
Elucidate the structure of fructose?
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Fructose is a simple ketonic monosaccharide having 6 carbons in its chemical structure. Fructose forms a five membered ring which we call a furanose ring. Now try to use these hints and describe the structure of fructose.
Complete answer:
Fructose was discovered in the year 1847 by a French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut. As we already know Fructose is a simple ketonic monosaccharide. These monosaccharides are the fundamental units of carbohydrates that cannot be further reduced to simpler compounds.
We mostly find fructose in plants and their fruits, flowers, and root vegetables, hence it is known as fruit sugar.
Structure of fructose -
The chemical formula of fructose is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$.
It has its carbonyl group at its number two carbon. In this arrangement, C5-OH combines with the ketonic group present in the second position.
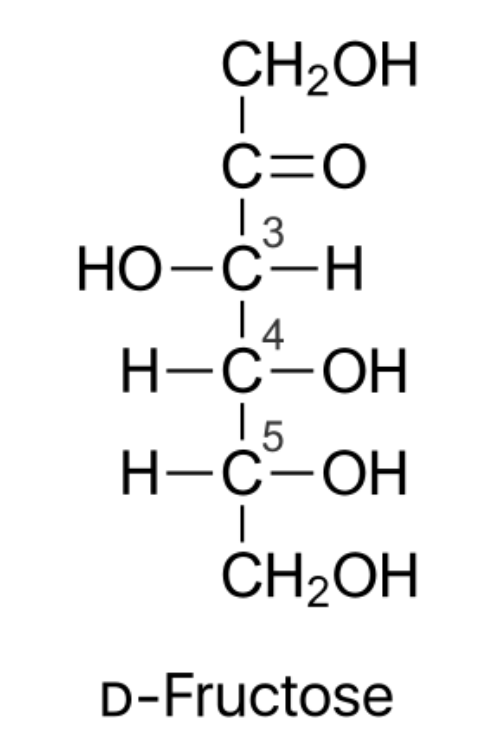
Due to the presence of the keto group, it results in the formation of the intramolecular hemiacetal. This results in the formation of chiral carbon and two arrangements of ${ CH }_{ 2 }OH$ and OH group.
Fructose in its cyclic form has a five-member ring which we call a Furanose ring. Hence D-fructose exhibits stereoisomerism in which $\alpha $-D-fructopyranose and $\beta $-D-fructopyranose are isomers.
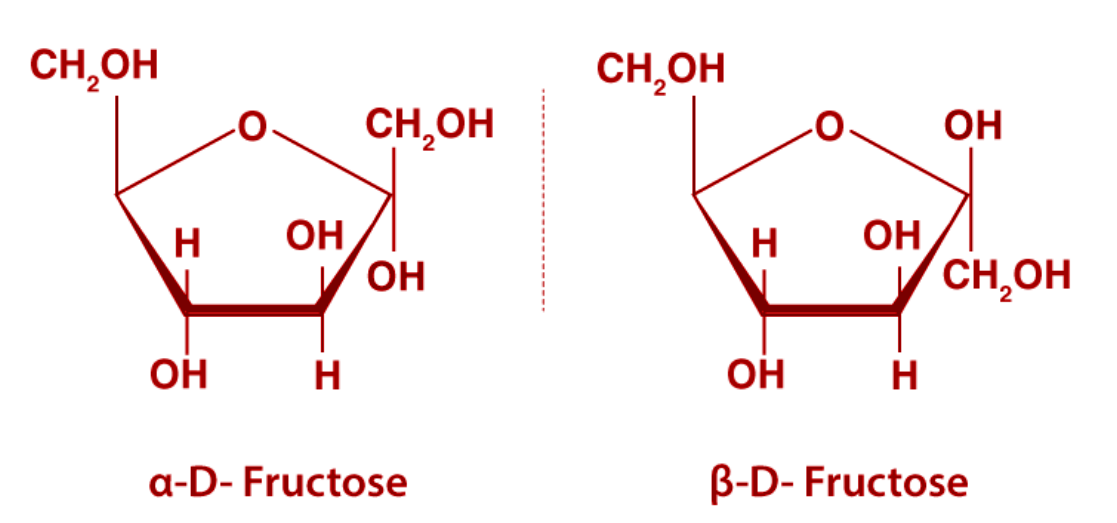
Note: The D and L configuration assigned on the basis of configuration of glyceraldehyde molecule which contains one chiral atom. If the OH group of glyceraldehyde molecules lies towards the right side, it is called D- configuration and if it is on the left side, it will be L-configuration. The same concept applies to the fructose molecule.
Complete answer:
Fructose was discovered in the year 1847 by a French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut. As we already know Fructose is a simple ketonic monosaccharide. These monosaccharides are the fundamental units of carbohydrates that cannot be further reduced to simpler compounds.
We mostly find fructose in plants and their fruits, flowers, and root vegetables, hence it is known as fruit sugar.
Structure of fructose -
The chemical formula of fructose is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$.
It has its carbonyl group at its number two carbon. In this arrangement, C5-OH combines with the ketonic group present in the second position.

Due to the presence of the keto group, it results in the formation of the intramolecular hemiacetal. This results in the formation of chiral carbon and two arrangements of ${ CH }_{ 2 }OH$ and OH group.
Fructose in its cyclic form has a five-member ring which we call a Furanose ring. Hence D-fructose exhibits stereoisomerism in which $\alpha $-D-fructopyranose and $\beta $-D-fructopyranose are isomers.

Note: The D and L configuration assigned on the basis of configuration of glyceraldehyde molecule which contains one chiral atom. If the OH group of glyceraldehyde molecules lies towards the right side, it is called D- configuration and if it is on the left side, it will be L-configuration. The same concept applies to the fructose molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




