
Draw the ray diagrams of the geometric images for concave mirrors and also state the characteristics of images of the following: when the object is at principal focus.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that a concave mirror is formed by cutting a hollow sphere into parts and the inner surface of the cut acts as a reflection surface and the outer surface is painted. When the object is placed at six different locations.
Complete step by step answer:
Case 1: When the object is placed at infinity
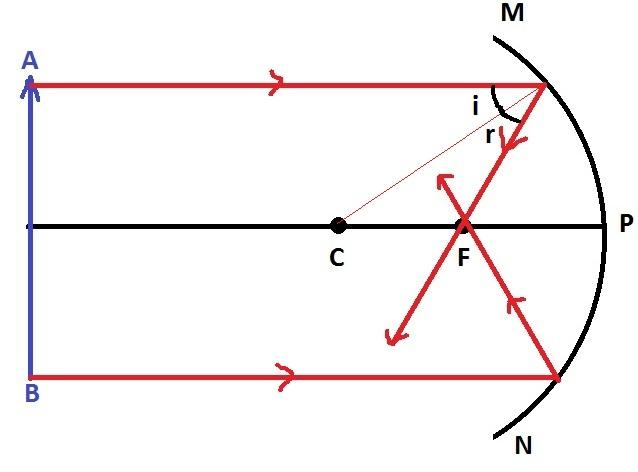
In this first case, we can see from the ray diagram that a real image is formed at the focus when an object is placed at infinity. The image is very much smaller than the real object.
Case 2: When the object is placed behind the center of curvature
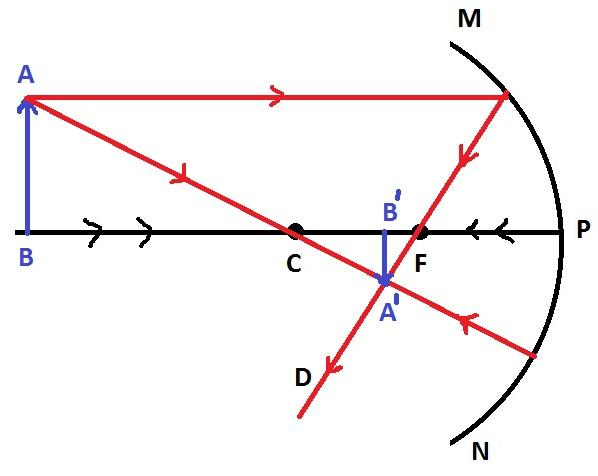
As shown in the ray diagram, the image formed is real and between the focal and the center of curvature. It is smaller than the real object.
Case 3: When the object is placed at the center of the curvature
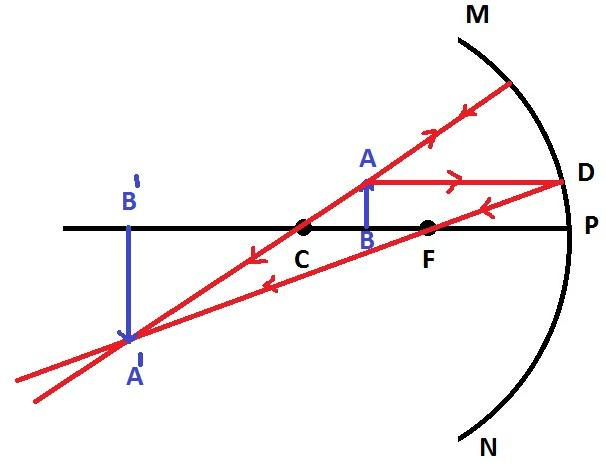
The image formed in this case is real and at the center of the curvature itself and it is of the same size as the real object.
Case 4: When the object is placed between the center of curvature and principal focus
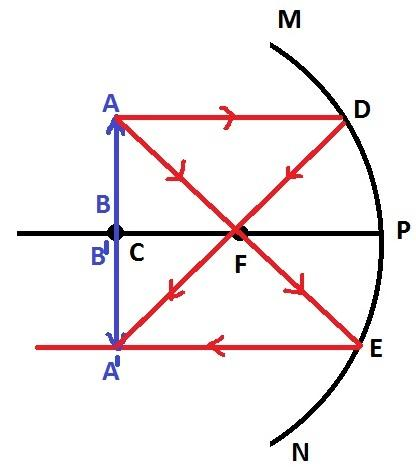
In this case, the formation of real images is obtained behind the center of curvature and the size of this image is bigger than the object.
Case 5: When the object is placed at the principal focus
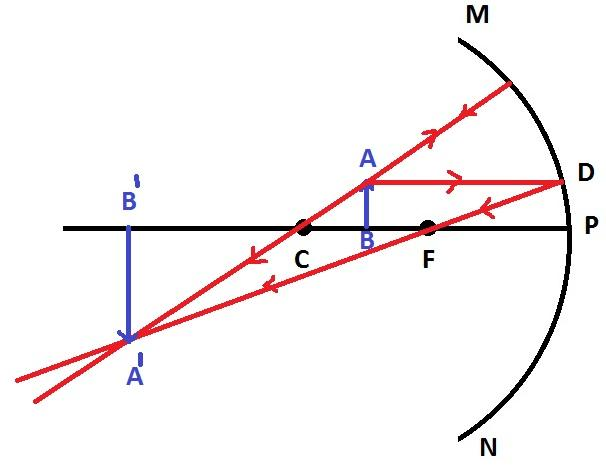
As shown in the ray diagram, when the object is placed at the principal focus, the real image is formed at an infinite distance. This image is much bigger than the object.
Case 6: When the object is placed between the principal focus and pole
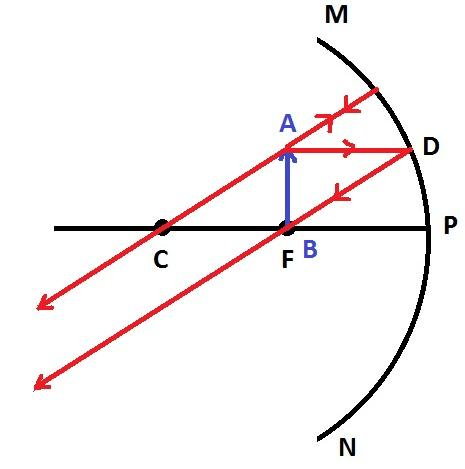
In this last case, we can see that the image formed is virtual and larger than the real object.
Note:
