
What is an electromagnet? Describe the construction and working of an electromagnet with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The electromagnet converts electrical energy into magnetic energy. To understand the mechanism of conversion, the relationship between the magnetic field produced by the electromagnet and the electric current flowing through it, must be described so as to explain the phenomenon.
Complete answer:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid
When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid:
Here is a detailed diagram indicating the parts of an electromagnet.
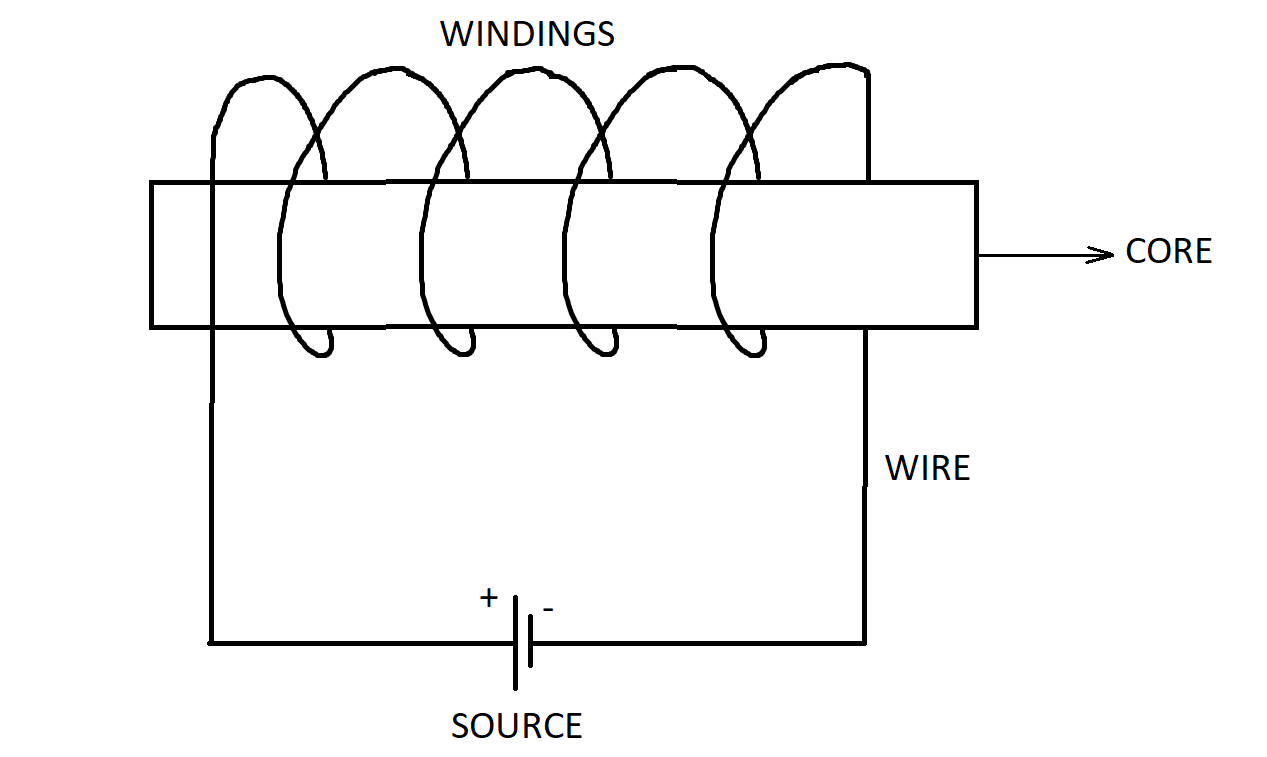 Construction –
Construction –
The electromagnet consists of copper wire which is wound across a magnetic material known as core. These windings are connected to an DC electric source. The magnetism exists in the electromagnet as long as the electric source is supplying current and it gets switched off the moment, the source is disconnected.
