
Explain the respiratory pathway which is common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer
480k+ views
Hint: The process of generating energy without the use of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration. In some cases, such as when sprinting, the body is unable to supply the muscles with the oxygen they require to generate energy.What is the difference between the two types of anaerobic respiration, Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation
Complete answer:
Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration use glycolysis as a common process. The glycolysis or EMP route is the mechanism by which glucose (6C substance) is divided into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C compound). It can be found in the cytoplasm. The following are the reactions that occur during glycolysis:
(i) ATP phosphorylates glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate. Hexokinase is the enzyme that catalyses the reaction.
(ii) Phosphoglucoisomerase isomerizes glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate.
(iii) Using ATP, fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Phosphofructokinase is the enzyme that catalyses this process. ADP is formed when ATP is dephosphorylated.
(iv) The enzyme aldolase cleaves fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate into two 3C compounds: dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde. These two groups of three are isomers.
(v) The action of triosephosphate isomerase allows DHAP and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde to be interconverted. The hexose phase is formed by these five series of reactions, which result in two molecules of the 3-carbon complex.
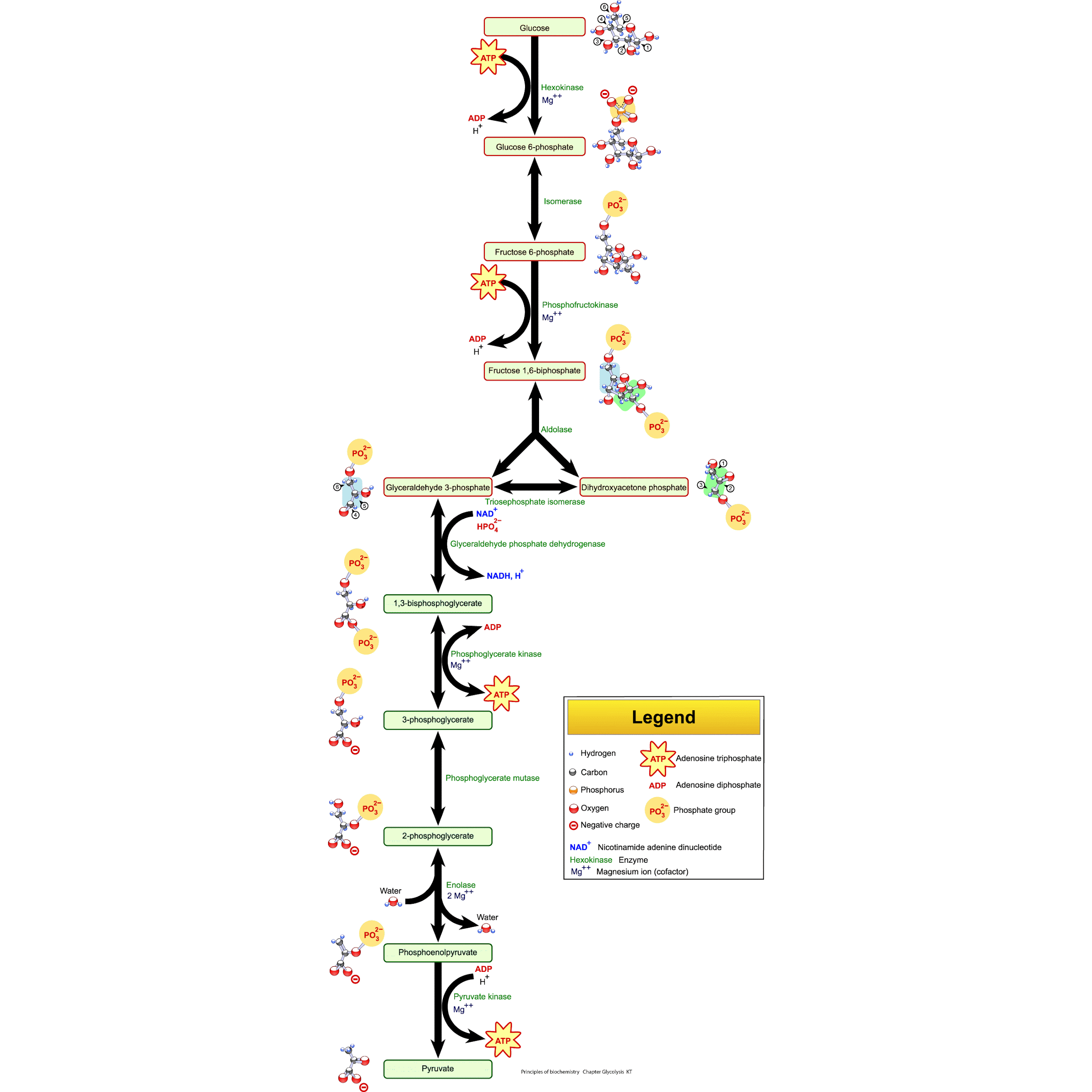
3-phosphoglyceraldehyde. Two ATP molecules are utilised during the hexose phase.
