
Explain how the formation of the rainbow occurs.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Rainbow is a phenomenon which is due to the diffractive nature of refraction and reflection inside the water molecule. Speed of light inside water depends on the wavelength of the light wave. That is why light splits into the constituent colours when it enters a water droplet.
Complete step by step answer:
If you face away from the sun, and it has just rained in your area, there is a chance that you may see a rainbow in the sky. Rainbow can be best seen in the afternoon when the rain clouds are moving towards the east.
The following diagram explains the position of the rainbow with respect to the observer, and sun position.
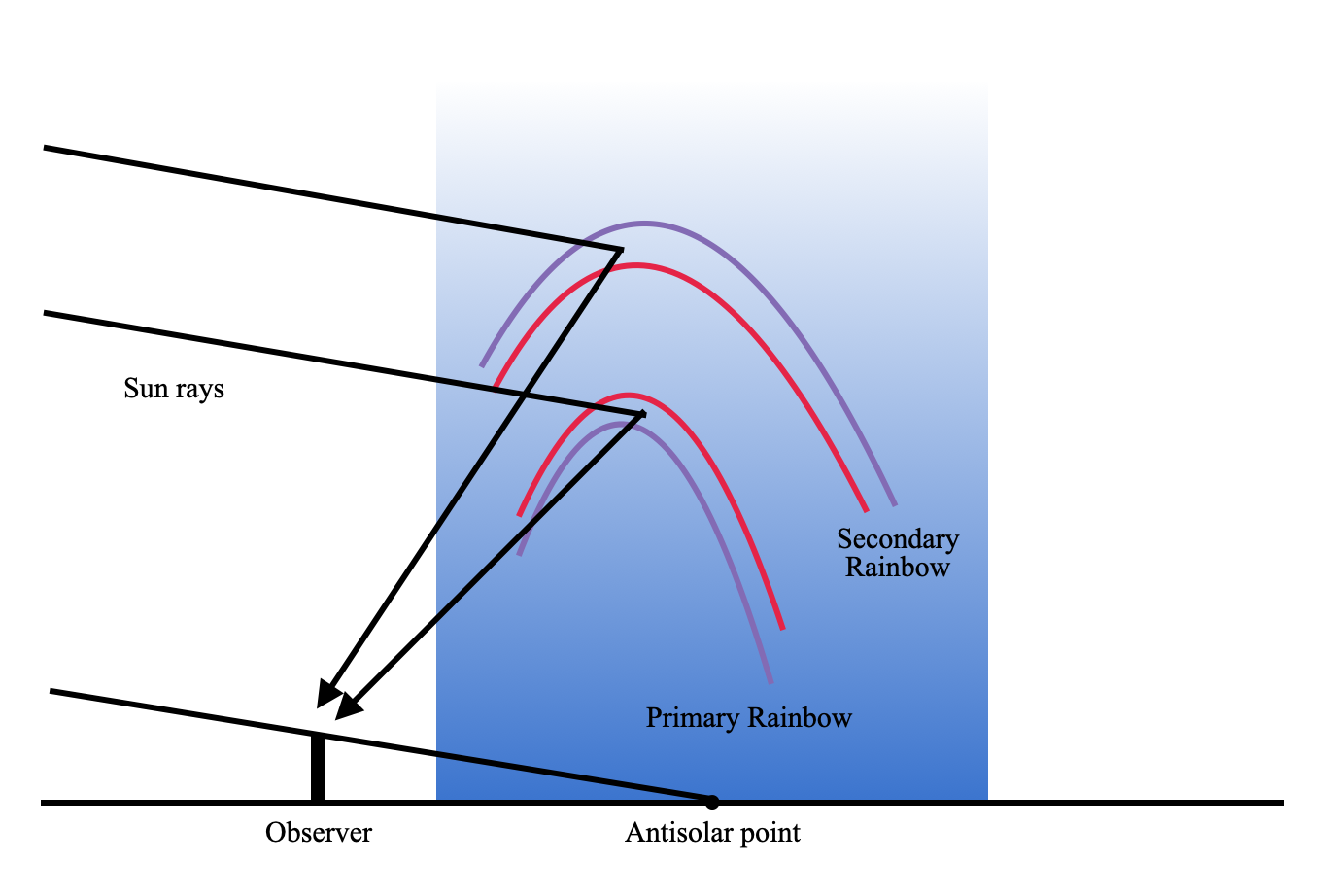
Rainbows occur due to the phenomena like diffraction and internal full reflections. Theoretically there are several rainbows possible, but we can only see one generally. If you are lucky, you can see two.
