
Find the area of the Quadrilateral ABCD whose vertices are A ( -3, -1), B (-2, -4), C (4, -1) and D (3,4)
Answer
617.7k+ views
Hint- Proceed the solution of this question by dividing the quadrilateral in two triangles (using either of the diagonals), calculate the (positive value of) the areas of each triangle, and add these values to get the total area of the quadrilateral.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the vertices of the quadrilateral be A (-3, -1), B (-2, -4), C (4, -1) and D (3, 4).
Let AC be the diagonal of quadrilateral ABCD.
In the following figure, quadrilateral ABCD has been divided into ΔABC and ΔADC
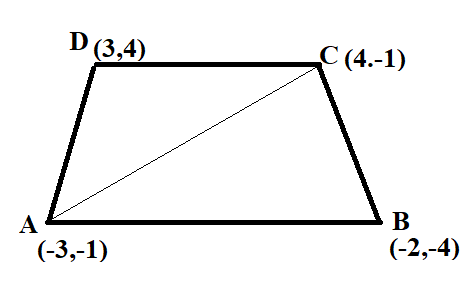
Therefore,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of Δ ABC + Area of Δ ADC ………… (1)
We know that,
Area of triangle = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[{{\text{x}}_1}({{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_3}) + {{\text{x}}_2}({{\text{y}}_3} - {{\text{y}}_1}) + {{\text{x}}_3}({{\text{y}}_1} - {{\text{y}}_2})]} \right|\]
Thus,
Let triangle be ABC, where A= (−3, −1), B= (−2, −4), C= (4, -1)
Let the coordinates of point A $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ ,B $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$ and C $\left( {{{\text{x}}_3},{{\text{y}}_3}} \right)$
So, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = - 3,{{\text{y}}_1} = - 1,{{\text{x}}_2} = - 2,{{\text{y}}_2} = - 4,{{\text{x}}_3} = 4,{{\text{y}}_3} = - 1\]
So using Above formula,
Area of triangle Δ ABC=
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {( - 4) - ( - 1)} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 4)} \right)]} \right|\]
On further solving
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {( - 4) + 1} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {( - 1) + 1} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) + 4} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( { - 3} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {(0} \right) + (4) \times \left( 3 \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[9 + 0 + 12]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[21]} \right| = \dfrac{{21}}{2}\] Sq. units
Now let triangle be ADC, where A= (−3, −1), D= (3, 4), C= (4, -1)
Let the coordinates of point A $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ ,D $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$ and C $\left( {{{\text{x}}_3},{{\text{y}}_3}} \right)$
So, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = - 3,{{\text{y}}_1} = - 1,{{\text{x}}_2} = 3,{{\text{y}}_2} = 4,{{\text{x}}_3} = 4,{{\text{y}}_3} = - 1\]
So using Above formula,
Area of triangle Δ ADC=
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {(4) - ( - 1)} \right) + (3) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - (4)} \right)]} \right|\]
On further solving
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {(4) + 1} \right) + (3) \times \left( {( - 1) + 1} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - 4} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( 5 \right) + (3) \times \left( 0 \right) + (4) \times \left( { - 5} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[ - 15 + 0 - 20]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[ - 35]} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{ - 35}}{2}} \right| = \dfrac{{35}}{2}\] Sq. units
Thus,
Substitute these values in equation (1), we have
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of Δ ABC + Area of Δ ADC
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = \[\dfrac{{21}}{2}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{35}}{2} = \dfrac{{56}}{2} = 28\] Sq. units
Hence, the area of the quadrilateral is 28 square units.
Note- In this particular question, sometimes it’s difficult to remember the formula of Area of triangle
which states above so there is also one other form of Area of triangle
Formula in determinant form which is as Area of triangle = $\left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{{\text{x}}_1}}&{{{\text{y}}_1}}&1 \\
{{{\text{x}}_2}}&{{{\text{y}}_2}}&1 \\
{{{\text{x}}_3}}&{{{\text{y}}_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|$
We can also find the area of a triangle using this formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the vertices of the quadrilateral be A (-3, -1), B (-2, -4), C (4, -1) and D (3, 4).
Let AC be the diagonal of quadrilateral ABCD.
In the following figure, quadrilateral ABCD has been divided into ΔABC and ΔADC

Therefore,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of Δ ABC + Area of Δ ADC ………… (1)
We know that,
Area of triangle = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[{{\text{x}}_1}({{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_3}) + {{\text{x}}_2}({{\text{y}}_3} - {{\text{y}}_1}) + {{\text{x}}_3}({{\text{y}}_1} - {{\text{y}}_2})]} \right|\]
Thus,
Let triangle be ABC, where A= (−3, −1), B= (−2, −4), C= (4, -1)
Let the coordinates of point A $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ ,B $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$ and C $\left( {{{\text{x}}_3},{{\text{y}}_3}} \right)$
So, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = - 3,{{\text{y}}_1} = - 1,{{\text{x}}_2} = - 2,{{\text{y}}_2} = - 4,{{\text{x}}_3} = 4,{{\text{y}}_3} = - 1\]
So using Above formula,
Area of triangle Δ ABC=
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {( - 4) - ( - 1)} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 4)} \right)]} \right|\]
On further solving
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {( - 4) + 1} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {( - 1) + 1} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) + 4} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( { - 3} \right) + ( - 2) \times \left( {(0} \right) + (4) \times \left( 3 \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[9 + 0 + 12]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[21]} \right| = \dfrac{{21}}{2}\] Sq. units
Now let triangle be ADC, where A= (−3, −1), D= (3, 4), C= (4, -1)
Let the coordinates of point A $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ ,D $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$ and C $\left( {{{\text{x}}_3},{{\text{y}}_3}} \right)$
So, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = - 3,{{\text{y}}_1} = - 1,{{\text{x}}_2} = 3,{{\text{y}}_2} = 4,{{\text{x}}_3} = 4,{{\text{y}}_3} = - 1\]
So using Above formula,
Area of triangle Δ ADC=
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {(4) - ( - 1)} \right) + (3) \times \left( {( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - (4)} \right)]} \right|\]
On further solving
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( {(4) + 1} \right) + (3) \times \left( {( - 1) + 1} \right) + (4) \times \left( {( - 1) - 4} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[( - 3) \times \left( 5 \right) + (3) \times \left( 0 \right) + (4) \times \left( { - 5} \right)]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[ - 15 + 0 - 20]} \right|\]
⇒\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {[ - 35]} \right| = \left| {\dfrac{{ - 35}}{2}} \right| = \dfrac{{35}}{2}\] Sq. units
Thus,
Substitute these values in equation (1), we have
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of Δ ABC + Area of Δ ADC
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = \[\dfrac{{21}}{2}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{35}}{2} = \dfrac{{56}}{2} = 28\] Sq. units
Hence, the area of the quadrilateral is 28 square units.
Note- In this particular question, sometimes it’s difficult to remember the formula of Area of triangle
which states above so there is also one other form of Area of triangle
Formula in determinant form which is as Area of triangle = $\left| {\dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{{\text{x}}_1}}&{{{\text{y}}_1}}&1 \\
{{{\text{x}}_2}}&{{{\text{y}}_2}}&1 \\
{{{\text{x}}_3}}&{{{\text{y}}_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|} \right|$
We can also find the area of a triangle using this formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




