
How garden peas (Pisum sativum) proved to be a suitable plant for Mendel’s work?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Let us revise, Gregor Mendel was the pioneer in the field of modern genetics. The experiments he conducted on pea plants and honey bees laid down the foundation for the rules of heredity that are now referred to as the laws of Mendelian Inheritance.
Complete answer:
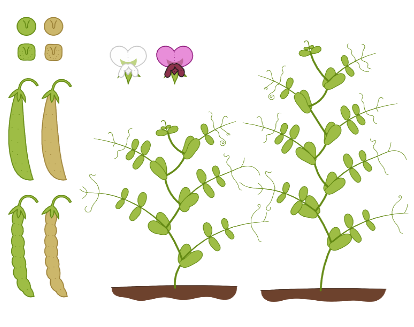
Mendel is known as the “Father of Modern Genetics”. As he was born in the family of farmers, Mendel was already familiar with gardening and bee-keeping. During his time in a monastery, Mendel chose to study hybridization and variation on plants in the monastery garden.
Pea, or Garden Pea or Pisum sativum prove to be a suitable candidate for studying variation for Mendel due to several reasons:
(a) It was commonly found.
(b) It was easy to grow.
(c) Pea is an annual plant (i.e., short life cycle hence multiple observations across seasons).
(d) Each generation produce multiple off-springs to observe inherited variations
(e) The traits selected for study (Plant height: Tall/Short; flower color: white/purple; flower position: axial/terminal; pod shape: smooth/constricted; pod color: green/yellow; seed color: green/yellow; seed shape: smooth/wrinkled) are easily observable.
(f) The ease of handling i.e. since the pea is a bisexual plant capable of self-pollination. It was easy to prevent unwanted pollination and promote only desired cross-pollination as per his necessity.
(g) All the hybrids produced are fertile.
Mendel, therefore, conducted hybridization experiments on over 28000 pea plants, all of which led him to lay two foundational laws of Mendelian Genetics, which are the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent assortment.
Note: If historians are to be believed, Mendel set out with his experiments to disapprove partly, the theory of Natural selection given by Charles Darwin. Darwin proposed the variability in organisms is the result of environmental change while Mendel believed it was due to the parental influence.
Despite its immense significance to modern genetics, Mendel died in obscurity, criticized. His peers didn’t understand the significance of his work, dismissing it since the distinct physical characteristics in the pea are typical for most species and therefore it was to be considered an exception and not the rule itself. It was only 20 years after his death that his work was rediscovered and appreciated.
Complete answer:

Mendel is known as the “Father of Modern Genetics”. As he was born in the family of farmers, Mendel was already familiar with gardening and bee-keeping. During his time in a monastery, Mendel chose to study hybridization and variation on plants in the monastery garden.
Pea, or Garden Pea or Pisum sativum prove to be a suitable candidate for studying variation for Mendel due to several reasons:
(a) It was commonly found.
(b) It was easy to grow.
(c) Pea is an annual plant (i.e., short life cycle hence multiple observations across seasons).
(d) Each generation produce multiple off-springs to observe inherited variations
(e) The traits selected for study (Plant height: Tall/Short; flower color: white/purple; flower position: axial/terminal; pod shape: smooth/constricted; pod color: green/yellow; seed color: green/yellow; seed shape: smooth/wrinkled) are easily observable.
(f) The ease of handling i.e. since the pea is a bisexual plant capable of self-pollination. It was easy to prevent unwanted pollination and promote only desired cross-pollination as per his necessity.
(g) All the hybrids produced are fertile.
Mendel, therefore, conducted hybridization experiments on over 28000 pea plants, all of which led him to lay two foundational laws of Mendelian Genetics, which are the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent assortment.
Note: If historians are to be believed, Mendel set out with his experiments to disapprove partly, the theory of Natural selection given by Charles Darwin. Darwin proposed the variability in organisms is the result of environmental change while Mendel believed it was due to the parental influence.
Despite its immense significance to modern genetics, Mendel died in obscurity, criticized. His peers didn’t understand the significance of his work, dismissing it since the distinct physical characteristics in the pea are typical for most species and therefore it was to be considered an exception and not the rule itself. It was only 20 years after his death that his work was rediscovered and appreciated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