When light falls on the spherical water droplet, it enters the droplet. As the speeds of different wavelengths of light are different in denser medium, light is split into its constituent colours. These light waves undergo a full internal reflection on the other side of the spherical water drop before leaving through the side it came inside.
The following diagram shows this phenomenon quite clearly,
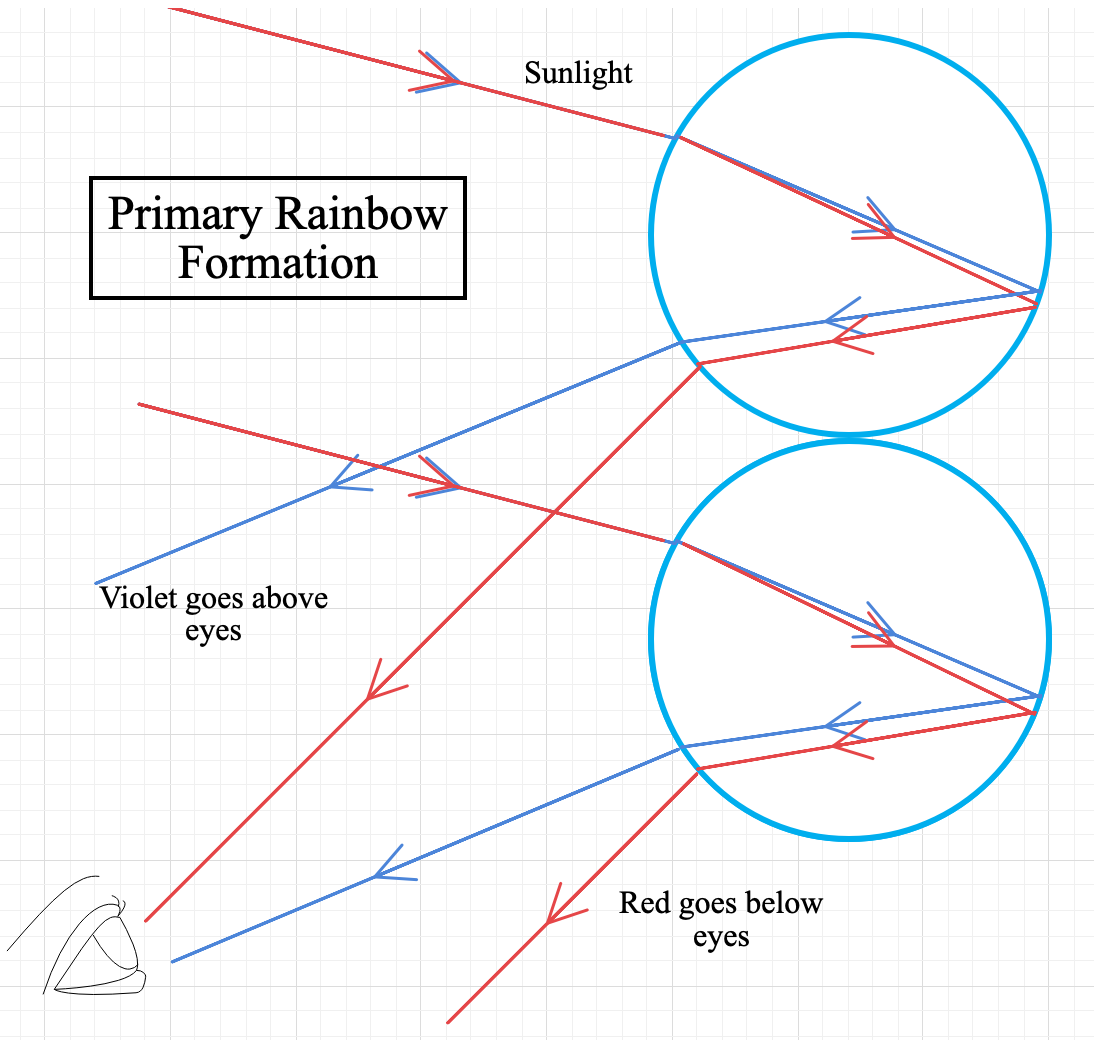
As you can see in the figure, the violet light from the higher droplet goes above our eyes, and the red light from the lower droplet goes below our eyes. As a result, red light is at the top and violet is at the bottom of the rainbow.
