
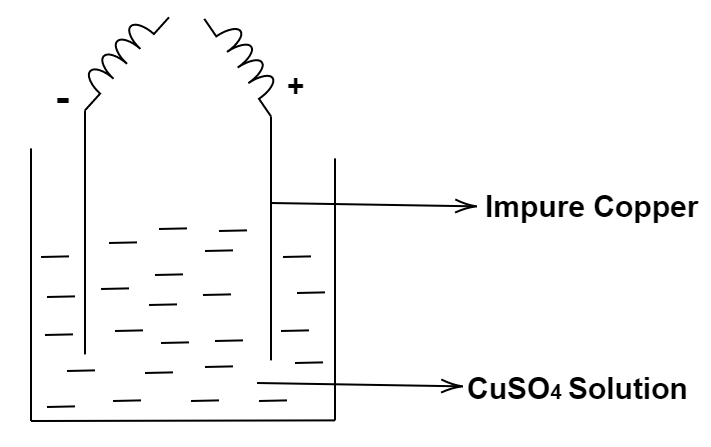
From the figure, give the electrode reaction. What is this process called?

Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: The above figure suggests that it is a kind of electrolysis reaction. So basically electrolysis reaction is the process by which electric current is passed through the substance to bring about the chemical change. By chemical change we refer to mean that in the process, either the electrons are gained or lost.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So, as the above is, the process is the application of electrolysis.
Now let’s look int0 more detail of the proper procedure and its name which is taking place.
So, this is the process of ‘Electrolytic refining’.
Basically electrolytic refining is the electrolysis process in which the impure substances are purified by passing electric current through them.
In this procedure, the impure metal is made into an anode and a thin strip of pure metal is made into a cathode. Plus the solution or electrolytic solution is made up of the salt of that metal. And both the electrodes i.e. the anode and the cathode are dipped into the electrolytic solution of that metal.
Mostly electrolytic refining is the process used for the purification of the impure metal- copper.
For the purification of the copper sulphate and the electrode reactions are:
At anode:
$ Cu \to C{u^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } $
At cathode:
$ C{u^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } \to Cu $
So, from the above discussion, the answer is clear.
Note:
When the electric current is passed through the solution, the pure metal is extracted near the pure electrode i.e. cathode. While on the other hand, the solid impurities get deposited near the bottom of the anode and are known as the ‘anode mud’. While the soluble impurities can be found in the electrolytic solution in which the electrodes are dipped as shown in above figure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So, as the above is, the process is the application of electrolysis.
Now let’s look int0 more detail of the proper procedure and its name which is taking place.
So, this is the process of ‘Electrolytic refining’.
Basically electrolytic refining is the electrolysis process in which the impure substances are purified by passing electric current through them.
In this procedure, the impure metal is made into an anode and a thin strip of pure metal is made into a cathode. Plus the solution or electrolytic solution is made up of the salt of that metal. And both the electrodes i.e. the anode and the cathode are dipped into the electrolytic solution of that metal.
Mostly electrolytic refining is the process used for the purification of the impure metal- copper.
For the purification of the copper sulphate and the electrode reactions are:
At anode:
$ Cu \to C{u^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } $
At cathode:
$ C{u^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } \to Cu $
So, from the above discussion, the answer is clear.
Note:
When the electric current is passed through the solution, the pure metal is extracted near the pure electrode i.e. cathode. While on the other hand, the solid impurities get deposited near the bottom of the anode and are known as the ‘anode mud’. While the soluble impurities can be found in the electrolytic solution in which the electrodes are dipped as shown in above figure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




