
Explain the working of Ruby Laser with the help of an energy level diagram.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: A ruby laser is a device that gives out an intense red light through the emission of energy radiation by electrons when they fall from a higher energy state to a lower energy state in the ruby crystal.
Complete step by step answer:
A ruby laser consists of a cylindrical crystal of ruby with flat ends. Ruby is nothing but aluminium oxide $\left( A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}} \right)$ where in some of the places of the crystal, $A{{l}^{3+}}$ ions are replaced by $C{{r}^{3+}}$ ions. The ends of the crystal are flat. One of them is completely silvered and reflects all of the light incident on it, while the other end is partially silvered (it reflects part of the light incident on it and lets the rest pass through it).
A ruby laser emits light by accumulating the emitted radiation when electrons drop from a higher energy state to the ground state and release it through the side of the partially silvered end. The light released is an intense red one.
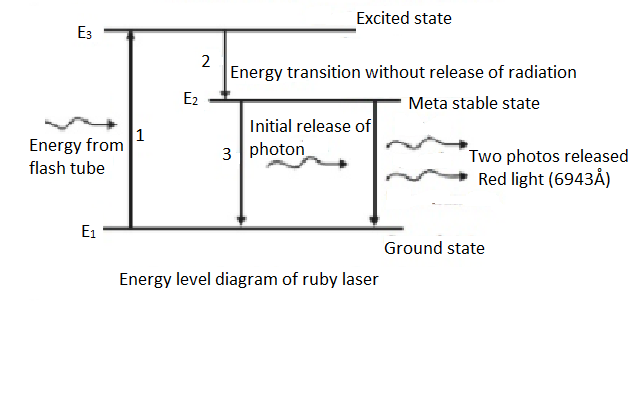
There are three energy levels in the ruby crystal, ground state $\left( {{E}_{1}} \right)$, metastable state $\left( {{E}_{2}} \right)$ and excited state $\left( {{E}_{3}} \right)$ where ${{E}_{3}}>{{E}_{2}}>{{E}_{1}}$. The electrons in the ground state are given energy through a device called the flash tube. Then the electrons jump up to the excited state ${{E}_{3}}$. At this level they quickly fall down to the metastable energy level ${{E}_{2}}$ and release energy but not in the form of radiation. Since, the electron is a bit more stable in this state, there is an accumulation of electrons at this energy level.
After this, one electron further falls back down to the ground state, while releasing energy in the form of a photon. This photon hits another electron in the ${{E}_{2}}$ level and the electron falls down to ${{E}_{1}}$ again releasing a photon making a total of two photons. This process happens many times and is aided by the fact that the completely silvered end reflects the light and the photons, so that there is more and more accumulation of photons by release of energy by the electrons. Finally, this forms a very intense red beam of light ($6943$Å) which is emitted from the partially silvered side.
Note: Students should know that the first photon that is released as per the above explanation is termed to be spontaneous emission, However, the second one that is released is termed to be stimulated emission. This is because the second release of a photon is stimulated by the first photon colliding with the electron. This is a characteristic of LASER where millions of stimulated emissions of radiation take place to get a strong beam of light. This is also known as light amplification. In fact, the full form of LASER is Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
A ruby laser consists of a cylindrical crystal of ruby with flat ends. Ruby is nothing but aluminium oxide $\left( A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}} \right)$ where in some of the places of the crystal, $A{{l}^{3+}}$ ions are replaced by $C{{r}^{3+}}$ ions. The ends of the crystal are flat. One of them is completely silvered and reflects all of the light incident on it, while the other end is partially silvered (it reflects part of the light incident on it and lets the rest pass through it).
A ruby laser emits light by accumulating the emitted radiation when electrons drop from a higher energy state to the ground state and release it through the side of the partially silvered end. The light released is an intense red one.
There are three energy levels in the ruby crystal, ground state $\left( {{E}_{1}} \right)$, metastable state $\left( {{E}_{2}} \right)$ and excited state $\left( {{E}_{3}} \right)$ where ${{E}_{3}}>{{E}_{2}}>{{E}_{1}}$. The electrons in the ground state are given energy through a device called the flash tube. Then the electrons jump up to the excited state ${{E}_{3}}$. At this level they quickly fall down to the metastable energy level ${{E}_{2}}$ and release energy but not in the form of radiation. Since, the electron is a bit more stable in this state, there is an accumulation of electrons at this energy level.
After this, one electron further falls back down to the ground state, while releasing energy in the form of a photon. This photon hits another electron in the ${{E}_{2}}$ level and the electron falls down to ${{E}_{1}}$ again releasing a photon making a total of two photons. This process happens many times and is aided by the fact that the completely silvered end reflects the light and the photons, so that there is more and more accumulation of photons by release of energy by the electrons. Finally, this forms a very intense red beam of light ($6943$Å) which is emitted from the partially silvered side.

Note: Students should know that the first photon that is released as per the above explanation is termed to be spontaneous emission, However, the second one that is released is termed to be stimulated emission. This is because the second release of a photon is stimulated by the first photon colliding with the electron. This is a characteristic of LASER where millions of stimulated emissions of radiation take place to get a strong beam of light. This is also known as light amplification. In fact, the full form of LASER is Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




