
What is SHE? Explain its construction and application.
Answer
524.2k+ views
Hint: ${\text{SHE}}$ stands for standard hydrogen electrode. The standard hydrogen electrode is used in half cells as a reference electrode for determining the electrode potential. SHE has zero electrode potential at the temperature of \[298K\].
Complete step by step answer:
The standard hydrogen electrode is an electrode which is used in laboratory for measurement of electric potential of other electrodes in comparison to SHE at the same temperature that is \[298K\] SHE is based upon the redox half-cell, whose reaction is:
\[2{H^ + }\left( {aq} \right) + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}\left( g \right)\]
In this process, a platinum electrode is used which is dipped in an acidic solution. Upon reaction, hydrogen gas is bubbled out. In the reaction, the concentration of both oxidized as well as reduced hydrogen is maintained at unity.
Construction of SHE is done as shown in the figure:
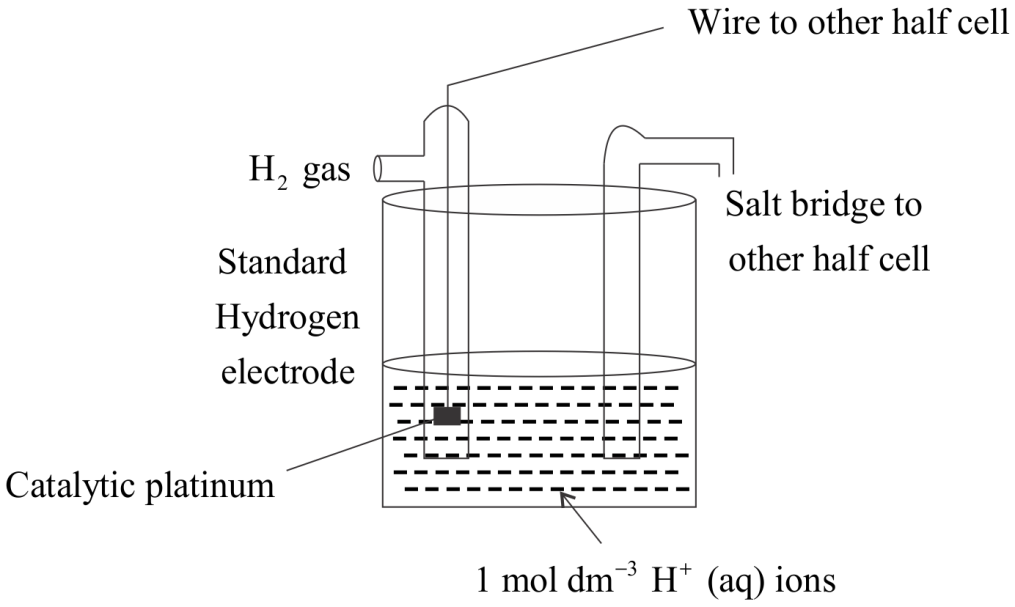
SHE consists of:
A platinum electrode covered in platinum black.
A hydrogen blow.
Acidic solution of concentration \[1\] mole \[d{m^{ - 3}}\]
It is also connected to another half life cell of the galvanic cell.
Application of SHE are:
SHE is used as an anode or cathode half cell
SHE is used to measure the potential of other electrodes. The unknown potential in this case would be equal to the EMF (Electromotive force) of the cell.
SHE also have some disadvantages such as:
It is difficult to construct, transport and maintain a SHE.
Pure hydrogen gas is yielding with difficulty.
The platinum electrode easily gets spoiled due to the presence of impurities.
Note:
A platinum electrode is used in SHE because of various reasons such as:
It forms an inert electrode, so the platinum itself does not participate in the reaction.
Platinum is a good absorber of \[{H_2}\] gas and helps in improving the chemical kinetics of the process.
Complete step by step answer:
The standard hydrogen electrode is an electrode which is used in laboratory for measurement of electric potential of other electrodes in comparison to SHE at the same temperature that is \[298K\] SHE is based upon the redox half-cell, whose reaction is:
\[2{H^ + }\left( {aq} \right) + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}\left( g \right)\]
In this process, a platinum electrode is used which is dipped in an acidic solution. Upon reaction, hydrogen gas is bubbled out. In the reaction, the concentration of both oxidized as well as reduced hydrogen is maintained at unity.
Construction of SHE is done as shown in the figure:

SHE consists of:
A platinum electrode covered in platinum black.
A hydrogen blow.
Acidic solution of concentration \[1\] mole \[d{m^{ - 3}}\]
It is also connected to another half life cell of the galvanic cell.
Application of SHE are:
SHE is used as an anode or cathode half cell
SHE is used to measure the potential of other electrodes. The unknown potential in this case would be equal to the EMF (Electromotive force) of the cell.
SHE also have some disadvantages such as:
It is difficult to construct, transport and maintain a SHE.
Pure hydrogen gas is yielding with difficulty.
The platinum electrode easily gets spoiled due to the presence of impurities.
Note:
A platinum electrode is used in SHE because of various reasons such as:
It forms an inert electrode, so the platinum itself does not participate in the reaction.
Platinum is a good absorber of \[{H_2}\] gas and helps in improving the chemical kinetics of the process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