In the presence of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde is phosphorylated and oxidised to 1, 3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. One $NADH_2$ is generated during this reaction.
(vii) The phosphoglyceric kinase dephosphorylates 1, 3-bisphosphoglyceric acid to a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceric acid. One ATP is generated during this process. Direct phosphorylation, often known as substrate phosphorylation, is a method of ATP synthesis.
(viii) Phosphoglycerate mutase converts a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceric acid into a molecule of 2-phosphoglyceric acid. The phosphate molecule is transferred from third to second carbon in this process.
Enolase dehydrates a molecule of 2-phosphoglyceric acid into a molecule of 2-phosphoenol pyruvic acid. Enolation is the process of removing a water molecule from a material.
(ix) Pyruvic acid is dephosphorylated to pyruvic acid and ADP is phosphorylated to ATP from a molecule of 2-phosphoenol pyruvic acid. The pyruvic kinase catalyses this process. Two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde create two molecules of pyruvic acid during the triose phase.
In the hexose phase of glycolysis, 4ATP and 2$NADH_2$ molecules are generated, while 2ATP molecules are consumed. As a result, the net gain is 2ATP and 2$NADH_2$.
Note:-
The Krebs citric acid cycle and the cytochrome chain are other names for the aerobic process. The by-products of the initial anaerobic glycolysis stage are oxidised in these two steps to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a large number of energy-rich ATP molecules. Cell respiration refers to all of these stages taken together.
Complete answer:
Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration use glycolysis as a common process. The glycolysis or EMP route is the mechanism by which glucose (6C substance) is divided into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C compound). It can be found in the cytoplasm. The following are the reactions that occur during glycolysis:
(i) ATP phosphorylates glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate. Hexokinase is the enzyme that catalyses the reaction.
(ii) Phosphoglucoisomerase isomerizes glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate.
(iii) Using ATP, fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Phosphofructokinase is the enzyme that catalyses this process. ADP is formed when ATP is dephosphorylated.
(iv) The enzyme aldolase cleaves fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate into two 3C compounds: dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde. These two groups of three are isomers.
(v) The action of triosephosphate isomerase allows DHAP and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde to be interconverted. The hexose phase is formed by these five series of reactions, which result in two molecules of the 3-carbon complex.

3-phosphoglyceraldehyde. Two ATP molecules are utilised during the hexose phase.
In the presence of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde is phosphorylated and oxidised to 1, 3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. One $NADH_2$ is generated during this reaction.
(vii) The phosphoglyceric kinase dephosphorylates 1, 3-bisphosphoglyceric acid to a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceric acid. One ATP is generated during this process. Direct phosphorylation, often known as substrate phosphorylation, is a method of ATP synthesis.
(viii) Phosphoglycerate mutase converts a molecule of 3-phosphoglyceric acid into a molecule of 2-phosphoglyceric acid. The phosphate molecule is transferred from third to second carbon in this process.
Enolase dehydrates a molecule of 2-phosphoglyceric acid into a molecule of 2-phosphoenol pyruvic acid. Enolation is the process of removing a water molecule from a material.
(ix) Pyruvic acid is dephosphorylated to pyruvic acid and ADP is phosphorylated to ATP from a molecule of 2-phosphoenol pyruvic acid. The pyruvic kinase catalyses this process. Two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde create two molecules of pyruvic acid during the triose phase.
In the hexose phase of glycolysis, 4ATP and 2$NADH_2$ molecules are generated, while 2ATP molecules are consumed. As a result, the net gain is 2ATP and 2$NADH_2$.
Note:-
The Krebs citric acid cycle and the cytochrome chain are other names for the aerobic process. The by-products of the initial anaerobic glycolysis stage are oxidised in these two steps to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a large number of energy-rich ATP molecules. Cell respiration refers to all of these stages taken together.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




