
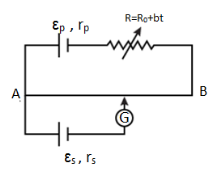
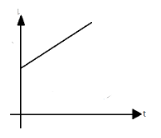
Figure shows a potentiometer in which resistance of rheostat is changing with time $ \left( t \right) $ as $ R = {R_0} + bt $ , where $ {R_0} $ and $ b $ are positive constant. Which of the following graphs best represents the balance length $ l $ (from $ A $ ) with respect to time $ t $ ? (Symbols have their usual meaning)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)





Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to first see the formula for the potentiometer representing the lengths, then by putting the values for the corresponding lengths and simplifying the relation, the equation is obtained for the graph that shows the nature of the curve.
For a potentiometer, if $ {l_1} $ and $ {l_2} $ are the two lengths of across the galvanometer, then,
$ {x_1}{l_1} = {x_2}{l_2} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As for the potentiometer given in this question, we know that if $ {l_1} $ and $ {l_2} $ are the two lengths of across the galvanometer, then,
$ {x_1}{l_1} = {x_2}{l_2} $
Putting here the values of the all four variables, we get the equation,
$ \left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _p}}}{{{r_p} + R + {R_0}}}} \right)\dfrac{R}{{{l_p}}}{l_0} = \left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _p}}}{{{r_p} + bt + R + {R_0}}}} \right)\dfrac{R}{{{l_p}}}{l_1} $
From this equation, we get to see here that,
$ {l_1} = {l_0} + \dfrac{{{l_0}bt}}{{{R_0} + R + {r_p}}} \\
\Rightarrow {l_1} = {l_0}\left[ {1 + \dfrac{{bt}}{{{R_0} + R + {r_p}}}} \right] \\ $
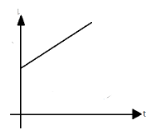
This equation here represents the first graph (A) with the intercept $ {l_0} $ on Y-axis.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note :
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the unknown voltage. The principle of a potentiometer is that the potential dropped across a segment of a wire of uniform cross-section carrying a constant current is directly proportional to its length.
For a potentiometer, if $ {l_1} $ and $ {l_2} $ are the two lengths of across the galvanometer, then,
$ {x_1}{l_1} = {x_2}{l_2} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As for the potentiometer given in this question, we know that if $ {l_1} $ and $ {l_2} $ are the two lengths of across the galvanometer, then,
$ {x_1}{l_1} = {x_2}{l_2} $
Putting here the values of the all four variables, we get the equation,
$ \left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _p}}}{{{r_p} + R + {R_0}}}} \right)\dfrac{R}{{{l_p}}}{l_0} = \left( {\dfrac{{{\varepsilon _p}}}{{{r_p} + bt + R + {R_0}}}} \right)\dfrac{R}{{{l_p}}}{l_1} $
From this equation, we get to see here that,
$ {l_1} = {l_0} + \dfrac{{{l_0}bt}}{{{R_0} + R + {r_p}}} \\
\Rightarrow {l_1} = {l_0}\left[ {1 + \dfrac{{bt}}{{{R_0} + R + {r_p}}}} \right] \\ $
This equation here represents the first graph (A) with the intercept $ {l_0} $ on Y-axis.
Hence, the correct option is (A).

Note :
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the unknown voltage. The principle of a potentiometer is that the potential dropped across a segment of a wire of uniform cross-section carrying a constant current is directly proportional to its length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




