
Explain the steps in the formation of an ovum from an oogonium in humans.
Answer
530k+ views
Hint: The process by which ovum is formed from oogonium is called oogenesis. It occurs in three phases: multiplication, growth, and then maturation.
Complete answer:
Oogenesis is the process by which an ovum or a secondary oocyte is produced from the oogonia.
Oogonium is the singular form, oogonia are plural.
First, during the embryonic period of a female, the primordial germ cells differentiate to form numerous oogonium or oogonial cells.
The cell pool is maintained by repeated mitotic divisions.
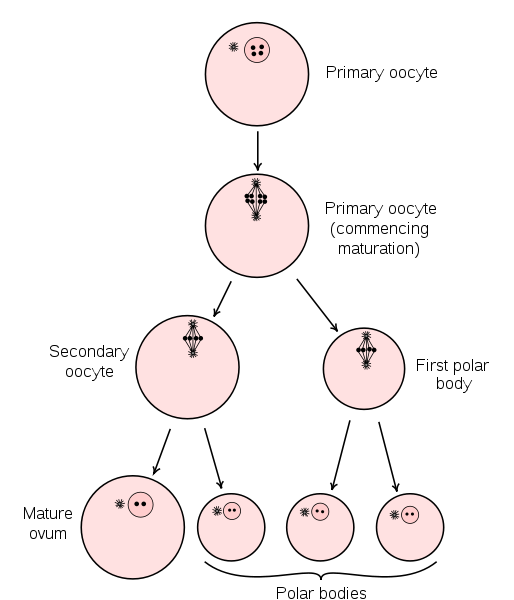
Now the oogonia grows into the primary oocytes as the onset of meiosis I occur. After completion of meiosis I, diploid primary oocytes produce two types of haploid cells- a secondary oocyte and the first polar body.
The secondary oocyte completes its meiotic division after sperm entry and produces another polar body and a mature ovum. The first polar body also divides to form two new polar bodies.
Note: Oogenesis is a discontinuous process. It is arrested twice.
First, the primary oocyte is arrested in prophase I; it releases after puberty.
Second, the secondary oocyte is arrested at metaphase II; it releases upon sperm entry.
Complete answer:
Oogenesis is the process by which an ovum or a secondary oocyte is produced from the oogonia.
Oogonium is the singular form, oogonia are plural.
First, during the embryonic period of a female, the primordial germ cells differentiate to form numerous oogonium or oogonial cells.
The cell pool is maintained by repeated mitotic divisions.

Now the oogonia grows into the primary oocytes as the onset of meiosis I occur. After completion of meiosis I, diploid primary oocytes produce two types of haploid cells- a secondary oocyte and the first polar body.
The secondary oocyte completes its meiotic division after sperm entry and produces another polar body and a mature ovum. The first polar body also divides to form two new polar bodies.
Note: Oogenesis is a discontinuous process. It is arrested twice.
First, the primary oocyte is arrested in prophase I; it releases after puberty.
Second, the secondary oocyte is arrested at metaphase II; it releases upon sperm entry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




