
Explain the structure and the properties of triacylglycerol.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Triacylglycerols are esters. An ester is formed when alcohol and carboxylic acid molecules condense. During condensation, a small water molecule is lost. The ester of glycerol with fatty acid is called triacylglycerol. Triacylglycerols are oily in nature and are soluble in non-polar solvents.
Complete Step by step answer: triacylglycerol is also called triglycerides. It is an ester of glycerol with fatty acids. The backbone contains glycerol. In triglycerides, one molecule of glycerol forms esters with three fatty acids. Sometimes in triacylglycerides, one molecule of glycerol forms esters with two fatty acids and one phosphoric acid group.
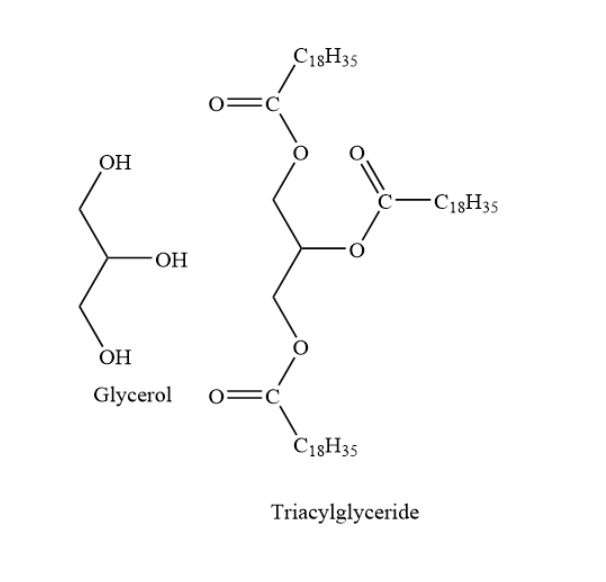
In triacylglycerides, the length of the fatty acid side chain may vary. Also, the degree of unsaturation of the fatty acid side chain may also vary. Here, the degree of unsaturation means the number of carbon-carbon double bonds present. Also, in a triacylglycerol, all the three fatty acids may be the same or they may be different.
Triacylglycerols are oily or greasy in nature. They are soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in water. This is due to the presence of long hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids.
Most part of cell membrane is made from triacylglycerols. Thus, triacylglycerols serve as an essential cell component.
The main constituent of body fat in humans and other vertebrates is triacylglycerol. In blood, triacylglycerols help in two-way transport of blood glucose and adipose fat from the liver. In human skin oils, triacylglycerols are present.
Note: Triacylglycerol is a part of the lipid family. Lipids contain several groups of compounds which have hydrocarbon chains in their backbone. Lipids constitute oils and fatty acids. Oils contain several carbon-carbon double bonds. Fats usually contain carbon-carbon single bonds. Thus, in triacylglycerol, the long hydrocarbon chains can have all carbon-carbon single bonds, or they can have one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
Complete Step by step answer: triacylglycerol is also called triglycerides. It is an ester of glycerol with fatty acids. The backbone contains glycerol. In triglycerides, one molecule of glycerol forms esters with three fatty acids. Sometimes in triacylglycerides, one molecule of glycerol forms esters with two fatty acids and one phosphoric acid group.

In triacylglycerides, the length of the fatty acid side chain may vary. Also, the degree of unsaturation of the fatty acid side chain may also vary. Here, the degree of unsaturation means the number of carbon-carbon double bonds present. Also, in a triacylglycerol, all the three fatty acids may be the same or they may be different.
Triacylglycerols are oily or greasy in nature. They are soluble in non-polar solvents and insoluble in water. This is due to the presence of long hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids.
Most part of cell membrane is made from triacylglycerols. Thus, triacylglycerols serve as an essential cell component.
The main constituent of body fat in humans and other vertebrates is triacylglycerol. In blood, triacylglycerols help in two-way transport of blood glucose and adipose fat from the liver. In human skin oils, triacylglycerols are present.
Note: Triacylglycerol is a part of the lipid family. Lipids contain several groups of compounds which have hydrocarbon chains in their backbone. Lipids constitute oils and fatty acids. Oils contain several carbon-carbon double bonds. Fats usually contain carbon-carbon single bonds. Thus, in triacylglycerol, the long hydrocarbon chains can have all carbon-carbon single bonds, or they can have one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




