
Find the dimension of the rectangle of perimeter 36 cm which will sweep out a volume as large as possible when revolved about one of its sides.
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: To understand the given question, visualize a rectangle paper and revolve about one of its sides. You’ll see it forms a cylinder with height as the length of the revolving side and radius as the other unequal side of rectangular paper.
Questions related to finding the largest or highest of some quantity can be solved by using the second derivative test.
Using the perimeter of the rectangle, find the relation between its length and breadth.
Write the function of the volume of the figure formed by revolving the given rectangle, and deduce the equation into one unknown parameter.
Find all critical points using the First Derivative at which maximum and minimum values of the function lies.
Use the Second Derivative Test to find maxima and minima.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Relation between length and breadth of the given rectangle

Figure: Rectangle ABCD
Let the length of the rectangle is l cm.
Let the Breadth of the rectangle be b cm.
Given that perimeter of the rectangle = 36 cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the rectangle $ = 2\left( {l + b} \right) = 36$
$
\Rightarrow l + b = 18 \\
\because l = 18 - b \\
$
Step 2: Find the function whose maximum or minimum value is asked:
Let the rectangle revolve about the breadth AD.
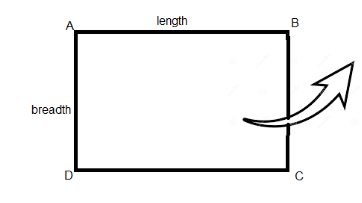
Figure: Rectangle ABCD
The volume sweep by the rectangle is in the shape of a cylinder.
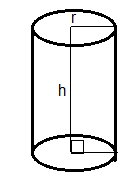
Figure: Cylinder
Hence, the height of the cylinder, h is the breadth of the rectangle.
i.e. h = b.
and, the radius of the cylinder, r is the length of the rectangle.
i.e. r = l.
Thus, the volume of the cylinder, $V = \pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h$
Deducing the function V in one parameter only i.e. b.
$
\Rightarrow \,{\text{ }}V = \pi \mathop l\nolimits^2 b \\
\; \Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \mathop {\left( {18 - b} \right)}\nolimits^2 b \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \left( {\mathop {18}\nolimits^2 + \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 36b} \right)b \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \left( {324b + \mathop b\nolimits^3 - 36\mathop b\nolimits^2 } \right) \\
$
Step 3: Find critical points:
On differentiating both sides with respect to b
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{db}} = \pi \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right)$ …… (1)
To find critical points:
$\dfrac{{dV}}{{db}} = 0$
$
\Rightarrow \pi \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 24b + 108 = 0 \\
$
Simplifying by the middle split method:
$
\Rightarrow \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 18b - 6b + 108 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow b\left( {b - 18} \right) - 6\left( {b - 18} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {b - 18} \right)\left( {b - 6} \right) = 0 \\
$
Hence, b = 6, 18.
Step 4: Find maxima or minima of the function:
On differentiating equation (1) both sides with respect to b.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}} = \pi \left( {6b - 72} \right)$
Checking the sign of $\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}$ at b = 6:
\[
\Rightarrow {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 6}} = \pi \left( {6(6) - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \pi \left( {36 - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = - 36\pi \\
\]
$\because {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 6}} < 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ The volume of the cylinder is maximum at b = 6.
Checking the sign of $\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}$ at b = 18:
\[
\Rightarrow {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 18}} = \pi \left( {6(18) - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \pi \left( {108 - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = 36\pi \\
\]
$\because {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 18}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ The volume of the cylinder is minimum at b = 18.
We needed the volume swept by the revolved rectangle to be the largest possible. The volume of the cylinder is largest at breadth b = 6.
We know, $l = 18 - b$
$ \Rightarrow l = 18 - 6 = 12$
Final answer: The breadth of the given rectangle is 6 cm and the length is 12 cm.
Note: If the second derivative of the function is greater than 0 (or positive) at a critical point, then the function has a minimum value at that critical point.
If the second derivative of the function is equal to 0 at a critical point, the critical point is the point of inflation, and the function can have either maximum or minimum value at that critical point.
Derivation (or differentiation) of function involving more than one parameter is known as partial derivation.
At the NCERT level, students have not yet learned the maxima and minima of partial derivatives. Therefore, to calculate the maximum or minimum value of the function (especially in types of given question) students must deduce the function into one parameter (or unknown) only.
Questions related to finding the largest or highest of some quantity can be solved by using the second derivative test.
Using the perimeter of the rectangle, find the relation between its length and breadth.
Write the function of the volume of the figure formed by revolving the given rectangle, and deduce the equation into one unknown parameter.
Find all critical points using the First Derivative at which maximum and minimum values of the function lies.
Use the Second Derivative Test to find maxima and minima.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Relation between length and breadth of the given rectangle

