
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in $C{H_3}Cl$.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should have knowledge about the conditions required for the formation of a covalent or an ionic bond. Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share a pair of electrons which helps them to reach a stable electronic configuration, i.e. completely fill their outer valence shell. Most of the organic compounds form covalent bonds. Ionic bonds are formed by a complete transfer of valence electrons between atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
In $C{H_3}Cl$, we know that carbon has an electronic configuration of $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ which means that it has 4 electrons in its valence orbital and it needs 4 more electrons to reach a stable configuration, i.e. fill its valence shell. For hydrogen, we know that its electronic configuration is $1{s^1}$ which means that it needs 1 electron to fill its valence shell and achieve stability. In the case of chlorine, its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5}$, this means that it has 7 electrons in its valence shell and needs only 1 electron to complete its octet and reach a stable configuration.
As a result, these 5 atoms come together and share their electrons with each other to fill their valence shells. Carbon shares 1 electron each with the 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 chlorine atom thereby completely filling their valence shells and the hydrogen and chlorine share 1 electron each with carbon thereby completing its octet as well. We can understand the bonding better by studying their Lewis structures:
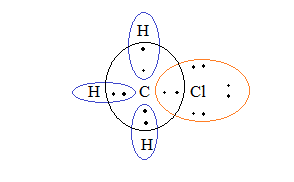
Overlapping of orbitals of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine as a result of sharing of electrons to form covalent bonds in $C{H_3}Cl$. Covalent bonds are usually formed best between atoms of similar electro-negativity. So, covalent molecules are generally non-polar. Ideally, there is an equal share of both the atoms over the shared pair of electrons. But, due to the difference in electronegativity of atoms, there is unequal sharing of the electrons which result in partial ionic character in covalent bonds.
Note:
Covalent bonds are usually formed between atoms with electron deficiency, i.e. mostly non-metals. Due to the directional nature of p-orbitals, there are two types of covalent bonds. Sigma bonds (σ) formed by head-on overlapping of orbitals of two different atoms. A single bond is usually a sigma bond. Pi bonds (π) are formed by the lateral overlapping of the orbitals. A double bond generally has 1 sigma bond and 1 pi bond while a triple bond has 1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
In $C{H_3}Cl$, we know that carbon has an electronic configuration of $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2}$ which means that it has 4 electrons in its valence orbital and it needs 4 more electrons to reach a stable configuration, i.e. fill its valence shell. For hydrogen, we know that its electronic configuration is $1{s^1}$ which means that it needs 1 electron to fill its valence shell and achieve stability. In the case of chlorine, its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5}$, this means that it has 7 electrons in its valence shell and needs only 1 electron to complete its octet and reach a stable configuration.
As a result, these 5 atoms come together and share their electrons with each other to fill their valence shells. Carbon shares 1 electron each with the 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 chlorine atom thereby completely filling their valence shells and the hydrogen and chlorine share 1 electron each with carbon thereby completing its octet as well. We can understand the bonding better by studying their Lewis structures:

Overlapping of orbitals of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine as a result of sharing of electrons to form covalent bonds in $C{H_3}Cl$. Covalent bonds are usually formed best between atoms of similar electro-negativity. So, covalent molecules are generally non-polar. Ideally, there is an equal share of both the atoms over the shared pair of electrons. But, due to the difference in electronegativity of atoms, there is unequal sharing of the electrons which result in partial ionic character in covalent bonds.
Note:
Covalent bonds are usually formed between atoms with electron deficiency, i.e. mostly non-metals. Due to the directional nature of p-orbitals, there are two types of covalent bonds. Sigma bonds (σ) formed by head-on overlapping of orbitals of two different atoms. A single bond is usually a sigma bond. Pi bonds (π) are formed by the lateral overlapping of the orbitals. A double bond generally has 1 sigma bond and 1 pi bond while a triple bond has 1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




