
Find B of the given reaction
\[{\text{H}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}\dfrac{{{\text{HgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}(\;{\text{A}})\dfrac{{(1){\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {\text{HCN}}}}{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}({\text{B}})\]
A.Glycine
B.Alanine
C.Valine
D.Leucine
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are chemical molecules that bind to form proteins. The building blocks of life are amino acids and proteins. Amino acids are left over after proteins are digested or broken down. Amino acids are used by the human body to produce proteins that aid in the following functions: Break down food. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the four essential elements of an amino acid, while other elements can be present in the side chains of certain amino acids.
Complete answer: A hydration reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs when a compound reacts with water. Water is applied to an unsaturated base in organic chemistry, which is typically an alkene or an alkyne.
\[{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{C}} \equiv {\mathbf{C}} - {\mathbf{H}} + {{\mathbf{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow[{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}]{{{\text{HgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{CH}} = {\mathbf{CH}} - {\text{OH}}\mathop {\xrightarrow{{{\text{ tautomerization }}}}}\limits^{} {\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{H}}_3} - {\mathbf{CHO}}\]
Ethyne reacts with sulphuric acid to get ethanal.
Tautomerism is a condition in which a single chemical element exists in two or more interconvertible systems of varying relative positions of one atomic nucleus, which is usually hydrogen.
The acetaldehyde then reacts with the cyanide compound $N{H_3} + HCN$ to form the cyanide compound.
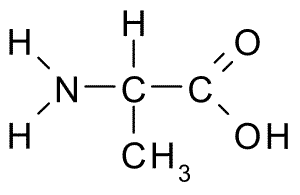
\[{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{C}} \equiv {\mathbf{C}} - {\mathbf{H}} + {{\mathbf{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow[{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}]{{{\text{HgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{CH}} = {\mathbf{CH}} - {\text{OH}}\mathop {\xrightarrow{{{\text{ tautomerization }}}}}\limits^{} {\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{H}}_3} - {\mathbf{CHO}}\xrightarrow[{HCN}]{{N{H_3}}}C{H_3} - CH(CN) - N{H_2}\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}C{H_3} - CH(COOH) - N{H_2}\]
This compound is then hydrolyzed, yielding alanine (alpha- amino acid) as a result.
A cyanide is a chemical compound with the CN group in its name. The cyano group is made up of a carbon atom that is triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. The cyanide group is present as the anion CN in inorganic cyanides. Sodium cyanide and potassium cyanide are highly toxic soluble salts.
Hence the final answer is B. Alanine.
Note:
Pyruvate and branched chain amino acids including valine, leucine, and isoleucine can be used to make alanine.
The two-step mechanism of reductive amination of pyruvate produces alanine. Glutamate dehydrogenase converts -ketoglutarate, ammonia, and NADH to glutamate,\[NA{D^ + }\], and water in the first phase. In the second step, an aminotransferase enzyme transfers the amino group of the newly formed glutamate to pyruvate, regenerating the alpha-ketoglutarate and transferring the pyruvate to alanine. As a result, pyruvate and ammonia are reduced to alanine, resulting in the consumption of one reducing counterpart.
Complete answer: A hydration reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs when a compound reacts with water. Water is applied to an unsaturated base in organic chemistry, which is typically an alkene or an alkyne.
\[{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{C}} \equiv {\mathbf{C}} - {\mathbf{H}} + {{\mathbf{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow[{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}]{{{\text{HgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{CH}} = {\mathbf{CH}} - {\text{OH}}\mathop {\xrightarrow{{{\text{ tautomerization }}}}}\limits^{} {\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{H}}_3} - {\mathbf{CHO}}\]
Ethyne reacts with sulphuric acid to get ethanal.
Tautomerism is a condition in which a single chemical element exists in two or more interconvertible systems of varying relative positions of one atomic nucleus, which is usually hydrogen.
The acetaldehyde then reacts with the cyanide compound $N{H_3} + HCN$ to form the cyanide compound.
\[{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{C}} \equiv {\mathbf{C}} - {\mathbf{H}} + {{\mathbf{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\xrightarrow[{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}]{{{\text{HgS}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\mathbf{H}} - {\mathbf{CH}} = {\mathbf{CH}} - {\text{OH}}\mathop {\xrightarrow{{{\text{ tautomerization }}}}}\limits^{} {\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{H}}_3} - {\mathbf{CHO}}\xrightarrow[{HCN}]{{N{H_3}}}C{H_3} - CH(CN) - N{H_2}\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}C{H_3} - CH(COOH) - N{H_2}\]
This compound is then hydrolyzed, yielding alanine (alpha- amino acid) as a result.

A cyanide is a chemical compound with the CN group in its name. The cyano group is made up of a carbon atom that is triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. The cyanide group is present as the anion CN in inorganic cyanides. Sodium cyanide and potassium cyanide are highly toxic soluble salts.
Hence the final answer is B. Alanine.
Note:
Pyruvate and branched chain amino acids including valine, leucine, and isoleucine can be used to make alanine.
The two-step mechanism of reductive amination of pyruvate produces alanine. Glutamate dehydrogenase converts -ketoglutarate, ammonia, and NADH to glutamate,\[NA{D^ + }\], and water in the first phase. In the second step, an aminotransferase enzyme transfers the amino group of the newly formed glutamate to pyruvate, regenerating the alpha-ketoglutarate and transferring the pyruvate to alanine. As a result, pyruvate and ammonia are reduced to alanine, resulting in the consumption of one reducing counterpart.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