Figure: Rectangle ABCD
Let the length of the rectangle is l cm.
Let the Breadth of the rectangle be b cm.
Given that perimeter of the rectangle = 36 cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the rectangle $ = 2\left( {l + b} \right) = 36$
$
\Rightarrow l + b = 18 \\
\because l = 18 - b \\
$
Step 2: Find the function whose maximum or minimum value is asked:
Let the rectangle revolve about the breadth AD.

Figure: Rectangle ABCD
The volume sweep by the rectangle is in the shape of a cylinder.

Figure: Cylinder
Hence, the height of the cylinder, h is the breadth of the rectangle.
i.e. h = b.
and, the radius of the cylinder, r is the length of the rectangle.
i.e. r = l.
Thus, the volume of the cylinder, $V = \pi \mathop r\nolimits^2 h$
Deducing the function V in one parameter only i.e. b.
$
\Rightarrow \,{\text{ }}V = \pi \mathop l\nolimits^2 b \\
\; \Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \mathop {\left( {18 - b} \right)}\nolimits^2 b \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \left( {\mathop {18}\nolimits^2 + \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 36b} \right)b \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }}V = \pi \left( {324b + \mathop b\nolimits^3 - 36\mathop b\nolimits^2 } \right) \\
$
Step 3: Find critical points:
On differentiating both sides with respect to b
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dV}}{{db}} = \pi \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right)$ …… (1)
To find critical points:
$\dfrac{{dV}}{{db}} = 0$
$
\Rightarrow \pi \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 324 + 3\mathop b\nolimits^2 - 72b = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 24b + 108 = 0 \\
$
Simplifying by the middle split method:
$
\Rightarrow \mathop b\nolimits^2 - 18b - 6b + 108 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow b\left( {b - 18} \right) - 6\left( {b - 18} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {b - 18} \right)\left( {b - 6} \right) = 0 \\
$
Hence, b = 6, 18.
Step 4: Find maxima or minima of the function:
On differentiating equation (1) both sides with respect to b.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}} = \pi \left( {6b - 72} \right)$
Checking the sign of $\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}$ at b = 6:
\[
\Rightarrow {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 6}} = \pi \left( {6(6) - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \pi \left( {36 - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = - 36\pi \\
\]
$\because {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 6}} < 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ The volume of the cylinder is maximum at b = 6.
Checking the sign of $\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}$ at b = 18:
\[
\Rightarrow {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 18}} = \pi \left( {6(18) - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \pi \left( {108 - 72} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = 36\pi \\
\]
$\because {\dfrac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{b^2}}}_{b = 18}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow $ The volume of the cylinder is minimum at b = 18.
We needed the volume swept by the revolved rectangle to be the largest possible. The volume of the cylinder is largest at breadth b = 6.
We know, $l = 18 - b$
$ \Rightarrow l = 18 - 6 = 12$
Final answer: The breadth of the given rectangle is 6 cm and the length is 12 cm.
Note: If the second derivative of the function is greater than 0 (or positive) at a critical point, then the function has a minimum value at that critical point.
If the second derivative of the function is equal to 0 at a critical point, the critical point is the point of inflation, and the function can have either maximum or minimum value at that critical point.
Derivation (or differentiation) of function involving more than one parameter is known as partial derivation.
At the NCERT level, students have not yet learned the maxima and minima of partial derivatives. Therefore, to calculate the maximum or minimum value of the function (especially in types of given question) students must deduce the function into one parameter (or unknown) only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