Note: Sometimes, we can also see a secondary rainbow if we are lucky. In that case, light undergoes two internal reflections on the water-air surface before finally leaving the droplet. Secondary rainbows are inverted in colour, and it generally forms above the primary rainbow. The following diagram shows the formation of secondary rainbow:
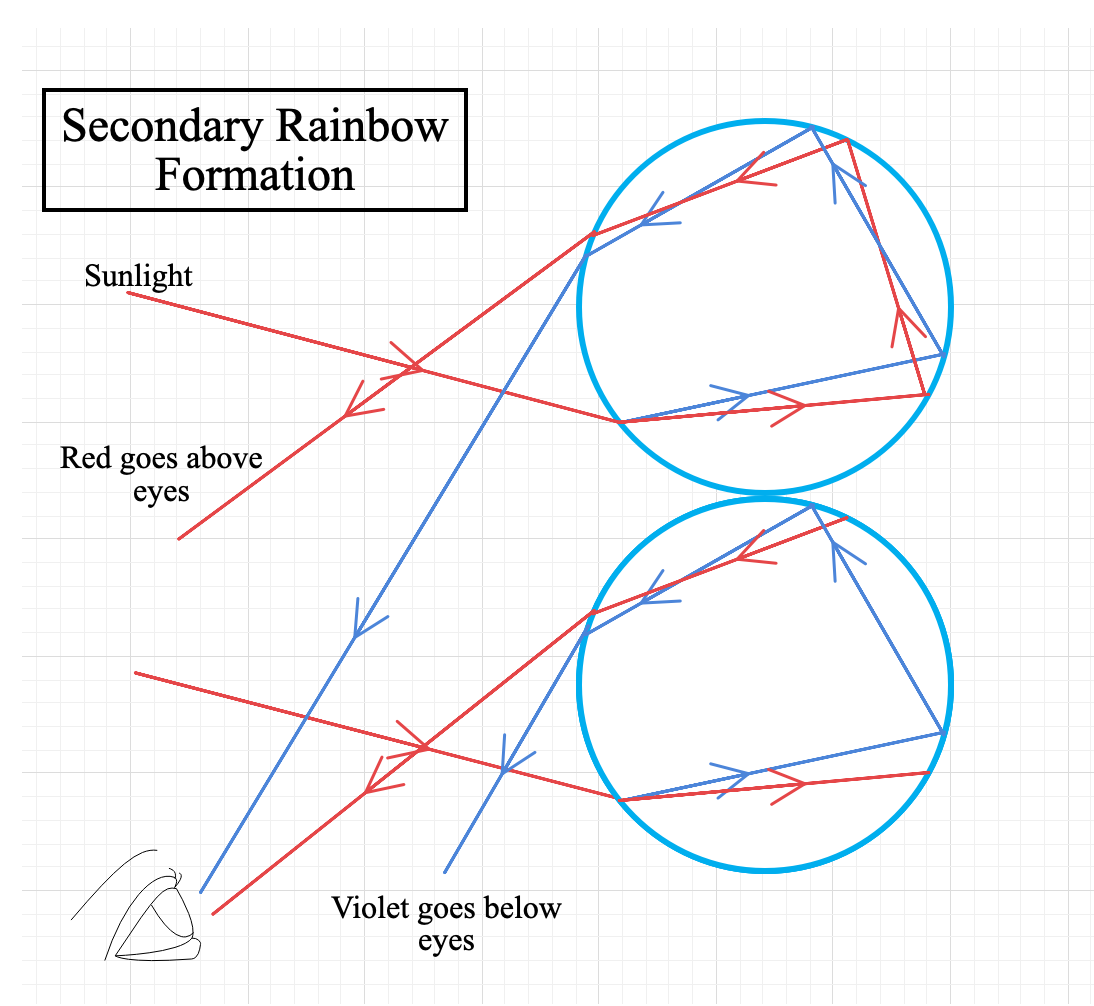
Complete step by step answer:
If you face away from the sun, and it has just rained in your area, there is a chance that you may see a rainbow in the sky. Rainbow can be best seen in the afternoon when the rain clouds are moving towards the east.
The following diagram explains the position of the rainbow with respect to the observer, and sun position.

Rainbows occur due to the phenomena like diffraction and internal full reflections. Theoretically there are several rainbows possible, but we can only see one generally. If you are lucky, you can see two.
When light falls on the spherical water droplet, it enters the droplet. As the speeds of different wavelengths of light are different in denser medium, light is split into its constituent colours. These light waves undergo a full internal reflection on the other side of the spherical water drop before leaving through the side it came inside.
The following diagram shows this phenomenon quite clearly,

As you can see in the figure, the violet light from the higher droplet goes above our eyes, and the red light from the lower droplet goes below our eyes. As a result, red light is at the top and violet is at the bottom of the rainbow.
Note: Sometimes, we can also see a secondary rainbow if we are lucky. In that case, light undergoes two internal reflections on the water-air surface before finally leaving the droplet. Secondary rainbows are inverted in colour, and it generally forms above the primary rainbow. The following diagram shows the formation of secondary rainbow:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




