
Explain with suitable examples, the different types of phyllotaxy.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: The term phyllotaxy has been derived from Greek words “phýllon” means leaf and “taxis” means arrangement. Therefore, phyllotaxy can be explained as the arrangements or pattern of leaves over the branch or stem of a plant. Phyllotaxy is majorly categorized into three types. They are alternate phyllotaxy, opposite phyllotaxy and whorled phyllotaxy.
Complete Answer:
Phyllotaxy is related to the arrangement of leaves, so it plays an important role during the photosynthesis process in plants. The detailed information regarding the three types of phyllotaxy is described below.
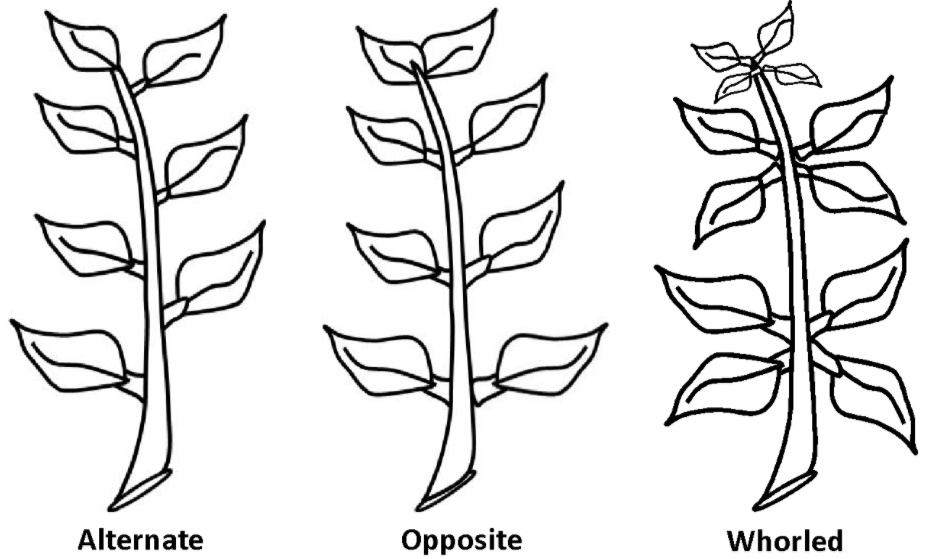
(i) Alternate phyllotaxy: In such a phyllotaxy, the arrangement is such that only a single leaf occurs alternatively from each node of a branch in a plant. This kind of arrangement is observed in the leaves of plants such as sunflower, mustard etc.
(ii) Opposite phyllotaxy: In this type of phyllotaxy, the arrangement is such that the pair of leaves arises from each node of a branch in a plant but in an opposite manner. The leave arrangements are opposite to each other. Such type of arrangement is observed in the guava and mint plants.
(iii) Whorled phyllotaxy: Such type of phyllotaxy is noticed in the plants developed with more than two leaves at the nodes of a branch and forms whorls of leaves. In other words, the whorled phyllotaxy could be described as the condition where more than two leaves appear at the same node of a branch. This type of phyllotaxy is noticed in the plants such as tulsi, sunflower etc.
Note: Phyllotaxy has its own significance in the development and growth of plants. It is associated with the arrangement of leaves and the leave arrangements allow the leaves for exposure to sunlight, which is an important factor during photosynthesis.
Complete Answer:
Phyllotaxy is related to the arrangement of leaves, so it plays an important role during the photosynthesis process in plants. The detailed information regarding the three types of phyllotaxy is described below.

(i) Alternate phyllotaxy: In such a phyllotaxy, the arrangement is such that only a single leaf occurs alternatively from each node of a branch in a plant. This kind of arrangement is observed in the leaves of plants such as sunflower, mustard etc.
(ii) Opposite phyllotaxy: In this type of phyllotaxy, the arrangement is such that the pair of leaves arises from each node of a branch in a plant but in an opposite manner. The leave arrangements are opposite to each other. Such type of arrangement is observed in the guava and mint plants.
(iii) Whorled phyllotaxy: Such type of phyllotaxy is noticed in the plants developed with more than two leaves at the nodes of a branch and forms whorls of leaves. In other words, the whorled phyllotaxy could be described as the condition where more than two leaves appear at the same node of a branch. This type of phyllotaxy is noticed in the plants such as tulsi, sunflower etc.
Note: Phyllotaxy has its own significance in the development and growth of plants. It is associated with the arrangement of leaves and the leave arrangements allow the leaves for exposure to sunlight, which is an important factor during photosynthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




