
Explain the process of grafting.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: This process method of asexual plant propagation joins plant parts from different plants together so they will heal and grow as one plant. It is useful in plants that cannot grow from cuttings.
Complete Answer:
- Many plant parts like root, leaves and stem, under the right conditions, can grow into new plants. This mode of reproduction is known as vegetative propagation. This vegetative propagation property is used for agricultural purposes, or for grafting or layering to grow several plants, such as rose, sugarcane, or grapes.
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seed.
- Plant grafting is a vegetative propagation technique that connects two severed plant segments together.
- The chimaera, created by the scion and rootstock, survives after wound healing as a new individual. The graft's success depends on the compatibility of rootstock to scion.
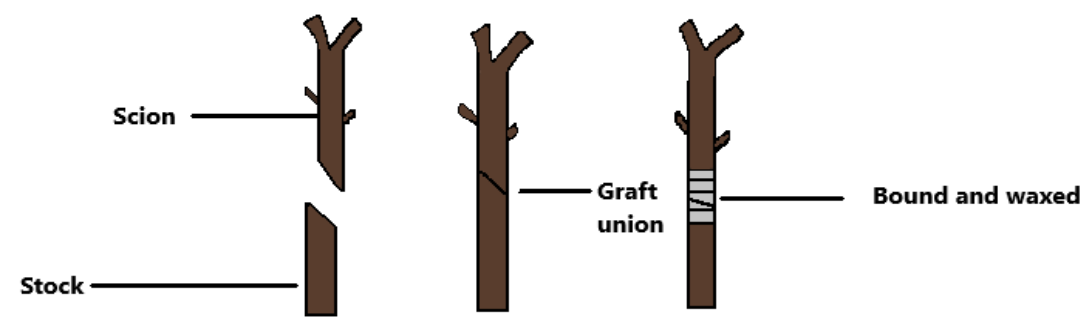
Fig: Grafting process
- The bottom portion of the plant used for grafting is called the rootstock. Usually this includes a healthy root system, and some part of the stem.
- The area above the graft portion is called the scion. It is a young plant shoot or bud with beneficial characteristics such as colour or resistance to disease.
- The cambium of both stock and scion are joined to make a connection. All of a grafted plant's top growth, leaves, flowers, fruits, etc., comes from the scion.
- The process of grafting is done to change or create a variety of plants, repair damaged plants, ensure pollination, or for propagating hybrid species.
Note: Stock cambium and scion cambium react to being cut by forming cell masses (callus tissues) that expand over the injured wound surfaces. The union arising from the interlocking of the callus tissues forms the basis of grafting.
Complete Answer:
- Many plant parts like root, leaves and stem, under the right conditions, can grow into new plants. This mode of reproduction is known as vegetative propagation. This vegetative propagation property is used for agricultural purposes, or for grafting or layering to grow several plants, such as rose, sugarcane, or grapes.
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seed.
- Plant grafting is a vegetative propagation technique that connects two severed plant segments together.
- The chimaera, created by the scion and rootstock, survives after wound healing as a new individual. The graft's success depends on the compatibility of rootstock to scion.

Fig: Grafting process
- The bottom portion of the plant used for grafting is called the rootstock. Usually this includes a healthy root system, and some part of the stem.
- The area above the graft portion is called the scion. It is a young plant shoot or bud with beneficial characteristics such as colour or resistance to disease.
- The cambium of both stock and scion are joined to make a connection. All of a grafted plant's top growth, leaves, flowers, fruits, etc., comes from the scion.
- The process of grafting is done to change or create a variety of plants, repair damaged plants, ensure pollination, or for propagating hybrid species.
Note: Stock cambium and scion cambium react to being cut by forming cell masses (callus tissues) that expand over the injured wound surfaces. The union arising from the interlocking of the callus tissues forms the basis of grafting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




