
Explain why images formed by magnifying glasses are free from chromatic aberration.
Answer
460.5k+ views
Hint: A magnifying glass (also known as a hand lens in scientific settings) is a convex lens that magnifies an image of an item. Typically, the lens is housed in a frame with a grip. A magnifying glass can be used to concentrate light, such as the sun's rays, to generate a hot spot at the focal point for starting a fire. A sheet magnifier is made up of a series of very narrow concentric ring-shaped lenses that work together as a single lens but are significantly thinner. A Fresnel lens is the name for this configuration.
Complete answer:
Chromatic aberration (CA), also known as chromatic distortion and spherochromatism in optics, occurs when a lens fails to focus all colours to the same spot. It's caused by dispersion, which occurs when the refractive index of the lens elements changes as the wavelength of light changes. With increasing wavelength, the refractive index of most transparent materials falls. Because a lens' focal length is determined by its refractive index, variations in the refractive index impact focusing. Chromatic aberration appears as "fringes" of colour at picture borders that divide dark and bright areas.
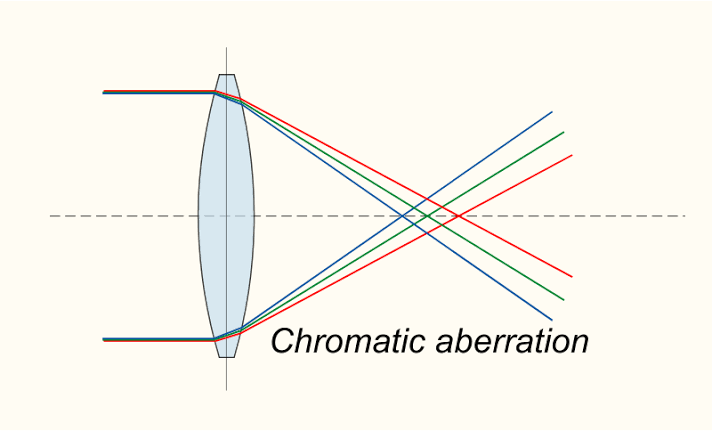
Axial (longitudinal) and transverse chromatic aberration are the two forms of chromatic aberration (lateral). When various wavelengths of light are focused at different distances from the lens, axial aberration develops (focus shift). At large focal lengths, longitudinal aberration is common. Because the magnification and/or distortion of the lens changes with wavelength, transverse aberration arises when various wavelengths are concentrated at different locations in the focal plane. At small focal lengths, transverse aberration is common. Longitudinal or lateral chromatic aberration is occasionally referred to by the confusing term LCA.
Chromatic aberration occurs in all lenses. By properly constructing a lens system to correct for chromatic aberrations, it may be minimised. This is generally accomplished by adding extra optical components, however such a magnifying glass would be prohibitively costly. Lens dispersion causes chromatic aberration, which occurs when various colours of light travel at different speeds through a lens.
Note:
In certain cases, digital post-processing can be used to rectify some of the effects of chromatic aberration. In real-world situations, however, chromatic aberration causes a permanent loss of picture detail. With a thorough understanding of the optical system that created the image, several beneficial corrections can be made. In an ideal world, post-processing to remove or correct lateral chromatic aberration would include scaling the fringed colour channels, or removing part of the scaled copies of the fringed channels, such that all channels in the final picture spatially overlap each other appropriately.
Complete answer:
Chromatic aberration (CA), also known as chromatic distortion and spherochromatism in optics, occurs when a lens fails to focus all colours to the same spot. It's caused by dispersion, which occurs when the refractive index of the lens elements changes as the wavelength of light changes. With increasing wavelength, the refractive index of most transparent materials falls. Because a lens' focal length is determined by its refractive index, variations in the refractive index impact focusing. Chromatic aberration appears as "fringes" of colour at picture borders that divide dark and bright areas.

Axial (longitudinal) and transverse chromatic aberration are the two forms of chromatic aberration (lateral). When various wavelengths of light are focused at different distances from the lens, axial aberration develops (focus shift). At large focal lengths, longitudinal aberration is common. Because the magnification and/or distortion of the lens changes with wavelength, transverse aberration arises when various wavelengths are concentrated at different locations in the focal plane. At small focal lengths, transverse aberration is common. Longitudinal or lateral chromatic aberration is occasionally referred to by the confusing term LCA.
Chromatic aberration occurs in all lenses. By properly constructing a lens system to correct for chromatic aberrations, it may be minimised. This is generally accomplished by adding extra optical components, however such a magnifying glass would be prohibitively costly. Lens dispersion causes chromatic aberration, which occurs when various colours of light travel at different speeds through a lens.
Note:
In certain cases, digital post-processing can be used to rectify some of the effects of chromatic aberration. In real-world situations, however, chromatic aberration causes a permanent loss of picture detail. With a thorough understanding of the optical system that created the image, several beneficial corrections can be made. In an ideal world, post-processing to remove or correct lateral chromatic aberration would include scaling the fringed colour channels, or removing part of the scaled copies of the fringed channels, such that all channels in the final picture spatially overlap each other appropriately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




