
Genetic material of HIV is-
A. ssDNA
B. ssRNA
C. dsRNA
D. dsDNA
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: The genetic material of HIV is the same as present in the Mumps virus, Measles virus, Hepatitis E virus, and Rabies virus. It can have either positive or negative polarity.
Complete answer:
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The core of HIV contains two molecules of single- stranded RNA (acts as genetic material). The virus causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), which is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
Additional Information
HIV is a retrovirus which is of two types i.e. HIV- 1 and HIV- 2. HIV is called a retrovirus because it works in a back- to- front manner. Unlike other viruses, these retroviruses store their genetic information in the form of RNA instead of DNA. They need to convert it into DNA with the help of an enzyme called Reverse transcriptase when they enter a human cell in order to make new copies of themselves. It is a retrovirus belonging to the family of Retroviridae.
Modes of transmission of HIV are -
- Blood products like unclean needles, infected surgical instruments, or unscreened blood.
- By having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- From mother to baby during pregnancy, labor, or nursing via the ruptured placenta or a breach in the epithelium.
So, the correct answer is ‘ssRNA’.
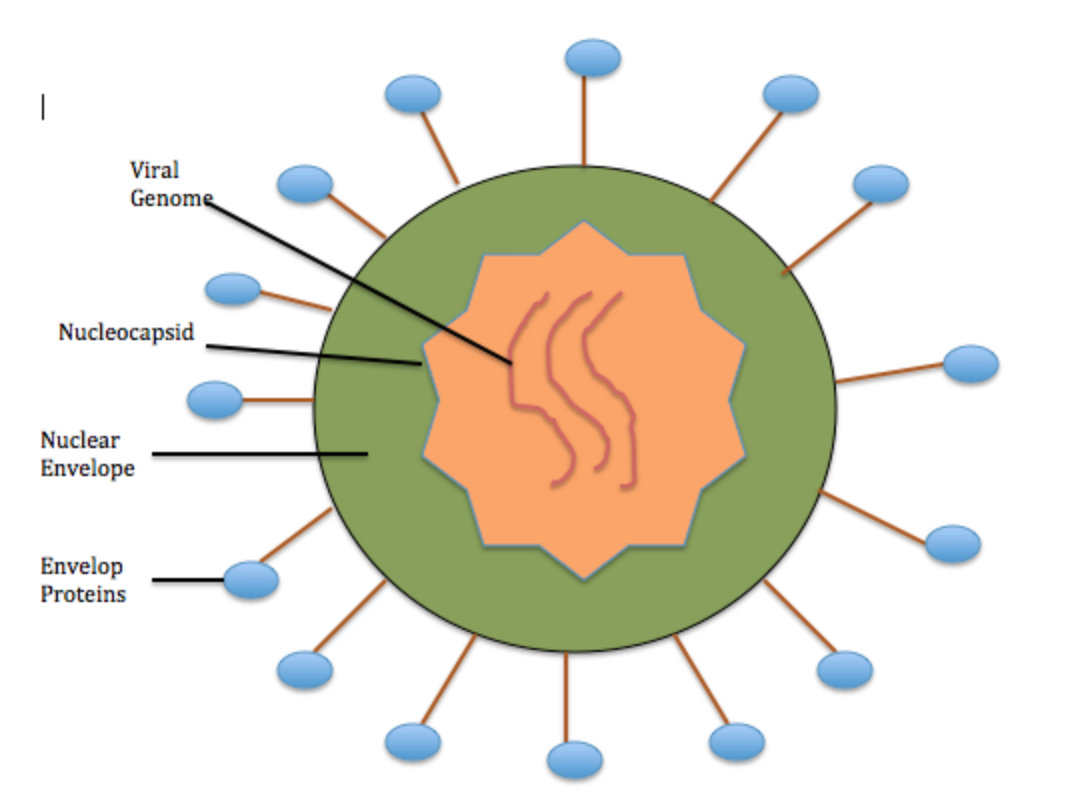
Note: HIV is different in structure from other retroviruses. It is roughly spherical with a diameter of about 120 nm. It is made up of two copies of single- stranded RNA that codes for the virus’s genes. It is enclosed by a conical capsid. The single- stranded RNA is tightly bound to nucleocapsid protein. The enzymes needed for the development of the virion (the proteinaceous component of the virus) include reverse transcriptase, proteases, ribonuclease, and integrase.
Complete answer:
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The core of HIV contains two molecules of single- stranded RNA (acts as genetic material). The virus causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), which is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
Additional Information
HIV is a retrovirus which is of two types i.e. HIV- 1 and HIV- 2. HIV is called a retrovirus because it works in a back- to- front manner. Unlike other viruses, these retroviruses store their genetic information in the form of RNA instead of DNA. They need to convert it into DNA with the help of an enzyme called Reverse transcriptase when they enter a human cell in order to make new copies of themselves. It is a retrovirus belonging to the family of Retroviridae.
Modes of transmission of HIV are -
- Blood products like unclean needles, infected surgical instruments, or unscreened blood.
- By having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- From mother to baby during pregnancy, labor, or nursing via the ruptured placenta or a breach in the epithelium.
So, the correct answer is ‘ssRNA’.

Note: HIV is different in structure from other retroviruses. It is roughly spherical with a diameter of about 120 nm. It is made up of two copies of single- stranded RNA that codes for the virus’s genes. It is enclosed by a conical capsid. The single- stranded RNA is tightly bound to nucleocapsid protein. The enzymes needed for the development of the virion (the proteinaceous component of the virus) include reverse transcriptase, proteases, ribonuclease, and integrase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




