
What functional groups are found in all Monosaccharides?
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: Functional group is a molecule that gives a particular characteristic in chemical reactions of any compound. It is attached to an organic compound. Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that contain a long chain of hydrocarbons. They have chain structures having different functional groups, while their ring structures give rise to different functional groups.
Complete answer:
Monosaccharide is a type of carbohydrate sugar that is formed of a carbon chain which cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler units. As we know functional groups are any molecule other than the normal carbon chain, when attached on an organic molecule gives specific chemical properties to the compound. Examples of some common functional groups are alcohol (hydroxyl, OH), ketones (CO), aldehydes (CHO), carboxylic acids (COOH), etc.
Monosaccharides consist of a carbon chain along with hydroxyl (OH) groups in all monosaccharide. Apart from the hydroxyl (OH) groups, monosaccharide also contains an aldehyde or a ketone. When they contain aldehyde they are called aldose sugar and with ketones they are called ketose sugar. Example, glucose (aldose), and fructose (ketose). The open chain examples with functional groups are:
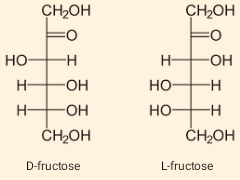
When monosaccharide forms a ring structure, then they consist of hemiacetal and a hemiketal group, which is a result when a hydroxyl group attaches adjacent to the functional group aldehyde and ketone respectively. The example is:
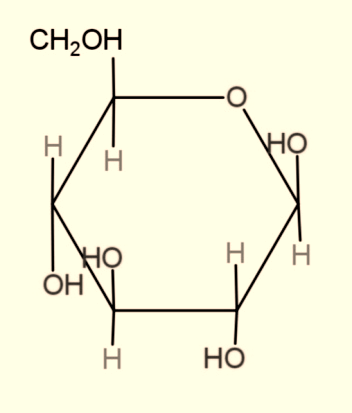
Hence, the functional groups in open structure of monosaccharide are hydroxyl, and aldehyde or ketone, while in ring structure it is hemiacetal or hemiketal.
Note:
As the open structure of monosaccharides (glucose or fructose) does not explain all of their properties, so a ring structure is employed that defines all its properties. For example, properties that are not explained by open structure but by ring are: glucose does not give 2,4 DNP hydrazine test, Schiff reagent test, it doesn’t react with sodium hydrogen sulphite, it does not form oxime.
Complete answer:
Monosaccharide is a type of carbohydrate sugar that is formed of a carbon chain which cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler units. As we know functional groups are any molecule other than the normal carbon chain, when attached on an organic molecule gives specific chemical properties to the compound. Examples of some common functional groups are alcohol (hydroxyl, OH), ketones (CO), aldehydes (CHO), carboxylic acids (COOH), etc.
Monosaccharides consist of a carbon chain along with hydroxyl (OH) groups in all monosaccharide. Apart from the hydroxyl (OH) groups, monosaccharide also contains an aldehyde or a ketone. When they contain aldehyde they are called aldose sugar and with ketones they are called ketose sugar. Example, glucose (aldose), and fructose (ketose). The open chain examples with functional groups are:

When monosaccharide forms a ring structure, then they consist of hemiacetal and a hemiketal group, which is a result when a hydroxyl group attaches adjacent to the functional group aldehyde and ketone respectively. The example is:

Hence, the functional groups in open structure of monosaccharide are hydroxyl, and aldehyde or ketone, while in ring structure it is hemiacetal or hemiketal.
Note:
As the open structure of monosaccharides (glucose or fructose) does not explain all of their properties, so a ring structure is employed that defines all its properties. For example, properties that are not explained by open structure but by ring are: glucose does not give 2,4 DNP hydrazine test, Schiff reagent test, it doesn’t react with sodium hydrogen sulphite, it does not form oxime.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




