
Explain the role of tapetum in the formation of the pollen-grain wall.
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: A pollen grain can be defined as a male gamete of plant species. It is a single celled structure with a hard outer covering. It's lightweight structure allows it to flow in air along with other dust particles.
Complete answer:
Tapetum is one of the most important layers of anther body that is concerned with supplying nutrition to developing microspores (to be pollen grains). Detailed discussion of structures of pollen grains and anthers will be helpful in making the concept as clear as crystal.
Structure of an Anther:
An Anther body consists of two lobes joint through a sterile connective tissue.
Each such lobe consists of two deep and hollow cavities called microsporangia or also called pollen sacs. These sacs hold premature pollen grains also called microspores.
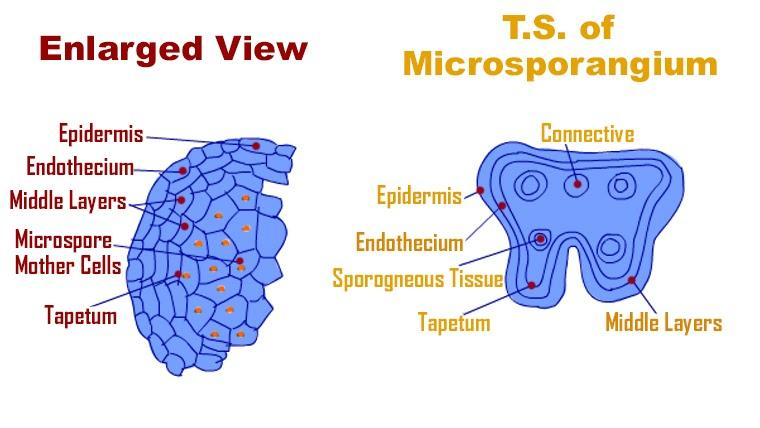
Microsporangia is a multi-layered structure. The outermost layer is called epidermis (outer covering of anther body) followed by Endothecium (a thick fibrous layer concerned with providing a cushion-like platform to developing microspores).
Endothecium is descended by the Tapetum layer. This layer consists of protoplasmic content that serves as a nutritional source to the developing microspores. Also, cells in this structure are multinucleated in order to provide more nutrition to these microspores by faster manufacturing of food. Therefore, it is evident that the Tapetum layer is one of the most important structures of anther body.
Additional Information:
The plant’s male reproductive organ contains a sporogonium structure called microsporangium, the site of pollen development. It is circular in outline in the transverse section. It is surrounded by four wall layers: the epidermis, endothecium, middle layer, and tapetum (from outside to inside). The cells develop thickenings at endothecium and the middle layer is made up of 2-4 cells. The function of the outer three layers i.e. epidermis, endothecium, and the middle layer is to protect the developing anthers and aids in dehiscence of anther to release pollen grains. At the center of the microsporangium, compactly arranged homogenous cells called sporogenous tissue are present. During another development, these tissues undergo meiotic divisions to form microspore tetrads, which results in pollen grains.
Note:
A pollen grain or male gametophyte is generally spherical in shape. It has hard covering all around that is absolutely resistant to adverse climatic conditions. Its diameter ranges from 25-50 µm. On maturation, anthers dehydrate resulting in the dissociation of microspores and development into pollen grains.
Complete answer:
Tapetum is one of the most important layers of anther body that is concerned with supplying nutrition to developing microspores (to be pollen grains). Detailed discussion of structures of pollen grains and anthers will be helpful in making the concept as clear as crystal.
Structure of an Anther:
An Anther body consists of two lobes joint through a sterile connective tissue.
Each such lobe consists of two deep and hollow cavities called microsporangia or also called pollen sacs. These sacs hold premature pollen grains also called microspores.
Microsporangia is a multi-layered structure. The outermost layer is called epidermis (outer covering of anther body) followed by Endothecium (a thick fibrous layer concerned with providing a cushion-like platform to developing microspores).
Endothecium is descended by the Tapetum layer. This layer consists of protoplasmic content that serves as a nutritional source to the developing microspores. Also, cells in this structure are multinucleated in order to provide more nutrition to these microspores by faster manufacturing of food. Therefore, it is evident that the Tapetum layer is one of the most important structures of anther body.

Additional Information:
The plant’s male reproductive organ contains a sporogonium structure called microsporangium, the site of pollen development. It is circular in outline in the transverse section. It is surrounded by four wall layers: the epidermis, endothecium, middle layer, and tapetum (from outside to inside). The cells develop thickenings at endothecium and the middle layer is made up of 2-4 cells. The function of the outer three layers i.e. epidermis, endothecium, and the middle layer is to protect the developing anthers and aids in dehiscence of anther to release pollen grains. At the center of the microsporangium, compactly arranged homogenous cells called sporogenous tissue are present. During another development, these tissues undergo meiotic divisions to form microspore tetrads, which results in pollen grains.
Note:
A pollen grain or male gametophyte is generally spherical in shape. It has hard covering all around that is absolutely resistant to adverse climatic conditions. Its diameter ranges from 25-50 µm. On maturation, anthers dehydrate resulting in the dissociation of microspores and development into pollen grains.
Watch videos on
Explain the role of tapetum in the formation of the pollen-grain wall.

Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class12 NCERT EXERCISE1.17| Class 12 Chapter1| Kanika Sharma
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
44 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
