
What will be formed in the following Kolbe’s electrolysis?
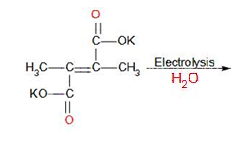
A.2-butene
B.1-butyne
C.2-butyne
D.Both b and c

Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Try to recall that when Kolbe’s electrolysis is carried then electrochemical decarboxylation of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid take place. Now, by using this we can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
Kolbe’s electrolysis synthesis is basically an organic reaction which is also known as decarboxylative dimerisation as the reaction proceeds with radical reaction mechanism and evolution of $C{O_2}$ takes place.
In Kolbe’s electrolysis method, the decarboxylation of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acids takes place and are converted into their corresponding alkanes.
As, the name suggests it is an electrolysis and occurs at cathode and anode.
Now coming to the question, we should know that the reaction mechanism of Kolbe’s electrolysis involves a two-stage radical process.
In the first stage, the decarboxylation of potassium salt of 2,3-dimethyl but-2-en-1,4 dioic acid takes place at anode and gives a radical intermediate. The reaction in first stage:
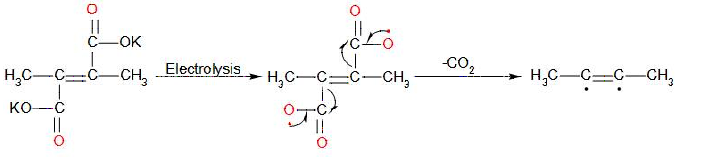
In the later stage, the radical intermediate undergoes intramolecular dimerisation and forms 2-butyne. The mechanism involved in this stage:
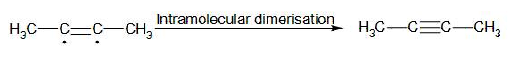
Therefore, from above we can easily conclude that option C is the correct answer to the given question.
Note: It should be remembered that this method is not used for the preparation of methane as well as alkanes having odd numbers of carbon atoms.
Also, you should know that during electrolysis pH of electrolyte increases progressively due to formation of alkalis like $NaOH,KOH$.
Electrolysis proceeds via formation of free radical intermediate.
Complete step by step answer:
Kolbe’s electrolysis synthesis is basically an organic reaction which is also known as decarboxylative dimerisation as the reaction proceeds with radical reaction mechanism and evolution of $C{O_2}$ takes place.
In Kolbe’s electrolysis method, the decarboxylation of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acids takes place and are converted into their corresponding alkanes.
As, the name suggests it is an electrolysis and occurs at cathode and anode.
Now coming to the question, we should know that the reaction mechanism of Kolbe’s electrolysis involves a two-stage radical process.
In the first stage, the decarboxylation of potassium salt of 2,3-dimethyl but-2-en-1,4 dioic acid takes place at anode and gives a radical intermediate. The reaction in first stage:

In the later stage, the radical intermediate undergoes intramolecular dimerisation and forms 2-butyne. The mechanism involved in this stage:
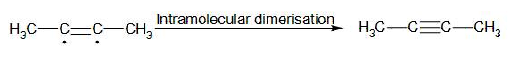
Therefore, from above we can easily conclude that option C is the correct answer to the given question.
Note: It should be remembered that this method is not used for the preparation of methane as well as alkanes having odd numbers of carbon atoms.
Also, you should know that during electrolysis pH of electrolyte increases progressively due to formation of alkalis like $NaOH,KOH$.
Electrolysis proceeds via formation of free radical intermediate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




