
Draw the electron dot structure for, (A) Ethanoic acid (B) Hydrogen sulphide (C) Propanone (D) dichlorine.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The Lewis dot structures are also known as electron dot structures. Basically it is the representation of valence electrons of an atom around its elemental symbol in a molecule. It shows how atoms in a molecule make a bond by sharing electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron dot structures are the representation of molecules. The electron dot structure shows the bonding between the atoms of a molecule and represents the electrons and lone pairs present on the atoms. Electron dot structures are called Lewis dot structures, Lewis dot diagrams. The ‘dot’ word is used in naming because the electrons present in the molecule are written as dots in diagrams.
The steps to represent a molecule in Lewis dot structure are:
The first to make Lewis dot structure is to find out the number of valence electrons of each atom present in the molecule.
Second step is to know the number of electrons required by each and every atom to complete its octet.
The third step is to find out the number of bonds included in the molecule.
The fourth step includes making a skeletal structure of the molecule.
And the last step includes the placing of electrons outside the atoms.
The Lewis dot structure of (A) Ethanoic acid is:
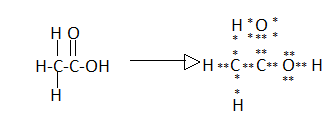
In the above structure we can see that each bond is shown as the sharing of electrons.
Similarly the Lewis dot structure of (B) Hydrogen sulphide is:
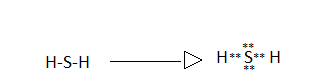
In the above structure we can see that sulphur atom has two lone pairs so they are represented above and below the element symbol written.
The Lewis dot structure of (C) Propanone is:
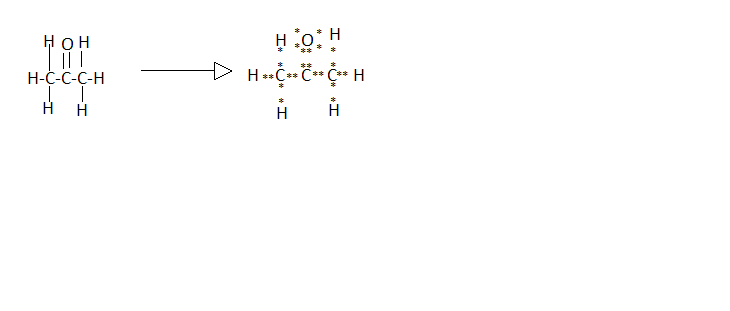
In the Lewis dot structure of propanone the six dots around the oxygen atom represents its valence electrons.
And the Lewis dot structure of (D) dichlorine is:
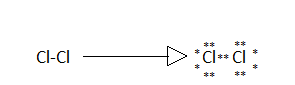
Chlorine atoms have seven electrons in their outermost shell, out of seven only one participates in bonding and the other electrons are represented as lone pairs.
Note:
The maximum number of common electrons present on adjacent atoms of a molecule takes part in bonding and sharing. If the element requires only one electron to complete its octet then the number of electrons present in the valence shell doesn’t matter.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron dot structures are the representation of molecules. The electron dot structure shows the bonding between the atoms of a molecule and represents the electrons and lone pairs present on the atoms. Electron dot structures are called Lewis dot structures, Lewis dot diagrams. The ‘dot’ word is used in naming because the electrons present in the molecule are written as dots in diagrams.
The steps to represent a molecule in Lewis dot structure are:
The first to make Lewis dot structure is to find out the number of valence electrons of each atom present in the molecule.
Second step is to know the number of electrons required by each and every atom to complete its octet.
The third step is to find out the number of bonds included in the molecule.
The fourth step includes making a skeletal structure of the molecule.
And the last step includes the placing of electrons outside the atoms.
The Lewis dot structure of (A) Ethanoic acid is:
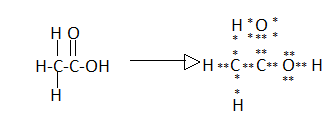
In the above structure we can see that each bond is shown as the sharing of electrons.
Similarly the Lewis dot structure of (B) Hydrogen sulphide is:

In the above structure we can see that sulphur atom has two lone pairs so they are represented above and below the element symbol written.
The Lewis dot structure of (C) Propanone is:
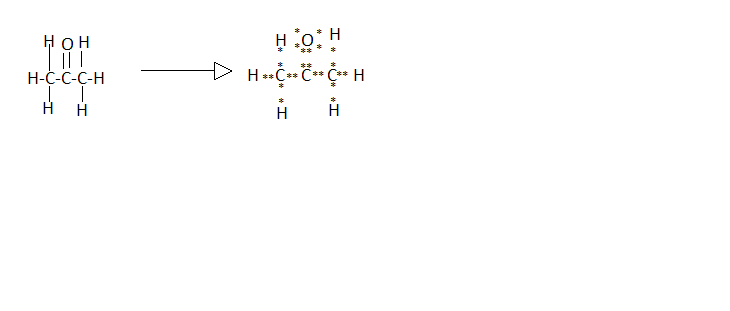
In the Lewis dot structure of propanone the six dots around the oxygen atom represents its valence electrons.
And the Lewis dot structure of (D) dichlorine is:

Chlorine atoms have seven electrons in their outermost shell, out of seven only one participates in bonding and the other electrons are represented as lone pairs.
Note:
The maximum number of common electrons present on adjacent atoms of a molecule takes part in bonding and sharing. If the element requires only one electron to complete its octet then the number of electrons present in the valence shell doesn’t matter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




