
Explain how a polycistronic gene structural gene is regulated by a common promoter and a combination of regulatory genes in lac-operon.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Polycistronic mRNA code for several proteins. The gene contains an intercistronic gene followed by another cistron. During post transcriptional modification, these regions are spliced to form a polycistronic mRNA. A classic example of such genes is the lac operon which contains a cluster of genes that help bacteria grow in a lactose enriched medium.
Complete answer:
The lac operon consists of the promoter(p) region to which the RNA polymerase binds, an operator(o) region to which the repressor protein binds, and a regulatory(i) genes that produce the repressor protein along with three structural genes (z, y and a) that are involved in the metabolism of lactose.
In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor binds to the operator region blocking the transcription of the gene by RNA polymerase. When lactose is present in the medium, lactose binds to the repressor protein forming an allolactose molecule that dissociates itself from the operator region making way for the RNA polymerase which transcribes the structural genes. The polycistronic mRNA is thus formed which later gets translated to form enzymes for lactose metabolism.
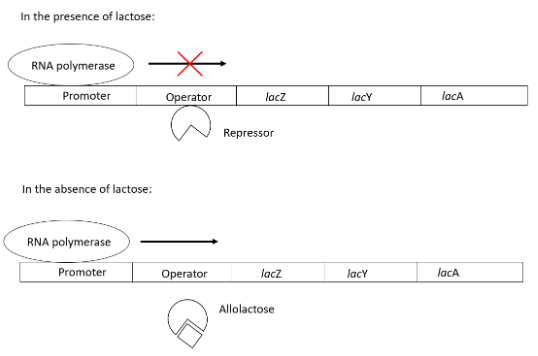
Note: Hydrolysis of lactose gives glucose and galactose. Intramolecular transfer of this galactose yields allolactose which turns in the lac operon and is thus also known as the inducer molecule. It binds to the allosteric site of the repressor protein. This binding brings about a conformational change in the repressor protein allowing it to dissociate from the operator region. Once it leaves, it gives way for the RNA polymerase for the transcription of the structural genes.
Complete answer:
The lac operon consists of the promoter(p) region to which the RNA polymerase binds, an operator(o) region to which the repressor protein binds, and a regulatory(i) genes that produce the repressor protein along with three structural genes (z, y and a) that are involved in the metabolism of lactose.
In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor binds to the operator region blocking the transcription of the gene by RNA polymerase. When lactose is present in the medium, lactose binds to the repressor protein forming an allolactose molecule that dissociates itself from the operator region making way for the RNA polymerase which transcribes the structural genes. The polycistronic mRNA is thus formed which later gets translated to form enzymes for lactose metabolism.

Note: Hydrolysis of lactose gives glucose and galactose. Intramolecular transfer of this galactose yields allolactose which turns in the lac operon and is thus also known as the inducer molecule. It binds to the allosteric site of the repressor protein. This binding brings about a conformational change in the repressor protein allowing it to dissociate from the operator region. Once it leaves, it gives way for the RNA polymerase for the transcription of the structural genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




