
Give a balanced equation to convert methyl cyanide to ethanol.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We know that amine is a functional group whose structure is $\left( { - {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right)$. Here, first we have to convert the cyanide to an amine. Then amine can be converted to the required alcohol by reacting with acids.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first understand the cyanide functional group. Cyanide is a functional group whose structure is $\left( {{\rm{C}} \equiv {\rm{N}}} \right)$. Some examples of cyanide containing compounds are methyl cyanide ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{CN}}$ , ethyl cyanide $\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{CN}}} \right)$etc.
Here, we have to reduce methyl cyanide to methyl amine. This can be achieved by reacting methyl cyanide with a reducing agent like ${\rm{LiAl}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$
.
Let’s discuss how ${\rm{LiAl}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$ reduces methyl cyanide to ethanamine in detail. During this reaction, the nucleophilic attack of hydride ions on the electrophilic carbon of the nitrile takes place to form an imine. Then, the second nucleophilic attack of hydride takes place to form dianion. Then, the conversion of dianion to amine occurs by addition of water.

Now, we have to convert ethanamine to ethanol. Ethanol can be formed by reacting the ethanamine with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salt. Diazonium salt formed is very unstable. Hence, it liberates nitrogen gas and forms alcohol. The reaction can be shown as follows:
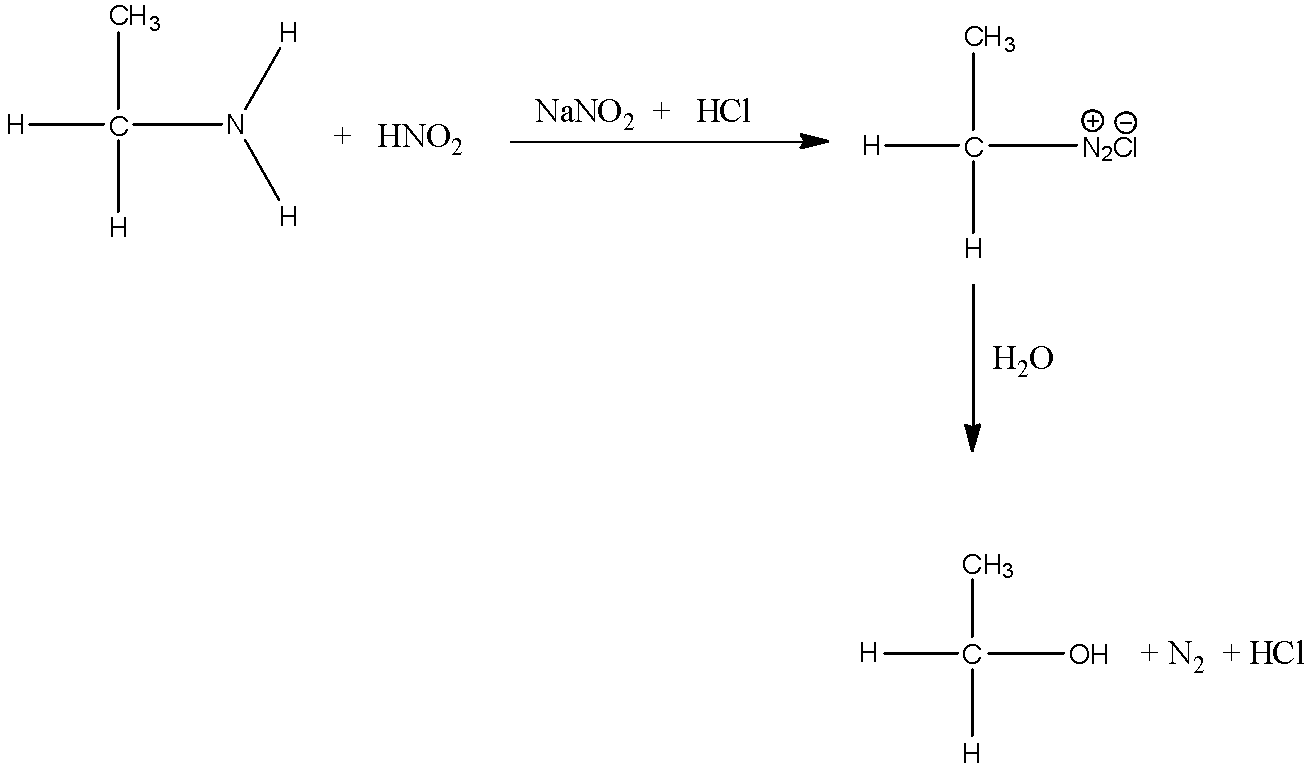
Therefore, the complete reaction of conversion of methyl cyanide to ethanol is,

Note: Remember that there are three types of amine, primary amine, secondary amine and tertiary amine.The amine in which one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl group is termed as primary amine. One example is${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$
.
Secondary amine is the amine in which two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by two alkyl groups, such as, $$

Tertiary amine is the amine in which, all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl groups, such as,

Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first understand the cyanide functional group. Cyanide is a functional group whose structure is $\left( {{\rm{C}} \equiv {\rm{N}}} \right)$. Some examples of cyanide containing compounds are methyl cyanide ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{CN}}$ , ethyl cyanide $\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} - {\rm{CN}}} \right)$etc.
Here, we have to reduce methyl cyanide to methyl amine. This can be achieved by reacting methyl cyanide with a reducing agent like ${\rm{LiAl}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$
.
Let’s discuss how ${\rm{LiAl}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$ reduces methyl cyanide to ethanamine in detail. During this reaction, the nucleophilic attack of hydride ions on the electrophilic carbon of the nitrile takes place to form an imine. Then, the second nucleophilic attack of hydride takes place to form dianion. Then, the conversion of dianion to amine occurs by addition of water.

Now, we have to convert ethanamine to ethanol. Ethanol can be formed by reacting the ethanamine with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salt. Diazonium salt formed is very unstable. Hence, it liberates nitrogen gas and forms alcohol. The reaction can be shown as follows:

Therefore, the complete reaction of conversion of methyl cyanide to ethanol is,

Note: Remember that there are three types of amine, primary amine, secondary amine and tertiary amine.The amine in which one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by an alkyl group is termed as primary amine. One example is${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$
.
Secondary amine is the amine in which two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by two alkyl groups, such as, $$

Tertiary amine is the amine in which, all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl groups, such as,

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




