
Draw the structure diagram of ammonia molecule as per the valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, or VSEPR theory, is a concept used in chemistry to determine the structure of single molecules from the number of pairs of electrons surrounding their central atoms. The formula of an ammonia molecule is $N{{H}_{3}}$.
Complete answer:
Valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory: The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory abbreviated as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimalized. This arrangement of the atom determines the geometry of the resulting molecule.
In a molecule two types of electron pair are there, bond pair and lone pair.
Bond pair: it is under the influence of two nuclei.
Loan pair: It is under the influence of one nucleus.
The repulsion between electron pairs follows the order, lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair > bond pair – bond pair, because different types of repulsion distortion in geometry will be observed from the standard geometry w.r.t hybridization.
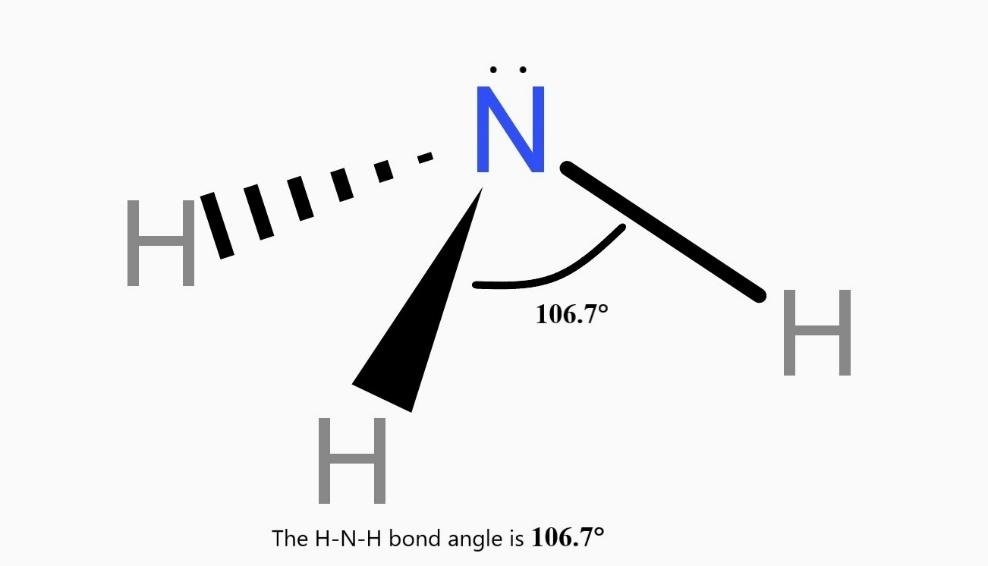
Ammonia is made up of 1 atom of nitrogen and 3 atoms of hydrogen. Nitrogen has 8 electrons around it i.e. it has 4 electron pairs. These pairs are arranged tetrahedrally. Of the 4 pairs: 1 pair is a lone pair. So, the resulting shape is a trigonal pyramid.
Note: The VSEPR theory assumes that each atom in a molecule will achieve a geometry that minimizes the repulsion between electrons in the valence shell of that atom.
The structure of ammonia molecules as per the valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory is trigonal pyramid.
The H-N-H bond angle is 106.7°.
Complete answer:
Valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory: The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory abbreviated as VSEPR theory is based on the premise that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimalized. This arrangement of the atom determines the geometry of the resulting molecule.
In a molecule two types of electron pair are there, bond pair and lone pair.
Bond pair: it is under the influence of two nuclei.
Loan pair: It is under the influence of one nucleus.
The repulsion between electron pairs follows the order, lone pair – lone pair > lone pair – bond pair > bond pair – bond pair, because different types of repulsion distortion in geometry will be observed from the standard geometry w.r.t hybridization.
Ammonia is made up of 1 atom of nitrogen and 3 atoms of hydrogen. Nitrogen has 8 electrons around it i.e. it has 4 electron pairs. These pairs are arranged tetrahedrally. Of the 4 pairs: 1 pair is a lone pair. So, the resulting shape is a trigonal pyramid.

Note: The VSEPR theory assumes that each atom in a molecule will achieve a geometry that minimizes the repulsion between electrons in the valence shell of that atom.
The structure of ammonia molecules as per the valence-shell electron pair repulsion theory is trigonal pyramid.
The H-N-H bond angle is 106.7°.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




