
What is gel electrophoresis? Explain how DNA fragments are separated and detected using this.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: The DNA is a negatively charged molecule. All DNA fragments have the same amount of e/m ratio, that is, charge per mass. It is most often used in life sciences to separate protein molecules or DNA.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis may be a technique to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, like RNA and proteins) that support their size and charge. By this the molecules will travel through the gel in several directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from each other.
All DNA molecules have an equivalent amount of charge per mass. Due to this, gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments separates them accordingly with those who have the correct size only. Using electrophoresis, we will see what percentage different DNA fragments are present during a sample and the way large they're relative to at least one another. we will also determine absolutely the size of a bit of DNA by examining it next to a typical "yardstick" made from DNA fragments of known sizes.
Additional Information: The movement of DNA fragments through the gel;
Once the gel is within the box, each of the DNA samples we would like to look at (for instance, each PCR reaction or each restriction-digested plasmid) is carefully transferred into one among the wells. One well is reserved for a DNA ladder, a typical reference that contains DNA fragments of known lengths. Commercial DNA ladders are available in different size ranges, so we might want to select one with good "coverage" of the dimensions range of our expected fragments.
Next, the facility to the gel box is turned on and currently begins to flow through the gel. The DNA molecules have a charge due to the phosphate groups in their sugar-phosphate backbone so that they start moving through the matrix of the gel towards the positive pole. When the facility is turned on and current is passing through the gel, the gel is claimed to be running.
After the gel has run awhile, the shortest pieces of DNA are going to be on the brink of the positive end of the gel, while the longest pieces of DNA will remain near the wells. Very short pieces of DNA may have run right off the top of the gel if we left it on for too long.
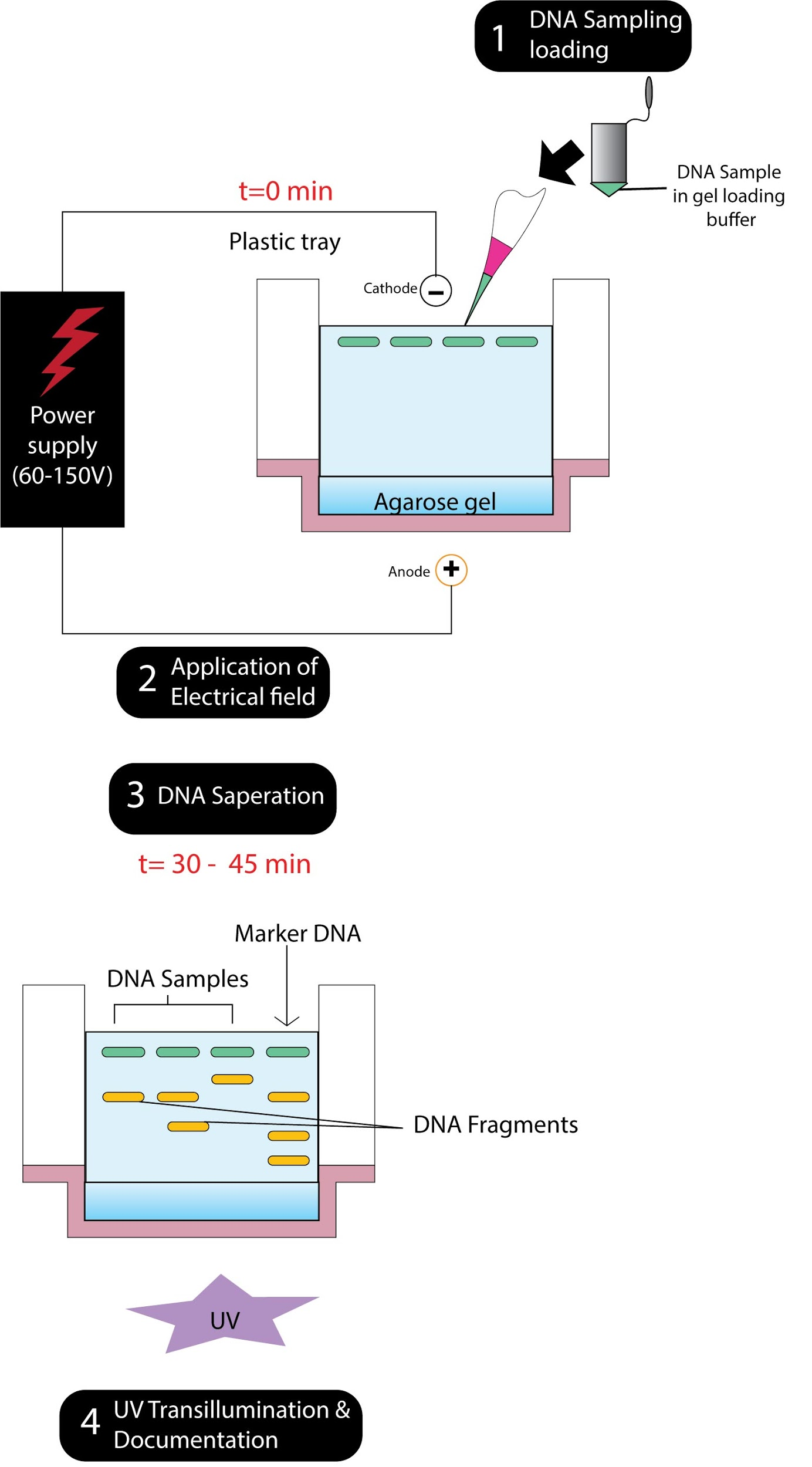
Note: Agarose gel electrophoresis is the method of gel electrophoresis carried out in biochemistry, biology , genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules like DNA, RNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose. Agarose is the natural linear polymer extracted from seaweed that forms a gel matrix by hydrogen-bonding when heated in a buffer and allowed to cool down. They are the most popular medium for the separation of moderate and large-sized nucleic acids and have a wide range of separation.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis may be a technique to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, like RNA and proteins) that support their size and charge. By this the molecules will travel through the gel in several directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from each other.
All DNA molecules have an equivalent amount of charge per mass. Due to this, gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments separates them accordingly with those who have the correct size only. Using electrophoresis, we will see what percentage different DNA fragments are present during a sample and the way large they're relative to at least one another. we will also determine absolutely the size of a bit of DNA by examining it next to a typical "yardstick" made from DNA fragments of known sizes.
Additional Information: The movement of DNA fragments through the gel;
Once the gel is within the box, each of the DNA samples we would like to look at (for instance, each PCR reaction or each restriction-digested plasmid) is carefully transferred into one among the wells. One well is reserved for a DNA ladder, a typical reference that contains DNA fragments of known lengths. Commercial DNA ladders are available in different size ranges, so we might want to select one with good "coverage" of the dimensions range of our expected fragments.
Next, the facility to the gel box is turned on and currently begins to flow through the gel. The DNA molecules have a charge due to the phosphate groups in their sugar-phosphate backbone so that they start moving through the matrix of the gel towards the positive pole. When the facility is turned on and current is passing through the gel, the gel is claimed to be running.
After the gel has run awhile, the shortest pieces of DNA are going to be on the brink of the positive end of the gel, while the longest pieces of DNA will remain near the wells. Very short pieces of DNA may have run right off the top of the gel if we left it on for too long.

Note: Agarose gel electrophoresis is the method of gel electrophoresis carried out in biochemistry, biology , genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules like DNA, RNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose. Agarose is the natural linear polymer extracted from seaweed that forms a gel matrix by hydrogen-bonding when heated in a buffer and allowed to cool down. They are the most popular medium for the separation of moderate and large-sized nucleic acids and have a wide range of separation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




