
During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\], the initiation step is:
A. Elimination of water
B. Formation of ester
C. Formation of carbocation
D. Protonation of alcohol molecule.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: In the dehydration of alcohol to form alkene by a strong acid mainly three steps occur. In the first step the lone pair present in the oxygen of the hydroxyl group of the alcohol act as a lewis base which abstract the hydrogen ion of the sulphuric acid.
Complete answer:
Dehydration is defined as the removal of water by reacting the alcohols with strong concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkene. This reaction takes place in three different steps.
(1) Formation of protonated alcohol
(2) Carbocation formation
(3) Alkene formation
(1) Formation of protonated alcohol: In the first step, the protonation of alcohol takes place. Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons in the oxygen atom, the oxygen acts as a lewis base which abstract the hydrogen ion of the protic acid.
(2) Carbocation formation: In this step, the carbon oxygen bond is broken to release water and form a carbocation or carbonium ion.
(3) Alkene formation: In this step the proton generated is removed with the help of a base which results in the formation of alkene.
The reaction of alcohol with sulphuric acid is shown below.
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]
In this reaction, ethanol reacts with sulphuric acid to form ethene.
The mechanism is shown below.
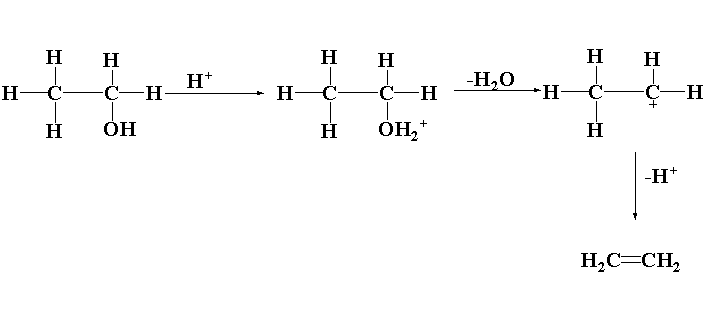
Thus, during dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\], the initiation step is protonation of alcohol molecules.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
In the formation of alkene from the dehydration of alcohol, the second step which is the formation of carbocation is the rate determining step of the mechanism.
Complete answer:
Dehydration is defined as the removal of water by reacting the alcohols with strong concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkene. This reaction takes place in three different steps.
(1) Formation of protonated alcohol
(2) Carbocation formation
(3) Alkene formation
(1) Formation of protonated alcohol: In the first step, the protonation of alcohol takes place. Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons in the oxygen atom, the oxygen acts as a lewis base which abstract the hydrogen ion of the protic acid.
(2) Carbocation formation: In this step, the carbon oxygen bond is broken to release water and form a carbocation or carbonium ion.
(3) Alkene formation: In this step the proton generated is removed with the help of a base which results in the formation of alkene.
The reaction of alcohol with sulphuric acid is shown below.
\[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]
In this reaction, ethanol reacts with sulphuric acid to form ethene.
The mechanism is shown below.

Thus, during dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\], the initiation step is protonation of alcohol molecules.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
In the formation of alkene from the dehydration of alcohol, the second step which is the formation of carbocation is the rate determining step of the mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




