
What is germination? What are its different types? Explain with examples.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Seeds are the products of sexual reproduction of the plants. These develop into new plants i.e. seedlings by the process known as germination. The meaning is ‘to sprout’.
Complete Answer:
Germination is the process by which a plant grows from the seed. Seeds first develop into seedlings and then the plant. The seedlings contain three major parts: the Radicle (embryonic root). The plumule (embryonic shoot) and the cotyledons (seed leaves).
Stages of Seed Germination
1. Pre Germination Stage:
- This is the preparatory stage of the seed.
- Before germination, the seeds take in water by the process known as imbibition.
- Oxygen enters the seeds and this starts the metabolism process.
- This results in hydrolysis of reserve food.
- Protein synthesis is initiated.
- Changes in cell structure seen.
- Cell growth and cell division begins.
2. Germination Stage:
- The seed coat ruptures.
- Seedlings emergence takes place.
3. Post Germination stage:
- Growth of roots and shoots.
- Senescence occurs.
- Depending on the fate of cotyledons, there are two main types of Germination.
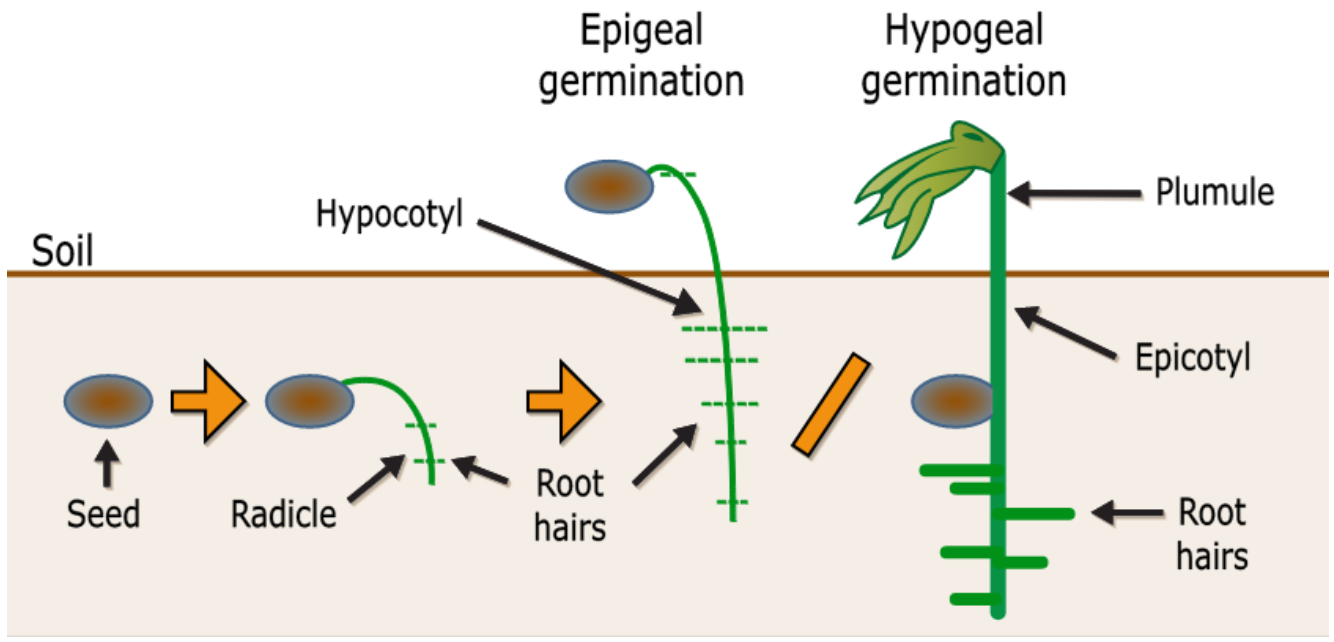
a. Epigeal Germination : (Epi means above , geal means ground)
- In this the cotyledons appear out of the soil.
- This is due to excessive growth of hypocotyl.
- The plumule is enclosed by the cotyledons.
- The cotyledons become photosynthetic in function till the seedlings become independent.
- Such a type of germination is seen in Castor, Papaya, Cotton, etc.
b. Hypogeal Germination : (Hypo means below, geal is ground)
- In this the cotyledon remains below the soil.
- This is because the length of hypocotyl is restricted.
- The epicotyl elongates which further does not allow hypocotyl to grow
- The epicotyl in turn causes the plumule to come out of the soil
- All monocots show this type of germination.
However dicots like gram pea and groundnut also show this type of germination
Note: Environmental factors responsible for the growth are light, temperature, moisture, oxygen and nutrients. There are many internal factors also that play a major role in germination. These factors are Seed vitality, Seed maturation and Seed dormancy.
Complete Answer:
Germination is the process by which a plant grows from the seed. Seeds first develop into seedlings and then the plant. The seedlings contain three major parts: the Radicle (embryonic root). The plumule (embryonic shoot) and the cotyledons (seed leaves).
Stages of Seed Germination
1. Pre Germination Stage:
- This is the preparatory stage of the seed.
- Before germination, the seeds take in water by the process known as imbibition.
- Oxygen enters the seeds and this starts the metabolism process.
- This results in hydrolysis of reserve food.
- Protein synthesis is initiated.
- Changes in cell structure seen.
- Cell growth and cell division begins.
2. Germination Stage:
- The seed coat ruptures.
- Seedlings emergence takes place.
3. Post Germination stage:
- Growth of roots and shoots.
- Senescence occurs.
- Depending on the fate of cotyledons, there are two main types of Germination.
a. Epigeal Germination : (Epi means above , geal means ground)
- In this the cotyledons appear out of the soil.
- This is due to excessive growth of hypocotyl.
- The plumule is enclosed by the cotyledons.
- The cotyledons become photosynthetic in function till the seedlings become independent.
- Such a type of germination is seen in Castor, Papaya, Cotton, etc.
b. Hypogeal Germination : (Hypo means below, geal is ground)
- In this the cotyledon remains below the soil.
- This is because the length of hypocotyl is restricted.
- The epicotyl elongates which further does not allow hypocotyl to grow
- The epicotyl in turn causes the plumule to come out of the soil
- All monocots show this type of germination.
However dicots like gram pea and groundnut also show this type of germination

Note: Environmental factors responsible for the growth are light, temperature, moisture, oxygen and nutrients. There are many internal factors also that play a major role in germination. These factors are Seed vitality, Seed maturation and Seed dormancy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




