
How do I find the genotypic and phenotypic ratio in a punnett square?
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Mendel conducted artificial pollination or cross-pollination experiments using several true-breeding pea lines A true breeding line is one that having undergone continuous self-pollination, shows the stable trait inheritance and expression for several generations.
Complete answer:
Mendel selected a total of 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, such as the height of the stem whether tall or dwarf as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits. It means, Mendel selected 7 characters that are seed shape, seed colour , pod colour in pea plant for carrying out hybridization experiments and to study inheritance
Genotype : genotype of an individual is referred to the sum total of genes inherited from both the parents irrespective of whether they are expressed or not.
Phenotype: phenotype of an individual is termed as the observable structural and functional traits produced by the interaction of genes and environment.
There are some steps to find the phenotypic ratio as Write the amount of homozygous (AA) and heterozygous (Aa) squares as one phenotypic group. In the next step Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group. Write the result as a ratio of the two groups.
For counting genotypes you represent a single character with two genes, so we have to calculate all the different numbers of pairs that come in a Punnett square.
For example:
Mendel crossed pea plants that differed in two characters and called this as a dihybrid cross. A cross was made that is they are allowed for pollination between a pure round yellow-seeded pea plant (RRYY) with wrinkled green-seeded pea plant (rryy).
Yellow colour is dominant that it can be shown with or without green seeds over green and round seed shape over wrinkled seed shape.
Such phenotypic ratio (9:3:3: 1) in $\mathop F\nolimits_2 $, generation was observed for several pairs of traits that Mendel studied. Mendel found that plants of the $\mathop F\nolimits_{\backslash 1} $, have all yellow and round seeds because yellow and round traits are respectively dominant and can be shown with each other or independently over green and wrinkled traits.
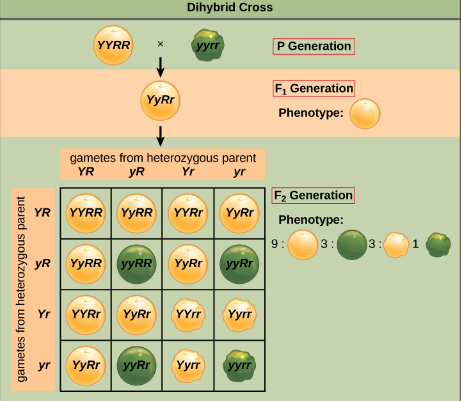
Diagram showing dihybrid cross
So as ratio comes to be 9:3:3:1
Here genotypes will be 1 YYRR + 2 YYRr + 2 YyRR + 4 YyRr
Note: Homozygous organisms: They are defined as an organism in which both the alleles of a single character at their loci in homologous chromosomes are identical is said to be homozygous or genetically pure for that character.
Heterozygous organism: They are defined as an organism in which two alleles of a character at their loci in homologous chromosomes is unlike are said to be heterozygous for that character.
Complete answer:
Mendel selected a total of 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, such as the height of the stem whether tall or dwarf as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits. It means, Mendel selected 7 characters that are seed shape, seed colour , pod colour in pea plant for carrying out hybridization experiments and to study inheritance
Genotype : genotype of an individual is referred to the sum total of genes inherited from both the parents irrespective of whether they are expressed or not.
Phenotype: phenotype of an individual is termed as the observable structural and functional traits produced by the interaction of genes and environment.
There are some steps to find the phenotypic ratio as Write the amount of homozygous (AA) and heterozygous (Aa) squares as one phenotypic group. In the next step Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group. Write the result as a ratio of the two groups.
For counting genotypes you represent a single character with two genes, so we have to calculate all the different numbers of pairs that come in a Punnett square.
For example:
Mendel crossed pea plants that differed in two characters and called this as a dihybrid cross. A cross was made that is they are allowed for pollination between a pure round yellow-seeded pea plant (RRYY) with wrinkled green-seeded pea plant (rryy).
Yellow colour is dominant that it can be shown with or without green seeds over green and round seed shape over wrinkled seed shape.
Such phenotypic ratio (9:3:3: 1) in $\mathop F\nolimits_2 $, generation was observed for several pairs of traits that Mendel studied. Mendel found that plants of the $\mathop F\nolimits_{\backslash 1} $, have all yellow and round seeds because yellow and round traits are respectively dominant and can be shown with each other or independently over green and wrinkled traits.

Diagram showing dihybrid cross
So as ratio comes to be 9:3:3:1
Here genotypes will be 1 YYRR + 2 YYRr + 2 YyRR + 4 YyRr
Note: Homozygous organisms: They are defined as an organism in which both the alleles of a single character at their loci in homologous chromosomes are identical is said to be homozygous or genetically pure for that character.
Heterozygous organism: They are defined as an organism in which two alleles of a character at their loci in homologous chromosomes is unlike are said to be heterozygous for that character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




