
Functional unit of chloroplast is?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: Chloroplasts are usually found in green plants and algae. Chloroplasts are also found in photosynthetic tissues that do not appear green in color, such as brown blades of giant kelp or the red leaves of certain plants. chloroplast is a pigment based on plastid types.
Complete Explanation:
The chloroplasts is an organelle that contains chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis.
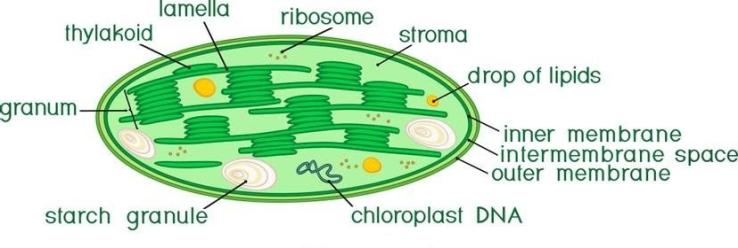
In leaf mesophyll cells, the majority of chloroplast is found in green plants. Chloroplasts are lens-shaped, oval, spherical, discoid or even ribbon-like organelles having variable length \[5 - 10{\text{ }}mm\]and width\[2 - 4mm\]. their number varies from \[1\]per cell as example – Chlamydomonas, green alga.
So, as we discussed about chloroplasts, the functional unit of chloroplast is Qunatasomes. Quantasomes are Para crystalline arrays of the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place.
Like mitochondria, chloroplasts are also double membrane organelle. One of the membranes is the inner membrane which is less permeable. Stroma is called the space limited by the chloroplast inner membrane. A number of organized flattened membranous sacs called thylakoids are present inside the stroma. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks like the piles of coin shaped known as grana. Also, there are flat membranous tubules called the stroma lamellae which connect the thylakoids of different grana. Chloroplast stroma contains many enzymes needed for carbohydrates and protein synthesis. The membrane of thylakoids is enclosed by a space which is called lumen.
The stroma also contains small, double stranded DNA molecules and ribosomes. The chloroplast ribosomes are less than the \[80s\]for the\[70s\].
As we discussed, those chloroplasts are required for photosynthesis mechanisms besides providing pigment to plants. Now let us see the machinery of photosynthesis and how it works.
The thylakoid membrane houses chlorophylls and different protein complexes, including photosystem I, photosystem II, and ATP synthase which are specialized for light-dependent photosynthesis. Chloroplasts have their own DNA.
Note:
In primitive red algae, the chloroplast DNA nucleoids are clustered in the center of the chloroplast, while in green plants and green algae, the nucleoids are dispersed throughout the stroma. Not all cells in a multicellular plant contain chloroplasts. The plant cells which contain chloroplasts are mostly parenchyma cells but also collenchyma tissue have some chloroplasts. A plant cell which contains chloroplasts is typically called a chlorenchyma cell.
Complete Explanation:
The chloroplasts is an organelle that contains chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis.

In leaf mesophyll cells, the majority of chloroplast is found in green plants. Chloroplasts are lens-shaped, oval, spherical, discoid or even ribbon-like organelles having variable length \[5 - 10{\text{ }}mm\]and width\[2 - 4mm\]. their number varies from \[1\]per cell as example – Chlamydomonas, green alga.
So, as we discussed about chloroplasts, the functional unit of chloroplast is Qunatasomes. Quantasomes are Para crystalline arrays of the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place.
Like mitochondria, chloroplasts are also double membrane organelle. One of the membranes is the inner membrane which is less permeable. Stroma is called the space limited by the chloroplast inner membrane. A number of organized flattened membranous sacs called thylakoids are present inside the stroma. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks like the piles of coin shaped known as grana. Also, there are flat membranous tubules called the stroma lamellae which connect the thylakoids of different grana. Chloroplast stroma contains many enzymes needed for carbohydrates and protein synthesis. The membrane of thylakoids is enclosed by a space which is called lumen.
The stroma also contains small, double stranded DNA molecules and ribosomes. The chloroplast ribosomes are less than the \[80s\]for the\[70s\].
As we discussed, those chloroplasts are required for photosynthesis mechanisms besides providing pigment to plants. Now let us see the machinery of photosynthesis and how it works.
The thylakoid membrane houses chlorophylls and different protein complexes, including photosystem I, photosystem II, and ATP synthase which are specialized for light-dependent photosynthesis. Chloroplasts have their own DNA.
Note:
In primitive red algae, the chloroplast DNA nucleoids are clustered in the center of the chloroplast, while in green plants and green algae, the nucleoids are dispersed throughout the stroma. Not all cells in a multicellular plant contain chloroplasts. The plant cells which contain chloroplasts are mostly parenchyma cells but also collenchyma tissue have some chloroplasts. A plant cell which contains chloroplasts is typically called a chlorenchyma cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




