
Epistasis in which dihybrid ratio of 9:3:3:1 between AaBb X AaBb is modified is
(a) Dominance of one allele on another allele at the same locus
(b) Dominance of one allele on another allele at both its loci
(c) Interaction of two alleles at different loci
(d) Interaction between two alleles at the same locus
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: In this, the dominant allele of one gene hides the effect of the allele gene and expresses itself phenotypically. This involves intra-allelic gene interaction where one allele hides the effect of other alleles at the same gene pair.
Complete step by step answer:
Epistasis occurs when one allele of a gene masks the expression of alleles of another gene.When a dominant allele at one locus can mask the expression of both alleles at another locus, it is known as dominant epistasis. The expression of one dominant and recessive allele is masked by another dominant gene. This is also referred to as simple epistasis.
The hypostatic B allele will be expressed only when gene locus A contains two recessive alleles. Thus, the genotype AA BB or Aa Bb and AA bb or Aa bb produce the same phenotype- genotype aa BB or aa Bb and aa bb produce two additional phenotypes. This type of dominant epistasis which modifies the classical ratio of 9:3:3:1 into 12:3:1.
Example in summer squash (Cucurbita pepo):
Common fruit colours- white, yellow & green White (A) is dominant over coloured squash Yellow (B) is dominant over green squash Pure breeding white fruited variety is crossed with the double recessive green variety, ${{F}_{1}}$ hybrids are all white When the hybrids are selfed- white, yellow & green fruited plants arise in the ratio of 12:3:1
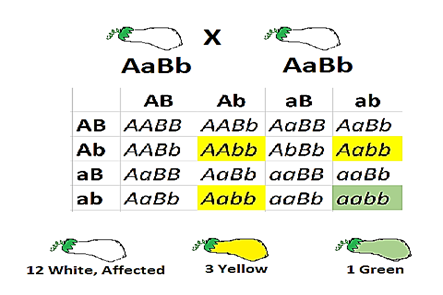
So, the correct answer is, ‘Dominance of one allele on another allele at both its loci.’
Note:
- Involves intra-allelic gene interaction Involves inter- allelic gene interaction
- One allele mask the effect of other alleles of the same gene One allele hides the effect of other alleles of the different gene
- Kinds of Epistasis:
Dominant Epistasis.
Recessive epistasis
Duplicate Recessive Genes
Duplicate Dominant Genes
Duplicate Genes with Cumulative Effect
Dominant Recessive Interaction
Complete step by step answer:
Epistasis occurs when one allele of a gene masks the expression of alleles of another gene.When a dominant allele at one locus can mask the expression of both alleles at another locus, it is known as dominant epistasis. The expression of one dominant and recessive allele is masked by another dominant gene. This is also referred to as simple epistasis.
The hypostatic B allele will be expressed only when gene locus A contains two recessive alleles. Thus, the genotype AA BB or Aa Bb and AA bb or Aa bb produce the same phenotype- genotype aa BB or aa Bb and aa bb produce two additional phenotypes. This type of dominant epistasis which modifies the classical ratio of 9:3:3:1 into 12:3:1.
Example in summer squash (Cucurbita pepo):
Common fruit colours- white, yellow & green White (A) is dominant over coloured squash Yellow (B) is dominant over green squash Pure breeding white fruited variety is crossed with the double recessive green variety, ${{F}_{1}}$ hybrids are all white When the hybrids are selfed- white, yellow & green fruited plants arise in the ratio of 12:3:1

So, the correct answer is, ‘Dominance of one allele on another allele at both its loci.’
Note:
- Involves intra-allelic gene interaction Involves inter- allelic gene interaction
- One allele mask the effect of other alleles of the same gene One allele hides the effect of other alleles of the different gene
- Kinds of Epistasis:
Dominant Epistasis.
Recessive epistasis
Duplicate Recessive Genes
Duplicate Dominant Genes
Duplicate Genes with Cumulative Effect
Dominant Recessive Interaction
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