Working –
When the current flows in the windings, there is magnetic field set up in the core as per the concept of Ampere’s circuital law which states that –
The integrated magnetic field around a closed curve is equal to ${\mu _0}$ times the net current flowing in the circuit.
$\oint\limits_C {Bdl} = {\mu _0}I$
where ${\mu _0}$ is called permeability, which represents the ability of the core material to allow magnetic lines to pass through it.
The direction of the magnet field is given by the right-hand thumb rule which states that –
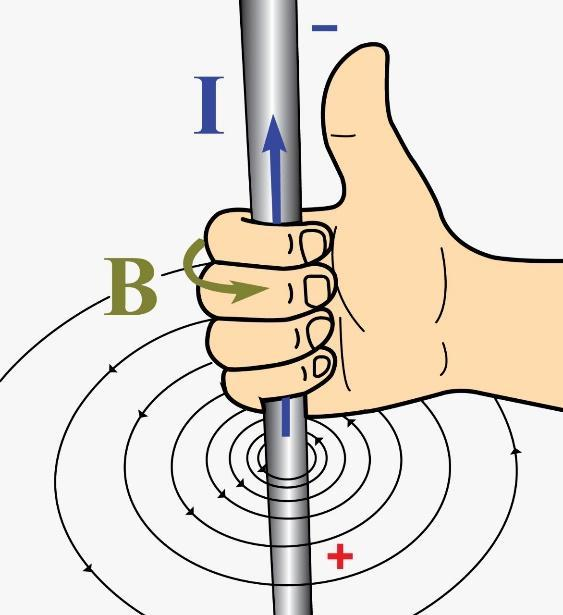
If the current is represented by the thumb of the right hand, the direction of curl of the remaining fingers represent the direction of magnetic field B.
Now, in the case of the electromagnet, the current is moving in a circular path. Now, if we apply the right-hand rule, the ends of the electromagnet behave as poles of an actual magnet as shown:
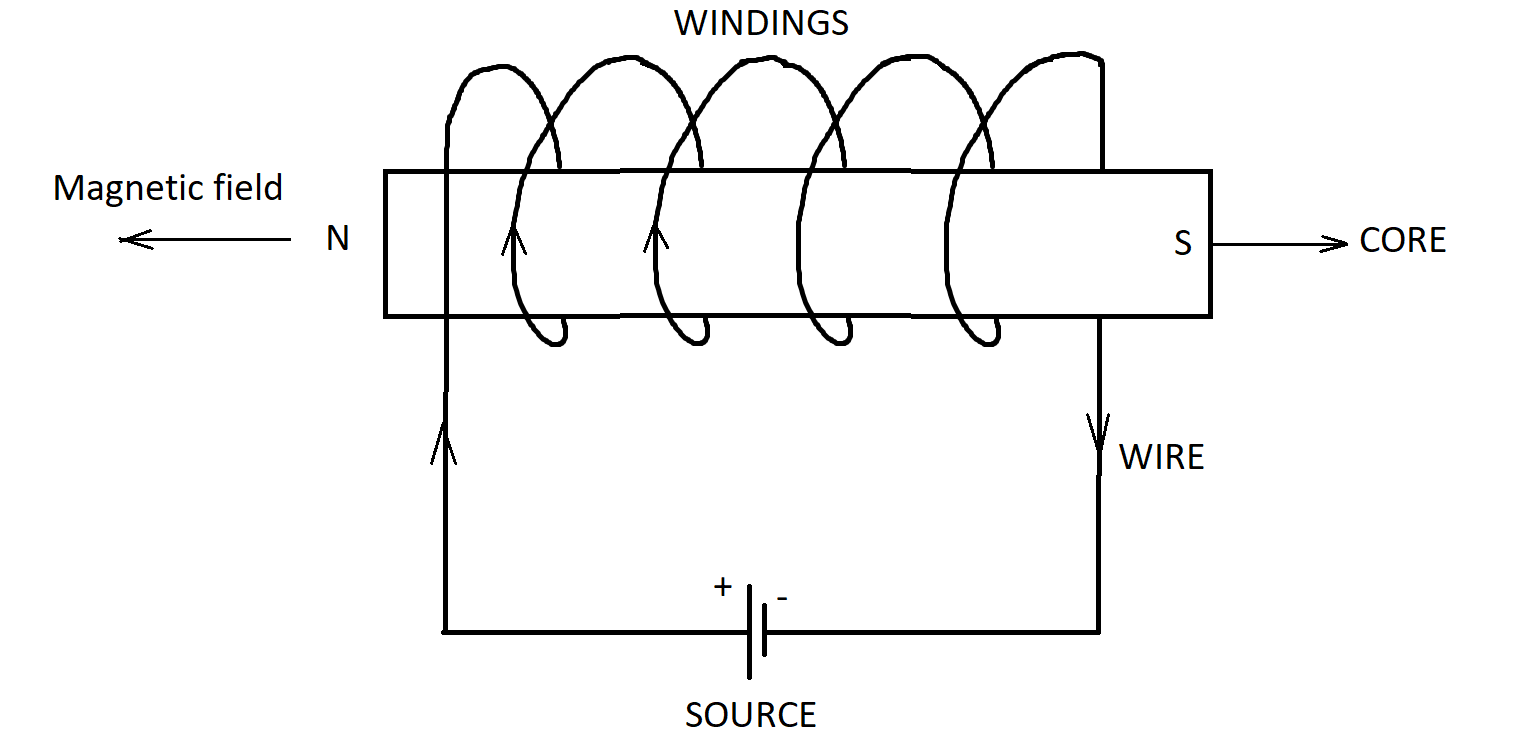
However, this temporary magnet switches off when the source is switched off.
The core enhances the strength of the magnetic field and is made of magnetic materials such as iron, carbon steel, nickel or even aluminium.
Uses of electromagnets:
i) Motors and generators
ii) Segregating metallic waste
iii) Loudspeakers and relay circuits.
Note: The electromagnet is not only stronger than a natural magnet but, its strength can also, be varied easily, by replacing the core of the magnet or altering the number of the turns in the winding. This makes electromagnets versatile in usage compared to ordinary natural magnets.
Complete answer:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid
When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid:
Here is a detailed diagram indicating the parts of an electromagnet.

