
How to find the volume of a sphere using integration?
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: We will draw a rough figure representing a sphere. We will consider a disc of a certain radius about the y-axis. Then we will find the value of the radius in terms of its height from the centre of the sphere and the radius of the sphere. We will integrate the area of this disc along the y-axis where the limits for integration will be the points where the height of the sphere is maximum and minimum.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The rough diagram of the sphere looks like the following,
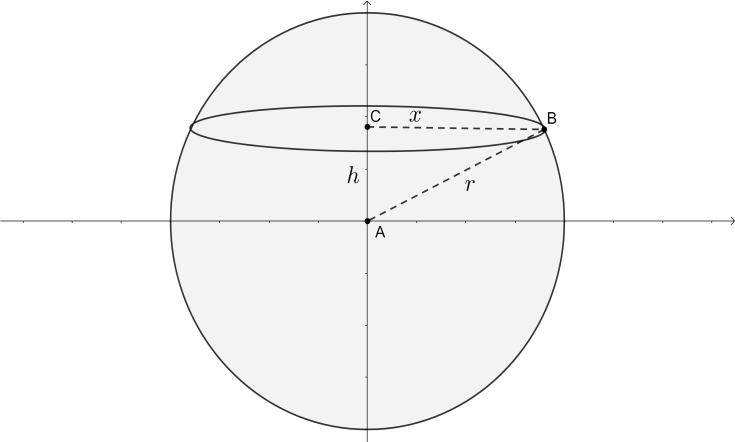
We have to find the volume of this sphere using integration. We have a sphere centered at the origin with radius $r$. Let us consider a disc about the y-axis at a height $h$ and having radius as $x$. The radius of the disc is $x$. Now, from the figure, we can see that $\Delta ACB$ is a right angled triangle with the hypotenuse AB. So, using the Pythagoras theorem in this triangle, we get the following,
$\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \\
& \therefore x=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of this disc is ${{A}_{Disc}}=\pi {{x}^{2}}$. Substituting the value of $x$ in this formula, we get
${{A}_{Disc}}=\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right)$
The discs from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere will fill up the sphere. So, we can calculate the volume of the sphere by integrating the areas of the discs from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere. The lowest height is $-r$ and the highest height of the sphere is $r$. So, we have the following integral,
${{V}_{sphere}}=\int\limits_{-r}^{r}{\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right)dh}$
Integrating the above expression, we get
\[{{V}_{sphere}}=\left. \pi \left( h{{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{3} \right) \right|_{-r}^{r}\]
Substituting the limits, we get the following,
\[{{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( r\cdot {{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right)-\pi \left( -r\cdot {{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( -r \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right)\]
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( \dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right)-\pi \left( -\dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( \dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3}-\left( -\dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right) \right) \\
& \therefore {{V}_{sphere}}=\dfrac{4\pi {{r}^{3}}}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, we have derived the formula for the volume of the sphere.
Note: The infinitesimal we used in the integration is $dh$ because we are integrating from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere. We can use the y-coordinate instead of the height variable. We should be careful with the signs while opening the brackets, so that we can avoid making errors in the calculations.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The rough diagram of the sphere looks like the following,

We have to find the volume of this sphere using integration. We have a sphere centered at the origin with radius $r$. Let us consider a disc about the y-axis at a height $h$ and having radius as $x$. The radius of the disc is $x$. Now, from the figure, we can see that $\Delta ACB$ is a right angled triangle with the hypotenuse AB. So, using the Pythagoras theorem in this triangle, we get the following,
$\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \\
& \therefore x=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of this disc is ${{A}_{Disc}}=\pi {{x}^{2}}$. Substituting the value of $x$ in this formula, we get
${{A}_{Disc}}=\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right)$
The discs from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere will fill up the sphere. So, we can calculate the volume of the sphere by integrating the areas of the discs from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere. The lowest height is $-r$ and the highest height of the sphere is $r$. So, we have the following integral,
${{V}_{sphere}}=\int\limits_{-r}^{r}{\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right)dh}$
Integrating the above expression, we get
\[{{V}_{sphere}}=\left. \pi \left( h{{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{3} \right) \right|_{-r}^{r}\]
Substituting the limits, we get the following,
\[{{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( r\cdot {{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right)-\pi \left( -r\cdot {{r}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{\left( -r \right)}^{3}}}{3} \right)\]
Simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( \dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right)-\pi \left( -\dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{sphere}}=\pi \left( \dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3}-\left( -\dfrac{2{{r}^{3}}}{3} \right) \right) \\
& \therefore {{V}_{sphere}}=\dfrac{4\pi {{r}^{3}}}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, we have derived the formula for the volume of the sphere.
Note: The infinitesimal we used in the integration is $dh$ because we are integrating from the lowest height of the sphere to the highest height of the sphere. We can use the y-coordinate instead of the height variable. We should be careful with the signs while opening the brackets, so that we can avoid making errors in the calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