Here, we have discussed all the ray diagrams in case of a concave mirror. It is observed that except when the object is between focal and pole, the image formed is real. It is also important to note that there is only one case when the real image formed is of the same size and at the same place as the real object and this case is when the object is placed on the center of the curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
Case 1: When the object is placed at infinity

In this first case, we can see from the ray diagram that a real image is formed at the focus when an object is placed at infinity. The image is very much smaller than the real object.
Case 2: When the object is placed behind the center of curvature

As shown in the ray diagram, the image formed is real and between the focal and the center of curvature. It is smaller than the real object.
Case 3: When the object is placed at the center of the curvature

The image formed in this case is real and at the center of the curvature itself and it is of the same size as the real object.
Case 4: When the object is placed between the center of curvature and principal focus

In this case, the formation of real images is obtained behind the center of curvature and the size of this image is bigger than the object.
Case 5: When the object is placed at the principal focus

As shown in the ray diagram, when the object is placed at the principal focus, the real image is formed at an infinite distance. This image is much bigger than the object.
Case 6: When the object is placed between the principal focus and pole

In this last case, we can see that the image formed is virtual and larger than the real object.
Note:
Here, we have discussed all the ray diagrams in case of a concave mirror. It is observed that except when the object is between focal and pole, the image formed is real. It is also important to note that there is only one case when the real image formed is of the same size and at the same place as the real object and this case is when the object is placed on the center of the curvature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




