
EDTA multidentate ligand. Its denticity (multicity) is
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Ligands are the donor atoms, molecules or anions which donate a pair of electrons to metal atoms or ions are called ligands. In EDTA there are four Oxygen atoms and two Nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen and oxygen both have lone pairs to coordinate with the central atom in the complex compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Denticity refers to the number of donor groups in a particular ligand that transfer lone pairs to the central atom and bind it in complex compounds. In most of the cases, only a single atom in the ligand binds to the metal, then the denticity equals one, and the ligand is said to be monodentate or bidentate. Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ions (EDTA) form a complex with metal ions in coordination compounds.
Denticity refers to the number of donor groups that are attached to the ligand to participate in forming coordinate bonds with the complex compounds. EDTA is a type of ligand in which donor atoms contain lone pairs of electrons and can donate electrons to positively charged central atom species to form complex compounds. EDTA is a multidentate ligand. Its denticity (multiplicity) is six.
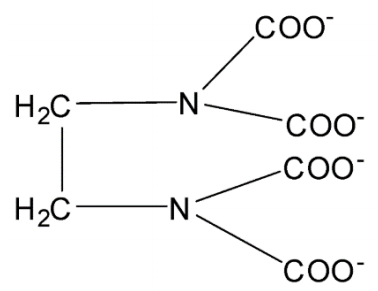
In EDTA, there are four Oxygen atoms and two Nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen and oxygen both have lone pairs to coordinate with the central atom in the complex compound. EDTA is also used extensively in the analysis of blood. It is an anticoagulant for blood samples in the field of medicine.
DTA is a polydentate ligand that has flexidentate character in which four Oxygen atoms and two Nitrogen atoms form coordinate bonds with the central metal atom or ion. Therefore, there are six donor atoms present in EDTA. Hence, EDTA is a hexadentate ligand. Its denticity or multiplicity is 6.
Note: The coordination compounds are of great importance and are widely present in minerals, plants and animals and are known to play many important functions in analytical chemistry, metallurgy, biological systems, industry and medicine. EDTA is used in treatment of lead poisoning. EDTA which is a hexadentate ligand also acts as tetradentate or pentadentate in certain complexes.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Denticity refers to the number of donor groups in a particular ligand that transfer lone pairs to the central atom and bind it in complex compounds. In most of the cases, only a single atom in the ligand binds to the metal, then the denticity equals one, and the ligand is said to be monodentate or bidentate. Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ions (EDTA) form a complex with metal ions in coordination compounds.
Denticity refers to the number of donor groups that are attached to the ligand to participate in forming coordinate bonds with the complex compounds. EDTA is a type of ligand in which donor atoms contain lone pairs of electrons and can donate electrons to positively charged central atom species to form complex compounds. EDTA is a multidentate ligand. Its denticity (multiplicity) is six.

In EDTA, there are four Oxygen atoms and two Nitrogen atoms. Nitrogen and oxygen both have lone pairs to coordinate with the central atom in the complex compound. EDTA is also used extensively in the analysis of blood. It is an anticoagulant for blood samples in the field of medicine.
DTA is a polydentate ligand that has flexidentate character in which four Oxygen atoms and two Nitrogen atoms form coordinate bonds with the central metal atom or ion. Therefore, there are six donor atoms present in EDTA. Hence, EDTA is a hexadentate ligand. Its denticity or multiplicity is 6.
Note: The coordination compounds are of great importance and are widely present in minerals, plants and animals and are known to play many important functions in analytical chemistry, metallurgy, biological systems, industry and medicine. EDTA is used in treatment of lead poisoning. EDTA which is a hexadentate ligand also acts as tetradentate or pentadentate in certain complexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




