
From the above reactions, the number of reactions that produces benzaldehyde is
A.

B.
C.
D.




Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Benzaldehyde is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formal substituent. The molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CHO\]. It is a colorless liquid having an almond-like odor. It can be extracted from a number of other natural sources. Synthetic benzaldehyde is the flavoring agent which is used to flavor cakes and other baked goods.
Complete step by step answer:
All the reactions given above gives benzaldehyde as their product let’s discuss all the reaction one by one
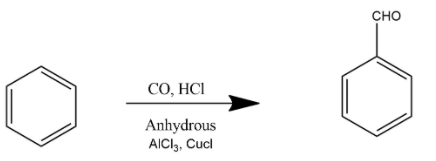
A. This is the example of Gatterman-Koch formylation reaction. In this reaction benzene is treated with $CO$ and $HCl$ under high pressure in the presence of anhydrous \[AlC{{l}_{3}},CuCl\] and formed benzaldehyde.
B. This reaction is simply hydrolysis and hydrolysis of benzoyl chloride with water will form benzaldehyde as a product.
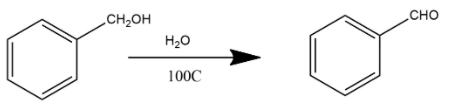
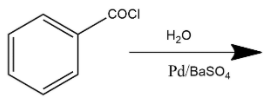
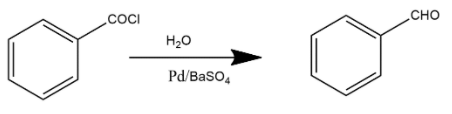
C. Reaction shown in option C is a rosenmund reduction. This reaction explains how acyl chlorides are selectively reduced into aldehydes. The Rosenmund reaction is a hydrogenation process where molecular hydrogen reacts with the acyl chloride where palladium or barium sulfate acts as a catalyst in this reaction which enhances the rate of reaction.
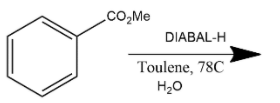
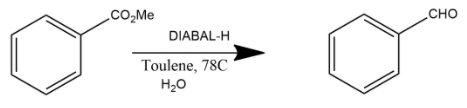
D. This reaction is generally a reduction reaction in which partial reduction of methyl benzoate with DIBAL-H in the presence of toluene gives benzaldehyde. Where DIBAL-H is diisobutylaluminium hydride which is generally used as a reducing agent.
From the above discussion we consider that all the reaction gives benzaldehyde as a product.
So the answer should be D.
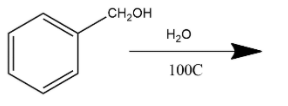
Note: Benzaldehyde can be oxidized to benzoic acid. The boiling point of benzoic acid is much higher than that of benzaldehyde; it can be purified by a simple process called distillation. Benzyl alcohol can be formed from benzaldehyde by means of hydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
All the reactions given above gives benzaldehyde as their product let’s discuss all the reaction one by one
A. This is the example of Gatterman-Koch formylation reaction. In this reaction benzene is treated with $CO$ and $HCl$ under high pressure in the presence of anhydrous \[AlC{{l}_{3}},CuCl\] and formed benzaldehyde.

B. This reaction is simply hydrolysis and hydrolysis of benzoyl chloride with water will form benzaldehyde as a product.

C. Reaction shown in option C is a rosenmund reduction. This reaction explains how acyl chlorides are selectively reduced into aldehydes. The Rosenmund reaction is a hydrogenation process where molecular hydrogen reacts with the acyl chloride where palladium or barium sulfate acts as a catalyst in this reaction which enhances the rate of reaction.

D. This reaction is generally a reduction reaction in which partial reduction of methyl benzoate with DIBAL-H in the presence of toluene gives benzaldehyde. Where DIBAL-H is diisobutylaluminium hydride which is generally used as a reducing agent.

From the above discussion we consider that all the reaction gives benzaldehyde as a product.
So the answer should be D.
Note: Benzaldehyde can be oxidized to benzoic acid. The boiling point of benzoic acid is much higher than that of benzaldehyde; it can be purified by a simple process called distillation. Benzyl alcohol can be formed from benzaldehyde by means of hydrogenation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




