
Explain Watson and Crick model of DNA.
Answer
519.9k+ views
Hint: DNA is a long polymer of de-oxy-ribonucleotides. The length of the DNA is usually defined as the number of nucleotides present in it.
Complete Answer:
- DNA as an acidic substance present in the nucleus was first identified by Frederich Meischer in 1869. He named it as 'nucleon'. Due to technical limitations in isolating such a long polymer intact the elucidation of structure of DNA remained elusive for a long period of time.
- It was only in 1953 that James Watson and Francis Crick proposed the very simple but famous double helix model for the structure of DNA. The main opposition was base pairing between the two strands of polynucleotide chains.
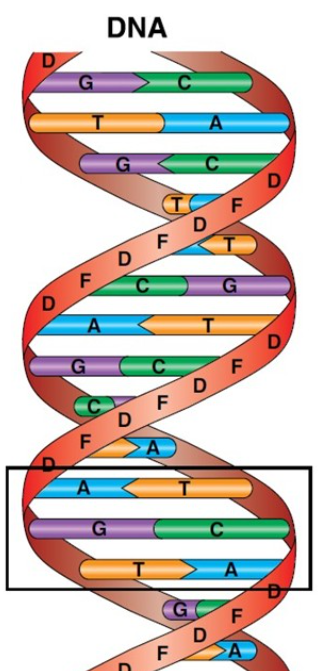
The salient features of double helix structure of DNA are as follows:
- It is made up of two polynucleotide chains.
- The two chains have antiparallel polarity if one has polarities and the second chain must have polarity.
- The base into strands is paired through hydrogen bond forming base pairs. Adenine forms to hydrogen bonds with thymine from opposite strands and vice versa.
- Similarly guanine forms three H bonds with cytosine. As a result, purine comes opposite to pyrimidine.
Because of this approximate a uniform distance between the two strengths of The Helix occurs.
- The two chains are called in a right-handed fashion. Pitch of the helix is and there are roughly 10bp in each turn.
- The plane of one base pair is stacked over the other in a double helix. This confirms stability of the helical structure.
Note: The proposition of a double helix structure for DNA and its simplicity in explaining the genetic implication become revolutionary.
Complete Answer:
- DNA as an acidic substance present in the nucleus was first identified by Frederich Meischer in 1869. He named it as 'nucleon'. Due to technical limitations in isolating such a long polymer intact the elucidation of structure of DNA remained elusive for a long period of time.
- It was only in 1953 that James Watson and Francis Crick proposed the very simple but famous double helix model for the structure of DNA. The main opposition was base pairing between the two strands of polynucleotide chains.

The salient features of double helix structure of DNA are as follows:
- It is made up of two polynucleotide chains.
- The two chains have antiparallel polarity if one has polarities and the second chain must have polarity.
- The base into strands is paired through hydrogen bond forming base pairs. Adenine forms to hydrogen bonds with thymine from opposite strands and vice versa.
- Similarly guanine forms three H bonds with cytosine. As a result, purine comes opposite to pyrimidine.
Because of this approximate a uniform distance between the two strengths of The Helix occurs.
- The two chains are called in a right-handed fashion. Pitch of the helix is and there are roughly 10bp in each turn.
- The plane of one base pair is stacked over the other in a double helix. This confirms stability of the helical structure.
Note: The proposition of a double helix structure for DNA and its simplicity in explaining the genetic implication become revolutionary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




