
Find the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical.
i. Outside the shell and
ii. Inside the shell
Plot the graph of electric distance from the center of the shell.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem we should understand about the electric field intensity and the concept behind it and then with the help of Gauss’s law and its formula, we will be finding the values required and hence we will approach our answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Gauss’s law- Gauss’s law is defined as the total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by the surface.
Surface on which Gauss’s law is Applicative is known as Gaussian surface which need not be a real surface.
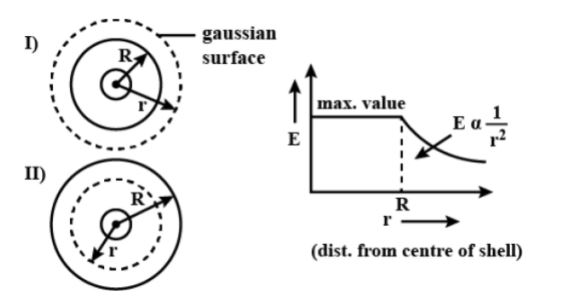
Let, a thin spherical shell of radius R having a positive charge q is uniformly distributed on the surface. As the electric field is symmetrical and directed radially outward, it means that the charge is distributed uniformly.
i. Electric field outside the shell:
For point r > R; let a spherical Gaussian surface of radius r.
Using gauss law,$\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{{{q_{end}}}}{{{q_0}}}} $
Since$\overrightarrow E $ is perpendicular to Gaussian surface , angle between$\overrightarrow E $ is 0
Also, $\overrightarrow E $ being constant, can be taken out of integral .
So,$E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{q}{{{q_0}}}$
So,$E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\,\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}$
Thus, the electric field outside a Shell is the same .
ii. Inside the shell:
Let, a Gaussian surface concentric with the shell of radius r (r >R)
So,$\oint {E.ds = E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right)} $
According to gauss law,
$E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{{{Q_{end}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The charge enclosed inside the spherical shell is 0.
So,$E = 0$
Therefore, due to the electric field, the uniformly charged spherical shell is zero at all points inside the shell.
Note - Gauss law is widely used in Electrostatics. Gauss’s law can be used to solve complex problems based on electric fields and also solve the complex electrostatic problems involving unique symmetries like cylindrical spherical or planar symmetry with the help of Gauss’s law.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Gauss’s law- Gauss’s law is defined as the total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by the surface.
Surface on which Gauss’s law is Applicative is known as Gaussian surface which need not be a real surface.
Let, a thin spherical shell of radius R having a positive charge q is uniformly distributed on the surface. As the electric field is symmetrical and directed radially outward, it means that the charge is distributed uniformly.
i. Electric field outside the shell:
For point r > R; let a spherical Gaussian surface of radius r.
Using gauss law,$\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{{{q_{end}}}}{{{q_0}}}} $
Since$\overrightarrow E $ is perpendicular to Gaussian surface , angle between$\overrightarrow E $ is 0
Also, $\overrightarrow E $ being constant, can be taken out of integral .
So,$E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{q}{{{q_0}}}$
So,$E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\,\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}$
Thus, the electric field outside a Shell is the same .
ii. Inside the shell:
Let, a Gaussian surface concentric with the shell of radius r (r >R)
So,$\oint {E.ds = E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right)} $
According to gauss law,
$E\left( {4\pi {r^2}} \right) = \dfrac{{{Q_{end}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
The charge enclosed inside the spherical shell is 0.
So,$E = 0$
Therefore, due to the electric field, the uniformly charged spherical shell is zero at all points inside the shell.

Note - Gauss law is widely used in Electrostatics. Gauss’s law can be used to solve complex problems based on electric fields and also solve the complex electrostatic problems involving unique symmetries like cylindrical spherical or planar symmetry with the help of Gauss’s law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