The electromagnet consists of copper wire which is wound across a magnetic material known as core. These windings are connected to an DC electric source. The magnetism exists in the electromagnet as long as the electric source is supplying current and it gets switched off the moment, the source is disconnected.
Working –
When the current flows in the windings, there is magnetic field set up in the core as per the concept of Ampere’s circuital law which states that –
The integrated magnetic field around a closed curve is equal to ${\mu _0}$ times the net current flowing in the circuit.
$\oint\limits_C {Bdl} = {\mu _0}I$
where ${\mu _0}$ is called permeability, which represents the ability of the core material to allow magnetic lines to pass through it.
The direction of the magnet field is given by the right-hand thumb rule which states that –

If the current is represented by the thumb of the right hand, the direction of curl of the remaining fingers represent the direction of magnetic field B.
Now, in the case of the electromagnet, the current is moving in a circular path. Now, if we apply the right-hand rule, the ends of the electromagnet behave as poles of an actual magnet as shown:

However, this temporary magnet switches off when the source is switched off.
The core enhances the strength of the magnetic field and is made of magnetic materials such as iron, carbon steel, nickel or even aluminium.
Uses of electromagnets:
i) Motors and generators
ii) Segregating metallic waste
iii) Loudspeakers and relay circuits.
Note: The electromagnet is not only stronger than a natural magnet but, its strength can also, be varied easily, by replacing the core of the magnet or altering the number of the turns in the winding. This makes electromagnets versatile in usage compared to ordinary natural magnets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




