in the molecules of these isomers are tend to be linked in different ways.
The compound given to us is $ {C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2} $ known as pentanoic acid.
The chain isomerism of pentanoic acid is the following:
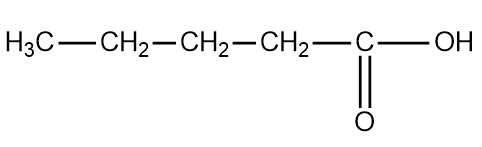
The above structure is pentanoic acid.
The second isomer of pentanoic acid is the following:
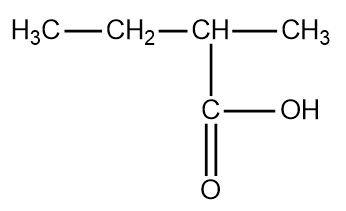
The structure is 2- methyl butanoic acid.
The third structure of pentanoic acid is the following:
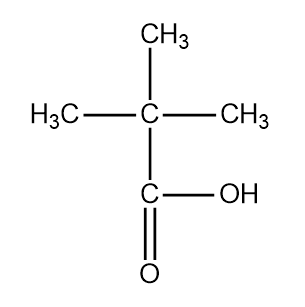
The structure is 2,2 dimethyl propanoic acid.
The fourth structure of pentanoic acid is the following:
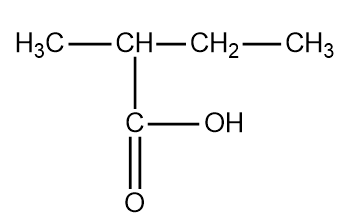
The structure is 3 methyl butanoic acid.
These are the four structural isomers of pentanoic acid.
Note :
The different types of structural isomers are chain isomerism, position isomerism, tautomerism, ring chain isomerism, etc. the chain isomerism is known as skeletal isomerism. In position isomerism the functional groups are present at different positions. In functional isomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the different functional groups are attached to it.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structural isomers are known as constitutional isomers. The functional groups and the atoms present in the molecules of these isomers are tend to be linked in different ways.
The compound given to us is $ {C_5}{H_{10}}{O_2} $ known as pentanoic acid.
The chain isomerism of pentanoic acid is the following:
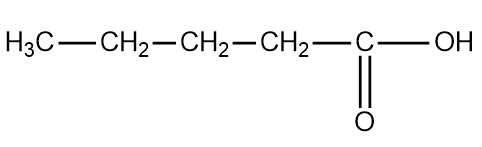
The above structure is pentanoic acid.
The second isomer of pentanoic acid is the following:

The structure is 2- methyl butanoic acid.
The third structure of pentanoic acid is the following:

The structure is 2,2 dimethyl propanoic acid.
The fourth structure of pentanoic acid is the following:

The structure is 3 methyl butanoic acid.
These are the four structural isomers of pentanoic acid.
Note :
The different types of structural isomers are chain isomerism, position isomerism, tautomerism, ring chain isomerism, etc. the chain isomerism is known as skeletal isomerism. In position isomerism the functional groups are present at different positions. In functional isomerism the compounds have the same chemical formula but the different functional groups are attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




