
Explain the symplastic movement and apoplastic movement of water in the cell.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The apoplastic pathway allows water movement through the cell wall and other intercellular spaces. The symplastic pathway provides plasmodesmata for moving the water from one cell to another.
Complete answer:To answer this question, first, we need to know how plants absorb water from soil. Water from the soil mostly enters the plant through root hairs in the root's piliferous layer.
The root hairs are tubular extensions of epidermal cells, and significantly increase the surface area for soil water absorption. Generally the soil solution has a higher potential for water than the piliferous layer cells. Root hairs are the plant’s principal water-absorbing organ. The root hairs are responsible for soil uptake of water and mineral nutrients. The root has unicellular hairs with the aid of which it can absorb water from the soil. Within the root, there are three water passageways from root hairs to xylem.
In the apoplastic pathway, water moves through the walls of intervening cells from root hair to xylem, without crossing any membrane or cytoplasm. This direction offers the least resistance to water movement. However, it is disrupted by the presence of impermeable Casparian lignosuberine strips in the endodermal cell walls. In the endodermal cell wall, the Casparian strips block the passage of water from outside to inside or back, unless it moves through the endodermal cell membrane and cytoplasm. These strips have waterproof compounds known as suberin which prevents water from moving apoplastically. Water and dissolved minerals never pass through the plasma membrane of a cell in this pathway but rather migrate through the porous cell walls that surround the plant cell.
Additional information:The symplast represents a continuous system. The cytoplasmic strands known as plasmodesmata join the protoplast of the cortex, vascular tissue and endodermis from cell to cell. In non-vacuolar symplast pathways water travels through their protoplasm from cell to cell. It does not pass the cell vacuoles.
Plasmodesmata joins the adjacent cell's cytoplasm. Water travels from one cell to the next through water channels in the plant cell plasma membrane, until it enters the xylem. Each root cell acts as a tiny osmotic system in the vascular symplast pathway. First the root hair cell absorbs soil water by osmosis. Then it moves by osmosis into vacuoles of neighboring cortical cells. The process continues till the parenchyma cells of the xylem enter water.
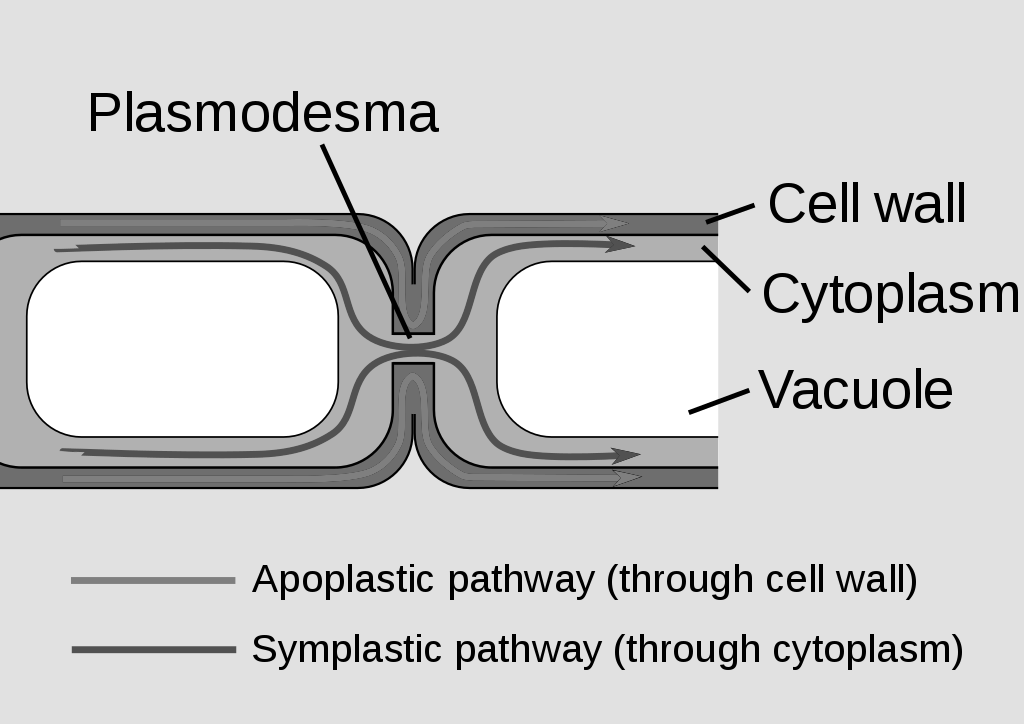
Note:The apoplastic pathway is the completely permeable route where passive diffusion of the water movement occurs. While the symplastic is a selectively permeable pathway where osmosis occurs in the movement of water.
Complete answer:To answer this question, first, we need to know how plants absorb water from soil. Water from the soil mostly enters the plant through root hairs in the root's piliferous layer.
The root hairs are tubular extensions of epidermal cells, and significantly increase the surface area for soil water absorption. Generally the soil solution has a higher potential for water than the piliferous layer cells. Root hairs are the plant’s principal water-absorbing organ. The root hairs are responsible for soil uptake of water and mineral nutrients. The root has unicellular hairs with the aid of which it can absorb water from the soil. Within the root, there are three water passageways from root hairs to xylem.
In the apoplastic pathway, water moves through the walls of intervening cells from root hair to xylem, without crossing any membrane or cytoplasm. This direction offers the least resistance to water movement. However, it is disrupted by the presence of impermeable Casparian lignosuberine strips in the endodermal cell walls. In the endodermal cell wall, the Casparian strips block the passage of water from outside to inside or back, unless it moves through the endodermal cell membrane and cytoplasm. These strips have waterproof compounds known as suberin which prevents water from moving apoplastically. Water and dissolved minerals never pass through the plasma membrane of a cell in this pathway but rather migrate through the porous cell walls that surround the plant cell.
Additional information:The symplast represents a continuous system. The cytoplasmic strands known as plasmodesmata join the protoplast of the cortex, vascular tissue and endodermis from cell to cell. In non-vacuolar symplast pathways water travels through their protoplasm from cell to cell. It does not pass the cell vacuoles.
Plasmodesmata joins the adjacent cell's cytoplasm. Water travels from one cell to the next through water channels in the plant cell plasma membrane, until it enters the xylem. Each root cell acts as a tiny osmotic system in the vascular symplast pathway. First the root hair cell absorbs soil water by osmosis. Then it moves by osmosis into vacuoles of neighboring cortical cells. The process continues till the parenchyma cells of the xylem enter water.

Note:The apoplastic pathway is the completely permeable route where passive diffusion of the water movement occurs. While the symplastic is a selectively permeable pathway where osmosis occurs in the movement of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




