
Explain Rosenmond’s reduction of benzoyl chloride.
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Rosenmund’s reduction is a hydrogenation process in which acid chloride is selectively reduced to aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
Acyl chlorides can be reduced into aldehydes with hydrogen in boiling xylene using palladium or platinum as catalyst supported on barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund’s reduction.
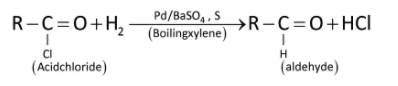
For example:
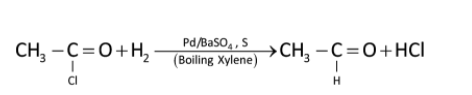
Similarly
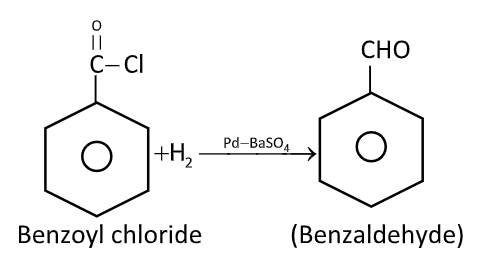
The function of $BaS{O_4}$is to poison the catalyst at the aldehyde stage. The catalyst is also poisoned to small extent by sulphur compounds to prevent further reaction of aldehyde to $1^\circ $ alcohols. Generally, a small amount of quinoline and sulphur is also added.
Note:
Rosenmund’s reduction is only for the preparation of aldehydes but ketones cannot be prepared by this method.
Acid chlorides are readily reduced to aldehydes by weaker reducing agents, like lithium tri – tertiary butoxy aluminium hydride.
Complete step by step answer:
Acyl chlorides can be reduced into aldehydes with hydrogen in boiling xylene using palladium or platinum as catalyst supported on barium sulphate. This reaction is called Rosenmund’s reduction.

For example:

Similarly

The function of $BaS{O_4}$is to poison the catalyst at the aldehyde stage. The catalyst is also poisoned to small extent by sulphur compounds to prevent further reaction of aldehyde to $1^\circ $ alcohols. Generally, a small amount of quinoline and sulphur is also added.
Note:
Rosenmund’s reduction is only for the preparation of aldehydes but ketones cannot be prepared by this method.
Acid chlorides are readily reduced to aldehydes by weaker reducing agents, like lithium tri – tertiary butoxy aluminium hydride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




